State of BER
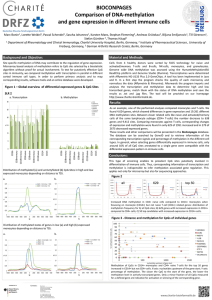
... Cassettes with promoters driving strong but not maximal rates of transcription support the fastest ethanologenic growth. Of two alcohol dehydrogenase genes tested, one was preferred for rapid growth. OptSSeq is a general tool for synthetic biology to tune pathway enzyme levels whose function c ...
... Cassettes with promoters driving strong but not maximal rates of transcription support the fastest ethanologenic growth. Of two alcohol dehydrogenase genes tested, one was preferred for rapid growth. OptSSeq is a general tool for synthetic biology to tune pathway enzyme levels whose function c ...
1. Introduction 2. Fact or Fiction?
... genetically unique. 3. All the genes a person has show up as observable traits. 4. Alcoholism is inherited. ...
... genetically unique. 3. All the genes a person has show up as observable traits. 4. Alcoholism is inherited. ...
our leaflet: Autism families study
... for the differences among us. Yet these DNA base sequence variations influence most of our physical differences and many of our other characteristics, as well. Sequence variations occur in our genes, and the resulting different forms of the same gene are called alleles. People can have two identical ...
... for the differences among us. Yet these DNA base sequence variations influence most of our physical differences and many of our other characteristics, as well. Sequence variations occur in our genes, and the resulting different forms of the same gene are called alleles. People can have two identical ...
August 2016 - Wessex AHSN
... neighbouring trusts to involve them as local delivery partners with an active role in this transformational change in practice. Building on progress to date, we are already starting to develop a Wessex personalised medicine service. The implementation of the project is showing us what needs to be in ...
... neighbouring trusts to involve them as local delivery partners with an active role in this transformational change in practice. Building on progress to date, we are already starting to develop a Wessex personalised medicine service. The implementation of the project is showing us what needs to be in ...
GENETICS The Future of Medicine
... Examining how a particular gene is spelled in an individual can serve quite a few uses: Diagnosis Genetic analysis now can classify some conditions, like colon cancer and skin cancer, into finer categories. This is important since classifying diseases more precisely can suggest more appropriate trea ...
... Examining how a particular gene is spelled in an individual can serve quite a few uses: Diagnosis Genetic analysis now can classify some conditions, like colon cancer and skin cancer, into finer categories. This is important since classifying diseases more precisely can suggest more appropriate trea ...
Genomics for Librarians
... Every human has essentially the same set of genes But there are different forms of each gene -- known as alleles – blue vs. brown eyes – genetic diseases such as cystic fibrosis or Huntington’s disease are caused by dysfunctional alleles ...
... Every human has essentially the same set of genes But there are different forms of each gene -- known as alleles – blue vs. brown eyes – genetic diseases such as cystic fibrosis or Huntington’s disease are caused by dysfunctional alleles ...
Ch. 18 - ltcconline.net
... 4. Control of gene expression makes it possible for cells to produce specific kinds of proteins when and where they are needed 5. Operons in e. coli, which changes its activities from time to time in response to its environment 6. The trp operon = repressible operon – turns off gene a. Repressor and ...
... 4. Control of gene expression makes it possible for cells to produce specific kinds of proteins when and where they are needed 5. Operons in e. coli, which changes its activities from time to time in response to its environment 6. The trp operon = repressible operon – turns off gene a. Repressor and ...
PowerPoint-Präsentation
... Genome wide DNA methylation was assessed using the HumanMethylation450 BeadChip platform and Genome Studio (Illumina). Transcriptomes were determined with Affymetrix HG-U133 Plus 2.0 GeneChips. A tool has been implemented in Java and R. In a first step the program checks the quality of each microarr ...
... Genome wide DNA methylation was assessed using the HumanMethylation450 BeadChip platform and Genome Studio (Illumina). Transcriptomes were determined with Affymetrix HG-U133 Plus 2.0 GeneChips. A tool has been implemented in Java and R. In a first step the program checks the quality of each microarr ...
2/14 - Utexas
... mitochondria and chloroplasts from freeliving bacteria to cellular organelles CB 26.13 ...
... mitochondria and chloroplasts from freeliving bacteria to cellular organelles CB 26.13 ...
Nicolo Riggi - Scientia Global
... to transform normal cells into cancerous cells. This alteration occurs when the normal EWS gene, whose function is poorly understood, fuses with a gene coding for a transcription factor known as FLI1, during a rare abnormal genetic event known as a chromosomal translocation. Transcription factors ar ...
... to transform normal cells into cancerous cells. This alteration occurs when the normal EWS gene, whose function is poorly understood, fuses with a gene coding for a transcription factor known as FLI1, during a rare abnormal genetic event known as a chromosomal translocation. Transcription factors ar ...
Sex Linked Traits
... uncontrolled bleeding • It is a sex linked disorder caused by errors in the DNA that codes for the proteins involved in clotting ...
... uncontrolled bleeding • It is a sex linked disorder caused by errors in the DNA that codes for the proteins involved in clotting ...
Lecture 19 Spring 2011
... replicating and nonreplicating DNA (e.g., alkylating agents and nitrous acid) Chemicals that are mutagenic only to replicating DNA (e.g., base analogs and ...
