ECONOMICS - University of Maryland, College Park
... Total Spending in a Simple Economy An economy producing total output of $10 trillion will, by definition, creates $10 trillion in total income (factor payments). If households spend all of this income on consumption goods, then total spending will equal $10 trillion as well. ...
... Total Spending in a Simple Economy An economy producing total output of $10 trillion will, by definition, creates $10 trillion in total income (factor payments). If households spend all of this income on consumption goods, then total spending will equal $10 trillion as well. ...
here
... 1) The lagged effect of the end of the mining boom, trailing of gradually 2) Some of the “income effects” will take some time to flow through Example of income shock being delayed: A booming Australia could get by with low tax rates and generous breaks in super, capital gains, negative gearing etc ...
... 1) The lagged effect of the end of the mining boom, trailing of gradually 2) Some of the “income effects” will take some time to flow through Example of income shock being delayed: A booming Australia could get by with low tax rates and generous breaks in super, capital gains, negative gearing etc ...
samenvatting IIOS h 2,3,4
... 3. Leading sectors will produce self-sustained growth (industries) Maturity stage: 1. Spread of technology and investment to other economic sectors 2. The economy is diversifying into new areas. 3. The economy is producing a wide range of goods and services and there is less reliance on imports. Hig ...
... 3. Leading sectors will produce self-sustained growth (industries) Maturity stage: 1. Spread of technology and investment to other economic sectors 2. The economy is diversifying into new areas. 3. The economy is producing a wide range of goods and services and there is less reliance on imports. Hig ...
Document
... spending, shift the AD curve to the right, and thus remove the economy from recessionary gap? • A change in interest rates, or business expectations , or both can cause a change in autonomous investment spending. • Investment is not always responsive to lower interest rates. Business expectations wi ...
... spending, shift the AD curve to the right, and thus remove the economy from recessionary gap? • A change in interest rates, or business expectations , or both can cause a change in autonomous investment spending. • Investment is not always responsive to lower interest rates. Business expectations wi ...
A. Unemployment
... negative GDP gap of about 2 percent occurs. This is known as “Okun’s law”. • The forgone outputs in this case when the economy fails to create enough jobs for all who are able and willing to work, potential production of goods and services is lost. ...
... negative GDP gap of about 2 percent occurs. This is known as “Okun’s law”. • The forgone outputs in this case when the economy fails to create enough jobs for all who are able and willing to work, potential production of goods and services is lost. ...
Sections 6-10
... • For an industrial policy to be successful, it should target sectors that conform to the economy’s latent comparative advantage: – Firms will be viable and the sectors will be competitive once the government helps the firms overcome coordination and externality issues. ...
... • For an industrial policy to be successful, it should target sectors that conform to the economy’s latent comparative advantage: – Firms will be viable and the sectors will be competitive once the government helps the firms overcome coordination and externality issues. ...
Chapter 1: Introduction
... The century after 1750 saw the industrial revolution proper: the invention of the steam engine, the spinning jenny, the power loom, the hydraulic press, the railroad locomotive, the water turbine, and the electric motor--as well as the hot-air balloon, gas lighting, photography, and the sewing machi ...
... The century after 1750 saw the industrial revolution proper: the invention of the steam engine, the spinning jenny, the power loom, the hydraulic press, the railroad locomotive, the water turbine, and the electric motor--as well as the hot-air balloon, gas lighting, photography, and the sewing machi ...
Date of Announcement Date of the next Announcement
... report of the number of individuals employed. Unemployment and unemployment rates receive much of the press attention and rightfully so. But employment and a loss or gain in jobs are also important indicators of progress in the economy. The failure of the economy to produce as many jobs as we have e ...
... report of the number of individuals employed. Unemployment and unemployment rates receive much of the press attention and rightfully so. But employment and a loss or gain in jobs are also important indicators of progress in the economy. The failure of the economy to produce as many jobs as we have e ...
E P CONOMIC ERSPECTIVE
... that it is possible to rapidly increase economic production of goods and services, at least in the short run, while simultaneously having these difficulties. The production of communications services, particularly wireless communications services, increased rapidly in 2001. In fact, the overcapacity ...
... that it is possible to rapidly increase economic production of goods and services, at least in the short run, while simultaneously having these difficulties. The production of communications services, particularly wireless communications services, increased rapidly in 2001. In fact, the overcapacity ...
Economic growth 2008-2013 Initial conditions
... especially on fiscal and structural front. Giving up further reforms or even worse going back on fiscal and structural change, would unavoidably create another wave of crisis, with related political upheavals. This is a specially case of large countries. On the other hand persisting with the reforms ...
... especially on fiscal and structural front. Giving up further reforms or even worse going back on fiscal and structural change, would unavoidably create another wave of crisis, with related political upheavals. This is a specially case of large countries. On the other hand persisting with the reforms ...
PDF Download
... of the state-led development era. The increase in the prices of commodities, in fact, favors the Brazilian expansion, since Brazil is not an importer of food, and is an exporter of commodities. The growth in exports, reduces the risks of external crises, and allows for more vigorous expansion of the ...
... of the state-led development era. The increase in the prices of commodities, in fact, favors the Brazilian expansion, since Brazil is not an importer of food, and is an exporter of commodities. The growth in exports, reduces the risks of external crises, and allows for more vigorous expansion of the ...
new classical vs keynesian viewpoint
... FOPs’ prices rise Segment 3: Economy at maximum capacity LRAS perfectly inelastic ...
... FOPs’ prices rise Segment 3: Economy at maximum capacity LRAS perfectly inelastic ...
