Summary Weil Openness
... Autarky: The situation in which a country does not interact economically at all with the rest of the world. Two primary forms of economic integration among countries: 1. Trade: The exchange of goods and services across national borders. 2. Flow of factors of production: The movement of a factor of p ...
... Autarky: The situation in which a country does not interact economically at all with the rest of the world. Two primary forms of economic integration among countries: 1. Trade: The exchange of goods and services across national borders. 2. Flow of factors of production: The movement of a factor of p ...
Economic Systems - Schoolwires.net
... Economic Systems & Measures of Wealth I. Economic Systems A. Traditional: People produce their __________________ and __________________ for what they need. B. Market: People and businesses _________________________________________. 1. Also known as __________________ and __________________. C. Comm ...
... Economic Systems & Measures of Wealth I. Economic Systems A. Traditional: People produce their __________________ and __________________ for what they need. B. Market: People and businesses _________________________________________. 1. Also known as __________________ and __________________. C. Comm ...
1. Mercantilism
... the development of a society public intervention may accelerate that development (England) or block (France) Support the economic freedom (free trade, private property and self-interest) but ... «Laissez faire, laissez passer, le monde va de lui même» (Vincent de Gournay) ... They praise absolutis ...
... the development of a society public intervention may accelerate that development (England) or block (France) Support the economic freedom (free trade, private property and self-interest) but ... «Laissez faire, laissez passer, le monde va de lui même» (Vincent de Gournay) ... They praise absolutis ...
Modernization: the nation`s strategic course of growth January 13
... However, because of scarcity of land and investment resources, a feature characteristic not only of the Uzbek economy, but the economies of many other countries, developed ones included, modernization togetherwith technical and technological re-equipment of existing enterprises are regarded as a pri ...
... However, because of scarcity of land and investment resources, a feature characteristic not only of the Uzbek economy, but the economies of many other countries, developed ones included, modernization togetherwith technical and technological re-equipment of existing enterprises are regarded as a pri ...
THE NON OBSERVED THE NON-OBSERVED ECONOMY (NOE): Current Practice in Mongolia
... — Part of HHs own final use was integrated as GCF (construction) ...
... — Part of HHs own final use was integrated as GCF (construction) ...
Economics1
... A.society is conserving resources in order to save them for the future. B. society's goods and services are distributed equally among society's members. C. society's goods and services are distributed fairly, though not necessarily equally, among society's members. D. society is getting the maximum ...
... A.society is conserving resources in order to save them for the future. B. society's goods and services are distributed equally among society's members. C. society's goods and services are distributed fairly, though not necessarily equally, among society's members. D. society is getting the maximum ...
CHAPTER # 6 - HOW THE MARKETS WORK - SUPPLY
... Competition among sellers lowers costs and prices, and encourages producers to produce more of what consumers are willing and able to buy. Competition among buyers increases prices and allocates goods and services to those people who are willing and able to pay the most for them. Related concepts: M ...
... Competition among sellers lowers costs and prices, and encourages producers to produce more of what consumers are willing and able to buy. Competition among buyers increases prices and allocates goods and services to those people who are willing and able to pay the most for them. Related concepts: M ...
Chapter 4
... residents and non-residents of that country. The U.S. population is shifting The mobile populations are attractive markets ...
... residents and non-residents of that country. The U.S. population is shifting The mobile populations are attractive markets ...
How Did WWII Pull the United States Out of Economic Stagnation?
... that Roosevelt’s New Deal stopped the Depression from spiraling further down into the abyss but to create real change, and an increase in real output and income, two thing would be required. First the United States needed to increase its inputs to the economy (inputs referring to land, labor, ca ...
... that Roosevelt’s New Deal stopped the Depression from spiraling further down into the abyss but to create real change, and an increase in real output and income, two thing would be required. First the United States needed to increase its inputs to the economy (inputs referring to land, labor, ca ...
Document
... • Whatever lowers the perceived risk of the firm (ke) will also raise firm value. • Whatever raises the price of the product (Pt) or the quantity sold (Qt ) will raise firm value. • Whatever raises variable cost (Vt )or fixed cost ( Ft ) will reduce firm value. Slide 8 ...
