Synthesis and characterization of the Polystyrene /GaAs
... photochemical, and nonlinear optical properties [1, 2, 3]. Semiconductor nano crystals, like CdTe, show size dependent optical properties and are very important in basic nano science research, colloidal science, biomedical labeling, light emitting diodes, solar cells, and lasers [4-5]. In general, s ...
... photochemical, and nonlinear optical properties [1, 2, 3]. Semiconductor nano crystals, like CdTe, show size dependent optical properties and are very important in basic nano science research, colloidal science, biomedical labeling, light emitting diodes, solar cells, and lasers [4-5]. In general, s ...
Characterization of Nano Materials using Electron Microscopy
... spectra made from the characteristic x-rays. Because the intensity of the BSE signal is strongly related to the atomic number (Z) of the specimen, BSE images can provide information about the distribution of different elements in the sample. For the same reason, BSE imaging can image, for example, c ...
... spectra made from the characteristic x-rays. Because the intensity of the BSE signal is strongly related to the atomic number (Z) of the specimen, BSE images can provide information about the distribution of different elements in the sample. For the same reason, BSE imaging can image, for example, c ...
BJ26404407
... also applied to high-power electronic devices and solar cells.With comparison of scattering effect in ZB-AlN and WZ-AlN structures, we result that for deformation potential scattering, the scattering of electron increased with increasing the energy. In piezoelectric scattering with increasing of ene ...
... also applied to high-power electronic devices and solar cells.With comparison of scattering effect in ZB-AlN and WZ-AlN structures, we result that for deformation potential scattering, the scattering of electron increased with increasing the energy. In piezoelectric scattering with increasing of ene ...
PDF
... The complexity and small size of photonic crystal structures has slowed progress in this area due to the difficulty in fabrication. However using variations in MEMS processing we have found that it is possible to fabricate a wide variety of such structures.iv,v We have fabricated 3-D metallic (tungs ...
... The complexity and small size of photonic crystal structures has slowed progress in this area due to the difficulty in fabrication. However using variations in MEMS processing we have found that it is possible to fabricate a wide variety of such structures.iv,v We have fabricated 3-D metallic (tungs ...
Eastern Kentucky University
... List and describe common terms related to the study of materials Describe and define terms and conditions associated with atomic structure and atomic theory Recognize and describe how the periodic table of elements is used and the structure of the table List and describe how the various bonding forc ...
... List and describe common terms related to the study of materials Describe and define terms and conditions associated with atomic structure and atomic theory Recognize and describe how the periodic table of elements is used and the structure of the table List and describe how the various bonding forc ...
Parametric generation of tunable infrared radiation in
... type-I phase matching the OPG linewidth is larger than in type II, especially near degeneracy. The walk-off length is given by pL, where p is a Poyntingvector walk-off angle'3 p (An/n)sin(20); An is a birefringence value and n is the mean refractive index. The effective crystal length is calculated ...
... type-I phase matching the OPG linewidth is larger than in type II, especially near degeneracy. The walk-off length is given by pL, where p is a Poyntingvector walk-off angle'3 p (An/n)sin(20); An is a birefringence value and n is the mean refractive index. The effective crystal length is calculated ...
Microwave Synthesis of Cu, Fe-doped TiO2 and Its
... In recent years, with increasingly worsen problems of environmental pollutions, we have been in urgent need of improving our gradually deteriorated living conditions. The technology of photocatalytic degradation technology can not only effectively degrade organic and inorganic pollutions without the ...
... In recent years, with increasingly worsen problems of environmental pollutions, we have been in urgent need of improving our gradually deteriorated living conditions. The technology of photocatalytic degradation technology can not only effectively degrade organic and inorganic pollutions without the ...
Post Print Electronic structure and chemical bonding in Ti2AlC
... friction.5 The physical properties of crystallographically oriented thin films of MAX phases thus provide opportunities for particular industrial applications such as protective coatings, sliding/gliding electrical contacts, and heating elements. Previous experimental investigations of the electroni ...
... friction.5 The physical properties of crystallographically oriented thin films of MAX phases thus provide opportunities for particular industrial applications such as protective coatings, sliding/gliding electrical contacts, and heating elements. Previous experimental investigations of the electroni ...
Liquid crystals
... A liquid crystal is a fluid like a liquid, but is anisotropic in its optical and electromagnetic characteristics like a solid. When the liquid crystal is formed from the isotropic state some amount of positional or orientation order is gained. It is this order that accounts for the anisotropies of t ...