Economic Growth
... Real GDP grows when the quantities of the factors of production grow or when persistent advances in technology make them increasingly productive. All the influences on real GDP growth can be divided into those that increase Aggregate hours Labour productivity ...
... Real GDP grows when the quantities of the factors of production grow or when persistent advances in technology make them increasingly productive. All the influences on real GDP growth can be divided into those that increase Aggregate hours Labour productivity ...
Presentation to the Bay Area Council 2006 Outlook Conference
... could surprise us in either direction. In other words, instead of the significant moderation I’ve built into my forecast, house price appreciation could either slow much more than I expect, or it could continue at its current pace. If it slows much faster—or, worse yet, reverses course—the impact co ...
... could surprise us in either direction. In other words, instead of the significant moderation I’ve built into my forecast, house price appreciation could either slow much more than I expect, or it could continue at its current pace. If it slows much faster—or, worse yet, reverses course—the impact co ...
economic polices to control inflation
... temporary working along with the expansion of flexible working hours are all moves that have increased flexibility in the labour market. If this does allow firms to control their labour costs it may reduce cost push inflationary pressure. Supply side reforms If a greater output can be produced at ...
... temporary working along with the expansion of flexible working hours are all moves that have increased flexibility in the labour market. If this does allow firms to control their labour costs it may reduce cost push inflationary pressure. Supply side reforms If a greater output can be produced at ...
short-run economic fluctuations
... Short-Run Economic Fluctuations • What causes short-run fluctuations in economic activity? • What, if anything, can the government do to stop GDP from falling and unemployment from rising? • And if the government can’t stop the occurrence of bad times, can it at least make them less damaging in ter ...
... Short-Run Economic Fluctuations • What causes short-run fluctuations in economic activity? • What, if anything, can the government do to stop GDP from falling and unemployment from rising? • And if the government can’t stop the occurrence of bad times, can it at least make them less damaging in ter ...
Eurozone Economic Outlook July 2014: Detailed analyses, figures and tables (PDF, 393 KB)
... quarter). Growth rates are forecasted to remain at this level in Q3 and Q4. The recovery is expected to be broad based across sectors and countries. The consolidation of the upturn will be mainly driven by progressive improvements in domestic demand and a marginal contribution by the external sector ...
... quarter). Growth rates are forecasted to remain at this level in Q3 and Q4. The recovery is expected to be broad based across sectors and countries. The consolidation of the upturn will be mainly driven by progressive improvements in domestic demand and a marginal contribution by the external sector ...
042.en
... In the first three quarters of 2011, GDP growth was mainly driven by manufacturing. Construction and information and communication activities started to contribute the most to economic growth since the second half-year. The increase in the value-added tax and excise duty collected also had a signifi ...
... In the first three quarters of 2011, GDP growth was mainly driven by manufacturing. Construction and information and communication activities started to contribute the most to economic growth since the second half-year. The increase in the value-added tax and excise duty collected also had a signifi ...
Plain Text
... heavily in building production capacity, such that low oil prices are less of a benefit to their economies than may have been the case historically. Consider all of the layoffs and deferred investment in the U.S. shale oil industry since oil prices started their descent. Clearly this has had an imme ...
... heavily in building production capacity, such that low oil prices are less of a benefit to their economies than may have been the case historically. Consider all of the layoffs and deferred investment in the U.S. shale oil industry since oil prices started their descent. Clearly this has had an imme ...
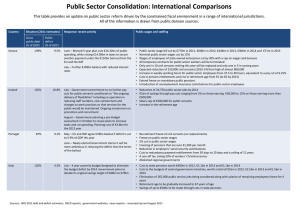
Transformation in economics
Transformation in economics refers to a long-term change in dominant economic activity in terms of prevailing relative engagement or employment of able individuals.Human economic systems undergo a number of deviations and departures from the ""normal"" state, trend or development. Among them are Disturbance (short-term disruption, temporary disorder), Perturbation (persistent or repeated divergence, predicament, decline or crisis), Deformation (damage, regime change, loss of self-sustainability, distortion), Transformation (long-term change, restructuring, conversion, new “normal”) and Renewal (rebirth, transmutation, corso-ricorso, renaissance, new beginning).Transformation is a unidirectional and irreversible change in dominant human economic activity (economic sector). Such change is driven by slower or faster continuous improvement in sector productivity growth rate. Productivity growth itself is fueled by advances in technology, inflow of useful innovations, accumulated practical knowledge and experience, levels of education, viability of institutions, quality of decision making and organized human effort. Individual sector transformations are the outcomes of human socio-economic evolution.Human economic activity has so far undergone at least four fundamental transformations:From nomadic hunting and gathering (H/G) to localized agricultureFrom localized agriculture (A) to internationalized industryFrom international industry (I) to global servicesFrom global services (S) to public sector (including government, welfare and unemployment, GWU)This evolution naturally proceeds from securing necessary food, through producing useful things, to providing helpful services, both private and public (See H/G→A→I→S→GWU sequence in Fig. 1). Accelerating productivity growth rates speed up the transformations, from millennia, through centuries, to decades of the recent era. It is this acceleration which makes transformation relevant economic category of today, more fundamental in its impact than any recession, crisis or depression. The evolution of four forms of capital (Indicated in Fig. 1) accompanies all economic transformations.Transformation is quite different from accompanying cyclical recessions and crises, despite the similarity of manifested phenomena (unemployment, technology shifts, socio-political discontent, bankruptcies, etc.). However, the tools and interventions used to combat crisis are clearly ineffective for coping with non-cyclical transformations. The problem is whether we face a mere crisis or a fundamental transformation (globalization→relocalization).