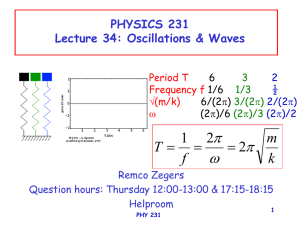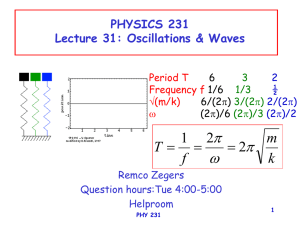
that begin or end on it. For example, figure x/2 shows eight lines at
... d, p, m . . . . . . other notations for the electric dipole moment Summary Experiments show that time is not absolute: it flows at different rates depending on an observer’s state of motion. This is an example of the strange effects predicted by Einstein’s theory of relativity. All of these effects, ...
... d, p, m . . . . . . other notations for the electric dipole moment Summary Experiments show that time is not absolute: it flows at different rates depending on an observer’s state of motion. This is an example of the strange effects predicted by Einstein’s theory of relativity. All of these effects, ...
Chapter_2 - Experimental Elementary Particle Physics Group
... absolute, and therefore perfectly detectable (in principle). In contrast, we hypothesize that velocity is perfectly undetectable, which explains why we cannot define our "ideal clock" to compensate for velocity (or, for that matter, position). The point is that these are both assumptions invoked by ...
... absolute, and therefore perfectly detectable (in principle). In contrast, we hypothesize that velocity is perfectly undetectable, which explains why we cannot define our "ideal clock" to compensate for velocity (or, for that matter, position). The point is that these are both assumptions invoked by ...
Question Paper - Revision Science
... Assuming that air resistance is negligible, which of the following would produce a more reliable value of g? A Drop the card from a greater height. B Ensure that the card is dropped from rest. C Make the card shorter. D Move the light gates further apart. (Total for Question 10 = 1 mark) TOTAL FOR S ...
... Assuming that air resistance is negligible, which of the following would produce a more reliable value of g? A Drop the card from a greater height. B Ensure that the card is dropped from rest. C Make the card shorter. D Move the light gates further apart. (Total for Question 10 = 1 mark) TOTAL FOR S ...
Lecture 3 - Propagetion trhough optical fiber
... joule-sec) and f is the frequency of light • Energy of light depends on its speed: E=mc^2 (Einstein’s Eqn.) • The relationship between frequency and speed: v=c/λ • Speed of light changes as it enters denser materials ...
... joule-sec) and f is the frequency of light • Energy of light depends on its speed: E=mc^2 (Einstein’s Eqn.) • The relationship between frequency and speed: v=c/λ • Speed of light changes as it enters denser materials ...
Time dilation

In the theory of relativity, time dilation is a difference of elapsed time between two events as measured by observers either moving relative to each other or differently situated from a gravitational mass or masses.An accurate clock at rest with respect to one observer may be measured to tick at a different rate when compared to a second observer's own equally accurate clocks. This effect arises neither from technical aspects of the clocks nor from the fact that signals need time to propagate, but from the nature of spacetime itself.