... A liquid crystal is a fluid like a liquid, but is anisotropic in its optical and electromagnetic characteristics like a solid. When the liquid crystal is formed from the isotropic state some amount of positional or orientation order is gained. It is this order that accounts for the anisotropies of t ...
Potentiated electron transference in
... bacteriostatic and bactericidal effects, but the irradiated sample is more efficient; i.e., a 4fold of the MRSA planktonic cells as compared to the nonirradiated sample was observed. In addition, first principles calculations were performed to obtain structural and electronic properties of AWO and metal ...
... bacteriostatic and bactericidal effects, but the irradiated sample is more efficient; i.e., a 4fold of the MRSA planktonic cells as compared to the nonirradiated sample was observed. In addition, first principles calculations were performed to obtain structural and electronic properties of AWO and metal ...
The Effect of Temperature and Solution pH on the Nucleation of
... crystallization solution in the inside well and adding 1.4 ml of the same solution without protein to the outside well of the sitting drop plate. The crystallization conditions for the x-ray diffraction analysis were chosen as a result of the findings in the nucleation rate work. This choice was a t ...
... crystallization solution in the inside well and adding 1.4 ml of the same solution without protein to the outside well of the sitting drop plate. The crystallization conditions for the x-ray diffraction analysis were chosen as a result of the findings in the nucleation rate work. This choice was a t ...
Chapter 5 Section 1 Characteristics of Minerals
... • Each type of mineral is characterized by a specific geometric arrangement of atoms, or its ______________________________. • Crystal – One way that scientists study the structure of crystals is by using ____________________. X rays that pass through a crystal and strike a photographic plate produc ...
... • Each type of mineral is characterized by a specific geometric arrangement of atoms, or its ______________________________. • Crystal – One way that scientists study the structure of crystals is by using ____________________. X rays that pass through a crystal and strike a photographic plate produc ...
Chapter 3: Atoms, Elements, Minerals, Rocks
... for another in a compound. The bonding in most common minerals is ionic. ...
... for another in a compound. The bonding in most common minerals is ionic. ...
Atomic model of human Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane
... pdb 1r0z; at left), for which only six amino acids at the centre of the loop (dotted line) are not seen and which thus directly allows to completely model this long insertion. The regulatory insertion starts with a typical amphipatic helix, which is centered on the hydrophobic cluster 10011001 (mous ...
... pdb 1r0z; at left), for which only six amino acids at the centre of the loop (dotted line) are not seen and which thus directly allows to completely model this long insertion. The regulatory insertion starts with a typical amphipatic helix, which is centered on the hydrophobic cluster 10011001 (mous ...
From Discrete Linear ZntBu2 Molecules to 1D Coordination
... [ZntBu2(bpene)] (3) were obtained from a THF solution at 0 °C. X-ray crystallographic analysis of 3 revealed the formation of the 1D zigzag-like inorganic-organic hybrid polymeric chains (Figure 3). The geometric parameters of 3 are similar to those of 2, with pyridine ligands completing a pseudotet ...
... [ZntBu2(bpene)] (3) were obtained from a THF solution at 0 °C. X-ray crystallographic analysis of 3 revealed the formation of the 1D zigzag-like inorganic-organic hybrid polymeric chains (Figure 3). The geometric parameters of 3 are similar to those of 2, with pyridine ligands completing a pseudotet ...
(S-Benzylthiuronium) Chloranilate Supramolecular Crystal Structure
... populated areas of SBT-cations. Each CA-dianion forms eight hydrogen bonds with the amine protons of six SBT-cations, through its oxygen atoms. In this way, an extended H-bond network, containing infinite chains of alternative R42(8) and R22(9) cyclic patterns, is obtained. The whole arrangement lea ...
... populated areas of SBT-cations. Each CA-dianion forms eight hydrogen bonds with the amine protons of six SBT-cations, through its oxygen atoms. In this way, an extended H-bond network, containing infinite chains of alternative R42(8) and R22(9) cyclic patterns, is obtained. The whole arrangement lea ...
Organization Brochure - Contract
... measurement procedure to be able to quantify a given polymorph and determine its presence with very low detection limits (typically in the range of 0.3 and 1%, depending on the API). The same procedure can be applied in mixtures of different crystalline products (API 1 + API 2, API + excipient, etc) ...
... measurement procedure to be able to quantify a given polymorph and determine its presence with very low detection limits (typically in the range of 0.3 and 1%, depending on the API). The same procedure can be applied in mixtures of different crystalline products (API 1 + API 2, API + excipient, etc) ...
