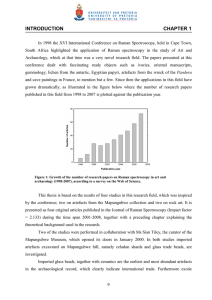
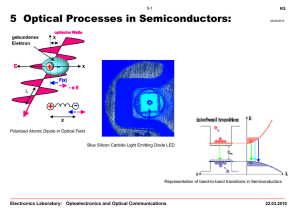
INTRODUCTION ...
... radiation) interact primarily with the electrons of a sample, while neutrons interact with the nuclei. The strength of the interaction is very dependent on the particular nuclide involved, isotopes and spin states. Another difference is that the wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation used for R ...
... radiation) interact primarily with the electrons of a sample, while neutrons interact with the nuclei. The strength of the interaction is very dependent on the particular nuclide involved, isotopes and spin states. Another difference is that the wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation used for R ...
Atomic structure via highly charged ions and
... (iv) Energy curves whose dominant configurations contain higher principal quantum number orbitals should converge to values greater than zero as 1/Z → 0, more explicitly to a(0) (N ) − a(0) GS (N ). These predictions are all beautifully confirmed by the experimental data, see Figure 4. Such plots (s ...
... (iv) Energy curves whose dominant configurations contain higher principal quantum number orbitals should converge to values greater than zero as 1/Z → 0, more explicitly to a(0) (N ) − a(0) GS (N ). These predictions are all beautifully confirmed by the experimental data, see Figure 4. Such plots (s ...
Chapter 5 Harmonic Oscillator and Coherent States
... The explicit form of the excited state wave functions will be calculated later on but we can for now reveal that they are proportional to a product of the ground state and a family of functions, the so-called Hermite polynomials Hn . The wave functions thus form a ladder of alternating even and odd ...
... The explicit form of the excited state wave functions will be calculated later on but we can for now reveal that they are proportional to a product of the ground state and a family of functions, the so-called Hermite polynomials Hn . The wave functions thus form a ladder of alternating even and odd ...
Stochastic thermodynamics: A brief introduction
... surmount several other difficulties that have plagued a statistical mechanical interpretation of the second law, notably the application to small systems and to systems far from equilibrium. The basic approach is inspired by the work of Onsager, in the sense that we will incorporate basic properties i ...
... surmount several other difficulties that have plagued a statistical mechanical interpretation of the second law, notably the application to small systems and to systems far from equilibrium. The basic approach is inspired by the work of Onsager, in the sense that we will incorporate basic properties i ...
Quantum Coherence in Biological Systems
... key features of quantum effects and point out how they could matter in biological systems. Chapter 2 deals with the avian compass, where spin coherences play a fundamental role. The experimental evidence on how weak oscillating fields disrupt a bird’s ability to navigate is summarized. Detailed calc ...
... key features of quantum effects and point out how they could matter in biological systems. Chapter 2 deals with the avian compass, where spin coherences play a fundamental role. The experimental evidence on how weak oscillating fields disrupt a bird’s ability to navigate is summarized. Detailed calc ...
Theoretical Investigations Regarding Single Molecules
... wavefunction is indexed by the principal quantum number n and the orbital quantum numbers l and m. ...
... wavefunction is indexed by the principal quantum number n and the orbital quantum numbers l and m. ...
Exploring Potential Energy Surfaces for Chemical
... region and a lower level of theory is used for the larger environment, as illustrated in Figure 2. Covalent bonds that cross the boundary between the two regions can be treated by using link atom or hybrid orbitals. Geometry optimization methods can take advantage of the fact that a large region is ...
... region and a lower level of theory is used for the larger environment, as illustrated in Figure 2. Covalent bonds that cross the boundary between the two regions can be treated by using link atom or hybrid orbitals. Geometry optimization methods can take advantage of the fact that a large region is ...
91, 053630 (2015).
... motion, or spin-orbit coupling, plays a crucial role in various nontrivial many-body phenomena, such as topological insulators and superconductors [1,2] in fermionic systems, as well as exotic spinor condensates and superfluids in bosonic ones. Considerable effort [3–40] has been devoted to the inve ...
... motion, or spin-orbit coupling, plays a crucial role in various nontrivial many-body phenomena, such as topological insulators and superconductors [1,2] in fermionic systems, as well as exotic spinor condensates and superfluids in bosonic ones. Considerable effort [3–40] has been devoted to the inve ...
Franck–Condon principle
The Franck–Condon principle is a rule in spectroscopy and quantum chemistry that explains the intensity of vibronic transitions. Vibronic transitions are the simultaneous changes in electronic and vibrational energy levels of a molecule due to the absorption or emission of a photon of the appropriate energy. The principle states that during an electronic transition, a change from one vibrational energy level to another will be more likely to happen if the two vibrational wave functions overlap more significantly.