... • Whatever lowers the perceived risk of the firm (ke) will also raise firm value. • Whatever raises the price of the product (Pt) or the quantity sold (Qt ) will raise firm value. • Whatever raises variable cost (Vt )or fixed cost ( Ft ) will reduce firm value. Slide 8 ...
ECONOMICS
... rolled around, the students who hadn't studied much for the first test had studied even less, and the ones who studied hard weren't motivated to study hard again, and they decided they wanted a free ride too; so they studied little. The second Test average was a D! No one was happy. When the 3rd tes ...
... rolled around, the students who hadn't studied much for the first test had studied even less, and the ones who studied hard weren't motivated to study hard again, and they decided they wanted a free ride too; so they studied little. The second Test average was a D! No one was happy. When the 3rd tes ...
Ptestch1
... 1. Economics deals primarily with the concept of a. scarcity. b. poverty. c. change. d. power. 2. The overriding reason as to why households and societies face many decisions is that a. resources are scarce. b. goods and services are not scarce. c. incomes fluctuate with business cycles. d. people, ...
... 1. Economics deals primarily with the concept of a. scarcity. b. poverty. c. change. d. power. 2. The overriding reason as to why households and societies face many decisions is that a. resources are scarce. b. goods and services are not scarce. c. incomes fluctuate with business cycles. d. people, ...
Israel Iran Turkey Saudi Arabia Economic Systems~ Student Copy
... • This system has not been very successful. More and more countries are abandoning it. • This system is very harsh to live under; because of this, there are no PURE command countries in the world today. • Some countries are close: Cuba, former Soviet Union, North Korea, former former East Germany, e ...
... • This system has not been very successful. More and more countries are abandoning it. • This system is very harsh to live under; because of this, there are no PURE command countries in the world today. • Some countries are close: Cuba, former Soviet Union, North Korea, former former East Germany, e ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... Traditional economy – goods and services are traded or exchanged without the use of money (barter) Command economy – production (ownership) of goods and services is controlled by a central government (planned), does not reflect consumer demand Market economy – production of goods and services is det ...
... Traditional economy – goods and services are traded or exchanged without the use of money (barter) Command economy – production (ownership) of goods and services is controlled by a central government (planned), does not reflect consumer demand Market economy – production of goods and services is det ...
CHATSWORTH SPORTS PRODUCTS – QUESTIONS
... opportunity cost of using the ten workers provided by the Sheltered Workshop in contrast to the opportunity cost of using existing Valley State staff and facilities.) ...
... opportunity cost of using the ten workers provided by the Sheltered Workshop in contrast to the opportunity cost of using existing Valley State staff and facilities.) ...
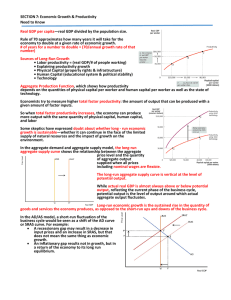
SECTION 7: Economic Growth & Productivity Need to Know —real GDP divided by the population size.
... Aggregate Production Function, which shows how productivity depends on the quantities of physical capital per worker and human capital per worker as well as the state of technology. ...
... Aggregate Production Function, which shows how productivity depends on the quantities of physical capital per worker and human capital per worker as well as the state of technology. ...
The Aggregate Production Function
... factories, hires workers, buys electricity and avionics, and uses them to produce aircraft. American Express’s credit card business uses computers, buildings, labor, and small amounts of plastic to produce payment services. Pfizer hires scientists, MBAs, and others to develop, produce, and market dr ...
... factories, hires workers, buys electricity and avionics, and uses them to produce aircraft. American Express’s credit card business uses computers, buildings, labor, and small amounts of plastic to produce payment services. Pfizer hires scientists, MBAs, and others to develop, produce, and market dr ...
Y/L
... framework within which economic data can be compiled and presented in a format that is designed for purposes of economic analysis, decisiontaking and policy-making. • Integrates a set of macroeconomic accounts, balance sheets and tables based on a set of internationally agreed concepts, definitions, ...
... framework within which economic data can be compiled and presented in a format that is designed for purposes of economic analysis, decisiontaking and policy-making. • Integrates a set of macroeconomic accounts, balance sheets and tables based on a set of internationally agreed concepts, definitions, ...