Module 6
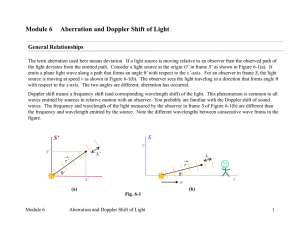
... their telescopes in viewing certain stars at different times, astronomers knew that the light was undergoing aberration. The mechanism for the aberration was not understood. Newtonian relativity predicts an aberration but only if one adheres to the straight Newtonian view that an observer can see li ...
... their telescopes in viewing certain stars at different times, astronomers knew that the light was undergoing aberration. The mechanism for the aberration was not understood. Newtonian relativity predicts an aberration but only if one adheres to the straight Newtonian view that an observer can see li ...
Maxwell and Special Relativity - Physics Department, Princeton
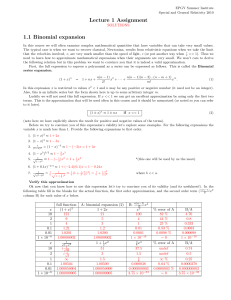
... The transformation (7) is compatible with both magnetic Galilean relativity, eq. (3), and the low-velocity limit of special relativity, eq. (4). These two version of relativity differ as to the transformation of the magnetic field. In particular, if B = 0 while E were due to a single electric charge a ...
... The transformation (7) is compatible with both magnetic Galilean relativity, eq. (3), and the low-velocity limit of special relativity, eq. (4). These two version of relativity differ as to the transformation of the magnetic field. In particular, if B = 0 while E were due to a single electric charge a ...
Semester Exam REVIEW PACKET KEY
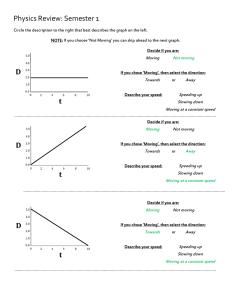
... iii. At t = 0, who is faster? Who has a greater positive starting position? Still A (see explanation in part i) and B has the greater positive starting position ...
... iii. At t = 0, who is faster? Who has a greater positive starting position? Still A (see explanation in part i) and B has the greater positive starting position ...
Time dilation

In the theory of relativity, time dilation is a difference of elapsed time between two events as measured by observers either moving relative to each other or differently situated from a gravitational mass or masses.An accurate clock at rest with respect to one observer may be measured to tick at a different rate when compared to a second observer's own equally accurate clocks. This effect arises neither from technical aspects of the clocks nor from the fact that signals need time to propagate, but from the nature of spacetime itself.