Electronic Shells of Dirac Fermions in Graphene Quantum Rings in
... shells of Dirac fermions in charge neutral graphene quantum rings and their evolution with perpendicular magnetic field. We then discuss the effect of filling of a degenerate shell with additional electrons. Using a combination of tight binding and configuration interaction methods we analyze ground ...
... shells of Dirac fermions in charge neutral graphene quantum rings and their evolution with perpendicular magnetic field. We then discuss the effect of filling of a degenerate shell with additional electrons. Using a combination of tight binding and configuration interaction methods we analyze ground ...
Phonon-like excitations in the two-state Bose
... spin-1 bosons where the multiplets of local states form the closely-spaced excited levels. It was shown in [21, 22] that MI-SF transition can be of the first order when a single-site spin interaction is of the antiferromagnetic type. A similar effect also takes place for multicomponent Bose system in ...
... spin-1 bosons where the multiplets of local states form the closely-spaced excited levels. It was shown in [21, 22] that MI-SF transition can be of the first order when a single-site spin interaction is of the antiferromagnetic type. A similar effect also takes place for multicomponent Bose system in ...
Analytical total photo cross section for atoms
... The total photo cross section of an atom is a ground-state property. Nevertheless, it is not readily calculated. Here, we present an approach which uses exact commutator relations for the hydrogenic time-dependent dipole moment and a classical approximation for the propagator to arrive at an analyti ...
... The total photo cross section of an atom is a ground-state property. Nevertheless, it is not readily calculated. Here, we present an approach which uses exact commutator relations for the hydrogenic time-dependent dipole moment and a classical approximation for the propagator to arrive at an analyti ...
LCAO Method: H2+ Molecule
... Quantum chemistry is the application of quantum mechanics to problems in chemistry. The description of the electronic behavior of atoms and molecules as pertains to their reactivity is an application of quantum chemistry. Since quantum-mechanical studies on atoms are considered to be on the borderli ...
... Quantum chemistry is the application of quantum mechanics to problems in chemistry. The description of the electronic behavior of atoms and molecules as pertains to their reactivity is an application of quantum chemistry. Since quantum-mechanical studies on atoms are considered to be on the borderli ...
Electronic state dependence in dissociation of core
... the fundamental addition of complexity arises from the possibility for the molecule to change its intrinsic framework due to nuclear motion. In a stable molecule this can be treated as two types of periodic motion: Rotation — where the whole nuclear framework is rotating — and vibration — where the ...
... the fundamental addition of complexity arises from the possibility for the molecule to change its intrinsic framework due to nuclear motion. In a stable molecule this can be treated as two types of periodic motion: Rotation — where the whole nuclear framework is rotating — and vibration — where the ...
Strict Relationship: Potential - energy levels
... different points x i allows to the elimination of X i and Yi , and leads to the following equation known as the energy quantification condition: Bn (E) a n Pn b n Qn 0 ...
... different points x i allows to the elimination of X i and Yi , and leads to the following equation known as the energy quantification condition: Bn (E) a n Pn b n Qn 0 ...
Figure 4 - University of Wisconsin–Madison
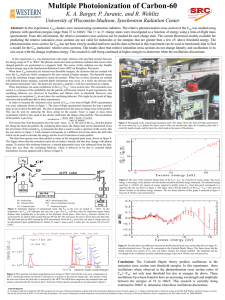
... photons with specified energies range from 37 to 160eV. The 1+ to 3+ charge states were investigated as a function of energy using a time-of-flight mass spectrometer. From this information, the relative ionization cross sections can be studied for each charge state. The current theoretical models av ...
... photons with specified energies range from 37 to 160eV. The 1+ to 3+ charge states were investigated as a function of energy using a time-of-flight mass spectrometer. From this information, the relative ionization cross sections can be studied for each charge state. The current theoretical models av ...
Photofragmentation-laser induced fluorescence: a
... gas lasers. Because of their rugged durability and very high energies at multiple wavelengths, we believe that a Nd:YAG system is the preferred driver laser. It should be noted also that, even in the case where two dye lasers are to be used to generate the X and X2 laser pulses, a single Nd:YAG driv ...
... gas lasers. Because of their rugged durability and very high energies at multiple wavelengths, we believe that a Nd:YAG system is the preferred driver laser. It should be noted also that, even in the case where two dye lasers are to be used to generate the X and X2 laser pulses, a single Nd:YAG driv ...
The Spectrophotometer
... slotted piece of metal which can be moved back and forth in the light path. The bulb produces varying intensities at different wavelengths. The light control decreases high intensities by blocking some of the light with the slotted metal. The right front knob controls this function. To use this knob ...
... slotted piece of metal which can be moved back and forth in the light path. The bulb produces varying intensities at different wavelengths. The light control decreases high intensities by blocking some of the light with the slotted metal. The right front knob controls this function. To use this knob ...
Photodissociation Dynamics of Molecular Fluorine in an Argon
... of molecular fluorine in an argon matrix are studied. The interactions of photofragments and host atoms are modeled using a diatomics-in-molecule Hamiltonian. Two types of methods are compared: (1) quantumclassical simulations where the nuclei are treated classically, with surface-hopping algorithms ...
... of molecular fluorine in an argon matrix are studied. The interactions of photofragments and host atoms are modeled using a diatomics-in-molecule Hamiltonian. Two types of methods are compared: (1) quantumclassical simulations where the nuclei are treated classically, with surface-hopping algorithms ...
Atomic spectra
... in an interaction the radiation behaves as a concentration of energy (photons) moving at the speed of light. Each photon carries very little energy. However, even an ordinary torch beam is a torrent of ~1017 photons.s-1. When we ‘see’ light, what we observe by eye or on film is the average energy pe ...
... in an interaction the radiation behaves as a concentration of energy (photons) moving at the speed of light. Each photon carries very little energy. However, even an ordinary torch beam is a torrent of ~1017 photons.s-1. When we ‘see’ light, what we observe by eye or on film is the average energy pe ...
Lecture #3-Molecular Polarity and Physical Properties
... Dipole–Dipole Attractions between Molecules Permanent polarity in molecules due to their structure Hydrogen Bonds between Molecules An especially strong dipole–dipole attraction resulting from the attachment of H to an extremely electronegative ...
... Dipole–Dipole Attractions between Molecules Permanent polarity in molecules due to their structure Hydrogen Bonds between Molecules An especially strong dipole–dipole attraction resulting from the attachment of H to an extremely electronegative ...
Enzymology Lecture 5 - ASAB-NUST
... C. In the transition state model, the enzyme’s reactive stage can be defined as: (1) Staying the same. (2) Changing before binding with substrate. (3) Changing after binding with substrate. (4) Changing during binding with substrate. ...
... C. In the transition state model, the enzyme’s reactive stage can be defined as: (1) Staying the same. (2) Changing before binding with substrate. (3) Changing after binding with substrate. (4) Changing during binding with substrate. ...
Franck–Condon principle
The Franck–Condon principle is a rule in spectroscopy and quantum chemistry that explains the intensity of vibronic transitions. Vibronic transitions are the simultaneous changes in electronic and vibrational energy levels of a molecule due to the absorption or emission of a photon of the appropriate energy. The principle states that during an electronic transition, a change from one vibrational energy level to another will be more likely to happen if the two vibrational wave functions overlap more significantly.