Adaptation and Natural Selection
... Important Ecological Terms Succession – The series of predictable changes that occurs in a community over time – Primary succession occurs on a surface where no soil exists. Ex. bare rock, areas covered by volcanic ash – Secondary succession occurs in an area where a disturbances changes an exist ...
... Important Ecological Terms Succession – The series of predictable changes that occurs in a community over time – Primary succession occurs on a surface where no soil exists. Ex. bare rock, areas covered by volcanic ash – Secondary succession occurs in an area where a disturbances changes an exist ...
Ecological Concerns
... Ozone is 731 miles above the earth Ozone depletion causes an increase in the amount of UV rays reaching the surface ...
... Ozone is 731 miles above the earth Ozone depletion causes an increase in the amount of UV rays reaching the surface ...
Admission Test For Admission to MS Degree in
... C) Solubility in fatty tissues D) Artificial manufacture by industry ...
... C) Solubility in fatty tissues D) Artificial manufacture by industry ...
Plants and Animals
... The processes by which an organism takes in and processes oxygen and releases carbon dioxide. ...
... The processes by which an organism takes in and processes oxygen and releases carbon dioxide. ...
Fundamental Ideas and Nature of Env Science
... • Our interactions with its other parts matter • We depend completely on the environment for survival • Natural systems have been degraded by pollution, soil erosion, species extinction, etc. • Environmental changes threaten our long-term wellbeing and survival ...
... • Our interactions with its other parts matter • We depend completely on the environment for survival • Natural systems have been degraded by pollution, soil erosion, species extinction, etc. • Environmental changes threaten our long-term wellbeing and survival ...
Ecology - St. Ambrose School
... Animals such as bison, prairie dogs and antelope thrive due to the amount of grass available to eat. Wolves and coyotes are natural ...
... Animals such as bison, prairie dogs and antelope thrive due to the amount of grass available to eat. Wolves and coyotes are natural ...
Living Things and the Environment
... Ecosystems contain more than one type of organism All the different populations that live together in an area make up a community To be considered a community the organisms must live together and interact with each other. They may interact by using the same types of shelter, food, or resources. ...
... Ecosystems contain more than one type of organism All the different populations that live together in an area make up a community To be considered a community the organisms must live together and interact with each other. They may interact by using the same types of shelter, food, or resources. ...
Chapter 5, Lesson 1 Interactions in an Ecosystem
... ecosystem – all the living and non-living things in an area Click to access link! ...
... ecosystem – all the living and non-living things in an area Click to access link! ...
The study of how living things interact with nature Biotic The living
... benefits from another but the second species isn’t affected ...
... benefits from another but the second species isn’t affected ...
How Do We Develop and Maintain a Sustainable
... Multidisciplinary field that draws from all the sciences, as well as other fields, to help us better understand the relationship between humans and the world in which we live. It focuses on three main areas: Conservation and protection of natural resources ...
... Multidisciplinary field that draws from all the sciences, as well as other fields, to help us better understand the relationship between humans and the world in which we live. It focuses on three main areas: Conservation and protection of natural resources ...
living
... fungus from the shark by feeding on it..... • That is Mutualism because both benefit • A tick sucks the blood from a deer... • That is Parasitism because the deer is harmed • A bird that lives in a hole in a tree is... • Commensalism (the tree is neither harmed nor helped, but the bird gets shelter) ...
... fungus from the shark by feeding on it..... • That is Mutualism because both benefit • A tick sucks the blood from a deer... • That is Parasitism because the deer is harmed • A bird that lives in a hole in a tree is... • Commensalism (the tree is neither harmed nor helped, but the bird gets shelter) ...
Unit 3: Evolution, Biodiversity, Climate, Weather, and Biomes
... contributing to global biodiversity 4.2.3 – Discuss current estimates of numbers of species and past and present rates of species extinction ...
... contributing to global biodiversity 4.2.3 – Discuss current estimates of numbers of species and past and present rates of species extinction ...
Chapter 3: Ecosystems: What Are They and How Do They Work
... Insects have a bad reputation but perform many beneficial services for the environment. Many plants need insects to pollinate their flowers. Insects eat other insects controlling population size. They have existed at least 400 million years, reproduce quickly, and rapidly develop new genetic traits. ...