5.1 Ni Redox Potential in Different Compounds
... levels. The oxygen p bands are filled and the transition metal d bands are empty or partially occupied. Crystal field theory [2-4] demonstrates that the interaction of the d orbitals with the electrostatic potential due to the negatively charged oxygen ions of the octahedron produces an increase in ...
... levels. The oxygen p bands are filled and the transition metal d bands are empty or partially occupied. Crystal field theory [2-4] demonstrates that the interaction of the d orbitals with the electrostatic potential due to the negatively charged oxygen ions of the octahedron produces an increase in ...
G070376-00
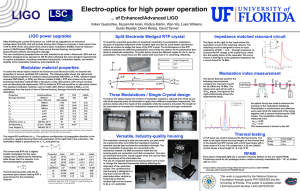
... To select the electro-optics material for Enhanced and Advanced LIGO, we examine the properties of several candidate EO materials. The following table shows the optical and electro-optical properties of rubidium titanyl phosphate (RbTiOPO4 or RTP), rubidium titanyl arsenate (RbTiOAsO4 or RTA) and li ...
... To select the electro-optics material for Enhanced and Advanced LIGO, we examine the properties of several candidate EO materials. The following table shows the optical and electro-optical properties of rubidium titanyl phosphate (RbTiOPO4 or RTP), rubidium titanyl arsenate (RbTiOAsO4 or RTA) and li ...
Lectures 18-20: Diffraction
... If two light sources are close together, the far-field intensity distributions of the two sources may overlap and make it impossible to separate the sources. In this section, we examine this problem quantitatively, and develop the Rayleigh criterion for resolving power. We begin our study of the que ...
... If two light sources are close together, the far-field intensity distributions of the two sources may overlap and make it impossible to separate the sources. In this section, we examine this problem quantitatively, and develop the Rayleigh criterion for resolving power. We begin our study of the que ...
Purification and - Jena Bioscience
... set were chosen at random for the calculation of Rfree. Both structures were refined in REFMAC5 (Murshudov et al., 1997) using tight noncrystallographic symmetry restraints for both main and side chains owing to the low resolution of the data sets. The structures were subsequently inspected in Coot ( ...
... set were chosen at random for the calculation of Rfree. Both structures were refined in REFMAC5 (Murshudov et al., 1997) using tight noncrystallographic symmetry restraints for both main and side chains owing to the low resolution of the data sets. The structures were subsequently inspected in Coot ( ...
X-ray crystallography

X-ray crystallography is a tool used for identifying the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline atoms cause a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal. From this electron density, the mean positions of the atoms in the crystal can be determined, as well as their chemical bonds, their disorder and various other information.Since many materials can form crystals—such as salts, metals, minerals, semiconductors, as well as various inorganic, organic and biological molecules—X-ray crystallography has been fundamental in the development of many scientific fields. In its first decades of use, this method determined the size of atoms, the lengths and types of chemical bonds, and the atomic-scale differences among various materials, especially minerals and alloys. The method also revealed the structure and function of many biological molecules, including vitamins, drugs, proteins and nucleic acids such as DNA. X-ray crystallography is still the chief method for characterizing the atomic structure of new materials and in discerning materials that appear similar by other experiments. X-ray crystal structures can also account for unusual electronic or elastic properties of a material, shed light on chemical interactions and processes, or serve as the basis for designing pharmaceuticals against diseases.In a single-crystal X-ray diffraction measurement, a crystal is mounted on a goniometer. The goniometer is used to position the crystal at selected orientations. The crystal is bombarded with a finely focused monochromatic beam of X-rays, producing a diffraction pattern of regularly spaced spots known as reflections. The two-dimensional images taken at different rotations are converted into a three-dimensional model of the density of electrons within the crystal using the mathematical method of Fourier transforms, combined with chemical data known for the sample. Poor resolution (fuzziness) or even errors may result if the crystals are too small, or not uniform enough in their internal makeup.X-ray crystallography is related to several other methods for determining atomic structures. Similar diffraction patterns can be produced by scattering electrons or neutrons, which are likewise interpreted by Fourier transformation. If single crystals of sufficient size cannot be obtained, various other X-ray methods can be applied to obtain less detailed information; such methods include fiber diffraction, powder diffraction and (if the sample is not crystallized) small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS).If the material under investigation is only available in the form of nanocrystalline powders or suffers from poor crystallinity, the methods of electron crystallography can be applied for determining the atomic structure.For all above mentioned X-ray diffraction methods, the scattering is elastic; the scattered X-rays have the same wavelength as the incoming X-ray. By contrast, inelastic X-ray scattering methods are useful in studying excitations of the sample, rather than the distribution of its atoms.