(Received February 12, 1988 by M. Cardona)
... contain, however, additional weak structures which have not yet been identified. In the present study we show that most of these lines, being observed in Faraday configuration, may be grouped in pairs with frequency separation ~:c, where v:c = eB/m* is the conduction band cyclotron frequency. Taking ...
... contain, however, additional weak structures which have not yet been identified. In the present study we show that most of these lines, being observed in Faraday configuration, may be grouped in pairs with frequency separation ~:c, where v:c = eB/m* is the conduction band cyclotron frequency. Taking ...
Polarization spectra of excited-state-Mg(3p)--rare-gas
... involving collisions between unpolarized atoms have investigated the dynamics of electronic orientation and alignment, and explored the efFects of nonadiabatic electronic energy transfer occurring during the collision [1-4]. Recently, measurements of polarization dynamics by two-photon optical colli ...
... involving collisions between unpolarized atoms have investigated the dynamics of electronic orientation and alignment, and explored the efFects of nonadiabatic electronic energy transfer occurring during the collision [1-4]. Recently, measurements of polarization dynamics by two-photon optical colli ...
Winter 2011
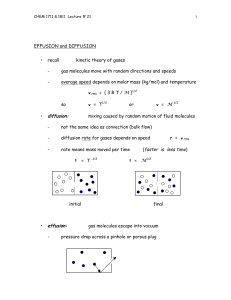
... (John Wiley & Sons, 2005). Topics covered by the course: Quantum mechanics (Ch. 9); atomic structure (Ch. 10); molecular structure (Ch. 11); rotational and vibrational spectroscopy (Ch. 13); electronic spectroscopy (Ch. 14); kinetic theory of gases (Ch. 17); chemical kinetics (Ch. 18). The emphasis ...
... (John Wiley & Sons, 2005). Topics covered by the course: Quantum mechanics (Ch. 9); atomic structure (Ch. 10); molecular structure (Ch. 11); rotational and vibrational spectroscopy (Ch. 13); electronic spectroscopy (Ch. 14); kinetic theory of gases (Ch. 17); chemical kinetics (Ch. 18). The emphasis ...
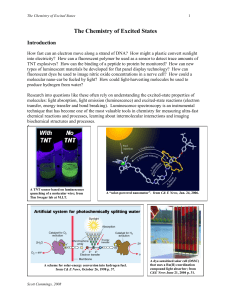
The Chemistry of Excited States
... When a molecule absorbs light in the UV-vis region, an electron is promoted from a lowerenergy occupied orbital to a higher-energy empty orbital resulting in an excited state molecule. One requirement for a molecule to absorb light is that the energy of the photon needs to match the energy differenc ...
... When a molecule absorbs light in the UV-vis region, an electron is promoted from a lowerenergy occupied orbital to a higher-energy empty orbital resulting in an excited state molecule. One requirement for a molecule to absorb light is that the energy of the photon needs to match the energy differenc ...
(pdf)
... at high energies but poorly describe the effective threshold. Since dissociation can occur down to the true threshold it is important to carry out a more detailed calculation in this regime. A full quantum mechanical calculation for CID is computationally challenging, particularly when such a large ...
... at high energies but poorly describe the effective threshold. Since dissociation can occur down to the true threshold it is important to carry out a more detailed calculation in this regime. A full quantum mechanical calculation for CID is computationally challenging, particularly when such a large ...
Environmental Effects on Atomic Energy Levels.
... Vertical electronic transitions are subject to the restrictions of the F r a n c k Condon principle. This requires that immediately after the excitation the nuclear configuration of the medium is the same as in the ground state, whereas the core electrons of the medium have adjusted themselves to th ...
... Vertical electronic transitions are subject to the restrictions of the F r a n c k Condon principle. This requires that immediately after the excitation the nuclear configuration of the medium is the same as in the ground state, whereas the core electrons of the medium have adjusted themselves to th ...
Methods of Statistical Spectroscopy as an Optimization
... In the traditional approach, spectral properties of atoms and molecules are determined using quantum chemical methods. In this approach individual energy levels and the appropriate transition probabilities are evaluated with a high precision but even for a few energy levels the computational effort ...
... In the traditional approach, spectral properties of atoms and molecules are determined using quantum chemical methods. In this approach individual energy levels and the appropriate transition probabilities are evaluated with a high precision but even for a few energy levels the computational effort ...
Franck–Condon principle
The Franck–Condon principle is a rule in spectroscopy and quantum chemistry that explains the intensity of vibronic transitions. Vibronic transitions are the simultaneous changes in electronic and vibrational energy levels of a molecule due to the absorption or emission of a photon of the appropriate energy. The principle states that during an electronic transition, a change from one vibrational energy level to another will be more likely to happen if the two vibrational wave functions overlap more significantly.