... replicating and nonreplicating DNA (e.g., alkylating agents and nitrous acid) Chemicals that are mutagenic only to replicating DNA (e.g., base analogs and ...
Uses of Genomic Information in the Diagnosis of Disease
... The DNA sample can come from any tissue including blood For some tests, probes, short pieces of DNA, are designed with sequences complimentary to the mutated sequence. The probe will seek its compliment among the base pairs and will bind to it and flag the mutation Other tests compare the base ...
... The DNA sample can come from any tissue including blood For some tests, probes, short pieces of DNA, are designed with sequences complimentary to the mutated sequence. The probe will seek its compliment among the base pairs and will bind to it and flag the mutation Other tests compare the base ...
What is Cloning?
... animal, or plant) and inserting it in the DNA of rapidly reproducing foreign cells, billions of copies of a single gene or DNA segment can be produced in a very short time. DNA to be cloned is inserted into a plasmid (a small, self-replicating circular molecule of DNA) that is separate from chromos ...
... animal, or plant) and inserting it in the DNA of rapidly reproducing foreign cells, billions of copies of a single gene or DNA segment can be produced in a very short time. DNA to be cloned is inserted into a plasmid (a small, self-replicating circular molecule of DNA) that is separate from chromos ...
Teacher PowerPoint - UNC Institute for the Environment
... Refers to changes in gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence. Enables a cell/organism to respond to its dynamic external environment during development and throughout life! Epigenetic changes to the genome can be inherited if these changes occur in cell ...
... Refers to changes in gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence. Enables a cell/organism to respond to its dynamic external environment during development and throughout life! Epigenetic changes to the genome can be inherited if these changes occur in cell ...
Companion PowerPoint slide
... Refers to changes in gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence. Enables a cell/organism to respond to its dynamic external environment during development and throughout life! Epigenetic changes to the genome can be inherited if these changes occur in cell ...
... Refers to changes in gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence. Enables a cell/organism to respond to its dynamic external environment during development and throughout life! Epigenetic changes to the genome can be inherited if these changes occur in cell ...
Evolution Review Guide
... Genes are located in the chromosomes of cells, with each chromosome pair containing two variants of each of many distinct genes. Each distinct gene chiefly controls the production of specific proteins, which in turn affects the traits of the individual. Changes (mutations) to genes can result in cha ...
... Genes are located in the chromosomes of cells, with each chromosome pair containing two variants of each of many distinct genes. Each distinct gene chiefly controls the production of specific proteins, which in turn affects the traits of the individual. Changes (mutations) to genes can result in cha ...
doc Review of Lecture 27
... o Less stable forms than bases, shift base-pairing affinities & lead to changes o 5-bromouracil (5-BU) – causes A-T G-C or G-C A-T ...
... o Less stable forms than bases, shift base-pairing affinities & lead to changes o 5-bromouracil (5-BU) – causes A-T G-C or G-C A-T ...
Study Guide
... ii. What are some practical applications? iii. DNA Fingerprinting –There are two types. What is this technique used for? b. What are Probes and what are they used for? c. Restriction Enzymes and sticky ends d. PCR i. What is it? What is PCR used for? e. DNA Sequencing and the Human Genome Project (H ...
... ii. What are some practical applications? iii. DNA Fingerprinting –There are two types. What is this technique used for? b. What are Probes and what are they used for? c. Restriction Enzymes and sticky ends d. PCR i. What is it? What is PCR used for? e. DNA Sequencing and the Human Genome Project (H ...
Oncogenomics
Oncogenomics is a relatively new sub-field of genomics that applies high throughput technologies to characterize genes associated with cancer. Oncogenomics is synonymous with ""cancer genomics"". Cancer is a genetic disease caused by accumulation of mutations to DNA leading to unrestrained cell proliferation and neoplasm formation. The goal of oncogenomics is to identify new oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes that may provide new insights into cancer diagnosis, predicting clinical outcome of cancers, and new targets for cancer therapies. The success of targeted cancer therapies such as Gleevec, Herceptin, and Avastin raised the hope for oncogenomics to elucidate new targets for cancer treatment.Besides understanding the underlying genetic mechanisms that initiates or drives cancer progression, one of the main goals of oncogenomics is to allow for the development of personalized cancer treatment. Cancer develops due to an accumulation of mutations in DNA. These mutations accumulate randomly, and thus, different DNA mutations and mutation combinations exist between different individuals with the same type of cancer. Thus, identifying and targeting specific mutations which have occurred in an individual patient may lead to increased efficacy of cancer therapy.The completion of the Human Genome Project has greatly facilitated the field of oncogenomics and has increased the abilities of researchers to find cancer causing genes. In addition, the sequencing technologies now available for sequence generation and data analysis have been applied to the study of oncogenomics. With the amount of research conducted on cancer genomes and the accumulation of databases documenting the mutational changes, it has been predicted that the most important cancer-causing mutations, rearrangements, and altered expression levels will be cataloged and well characterized within the next decade.Cancer research may look either on the genomic level at DNA mutations, the epigenetic level at methylation or histone modification changes, the transcription level at altered levels of gene expression, or the protein level at altered levels of protein abundance and function in cancer cells. Oncogenomics focuses on the genomic, epigenomic, and transcript level alterations in cancer.