... Insects have a bad reputation but perform many beneficial services for the environment. Many plants need insects to pollinate their flowers. Insects eat other insects controlling population size. They have existed at least 400 million years, reproduce quickly, and rapidly develop new genetic traits. ...
I. What is Ecology? A. Definition: The study of the interactions of
... 1. Humans are as dependent as other organisms on "the environment" - nutrient cycling (decomposition/ release of 'fertilizers') - atmospheric and climatic regulation (maintaining climate and oxygen levels fit for human existence) - water and air waste treatment - food, shelter, and energy (coal, tim ...
... 1. Humans are as dependent as other organisms on "the environment" - nutrient cycling (decomposition/ release of 'fertilizers') - atmospheric and climatic regulation (maintaining climate and oxygen levels fit for human existence) - water and air waste treatment - food, shelter, and energy (coal, tim ...
Chapter 36
... • A symbiotic relationship is a close interaction between species in which one of the species lives in or on the other. – Parasitism – one benefits and the other is harmed. – Mutualism – both species benefit – Commensalism – one benefits and the other is ...
... • A symbiotic relationship is a close interaction between species in which one of the species lives in or on the other. – Parasitism – one benefits and the other is harmed. – Mutualism – both species benefit – Commensalism – one benefits and the other is ...
Climate and Biodiversity
... •Grasslands are not taken over by shrubs and trees because of seasonal droughts, grazing by large herbivores, and occasional ...
... •Grasslands are not taken over by shrubs and trees because of seasonal droughts, grazing by large herbivores, and occasional ...
Organisms and their environment lecture 23.1
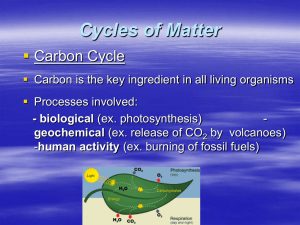
... Greenhouse effect • CO2, methane, water vapor trap heat energy • Maintains Earth’s temp range • Solar E is trapped, heat E doesn’t escape into space ...
... Greenhouse effect • CO2, methane, water vapor trap heat energy • Maintains Earth’s temp range • Solar E is trapped, heat E doesn’t escape into space ...
NICHE CONCEPT Every organism has a place to live in nature, a
... Every organism has a place to live in nature, a functional role in that place, and a complex set of adaptations for reproducing its kind. On the surface, this observation might seem to be obvious, even trivial. However, in order to understand our biological world—the biosphere, how it operates and u ...
... Every organism has a place to live in nature, a functional role in that place, and a complex set of adaptations for reproducing its kind. On the surface, this observation might seem to be obvious, even trivial. However, in order to understand our biological world—the biosphere, how it operates and u ...
Vocabulary - COSEE West
... adaptation/adaptacíon: the modification of characteristics of a species of organism over time to adjust to a new condition baleen/ballena: fibrous plates made from keratin that hang from the roof of baleen whales’ mouths used for filtering food from the water. Baleen whales are classified as Mystece ...
... adaptation/adaptacíon: the modification of characteristics of a species of organism over time to adjust to a new condition baleen/ballena: fibrous plates made from keratin that hang from the roof of baleen whales’ mouths used for filtering food from the water. Baleen whales are classified as Mystece ...
What four areas does population size depend on?
... • Temperate deciduous forest- deer, bobcats, and squirrels • Taiga- moose, beavers, and Timberwolves • Great Lakes/freshwater- trout, bass and pike • Ocean/California Coast- seals dolphins and whales ...
... • Temperate deciduous forest- deer, bobcats, and squirrels • Taiga- moose, beavers, and Timberwolves • Great Lakes/freshwater- trout, bass and pike • Ocean/California Coast- seals dolphins and whales ...
Chapter 5 Notes
... Is the natural association that consists of all populations of different species that live and interact together within an area at the same time. Ecosystem: A community and its physical environment. Landscape (seascape): Is a region that includes several interacting ecosystems Biosphere: The ...
... Is the natural association that consists of all populations of different species that live and interact together within an area at the same time. Ecosystem: A community and its physical environment. Landscape (seascape): Is a region that includes several interacting ecosystems Biosphere: The ...
Name: :__
... 17. In an energy pyramid, where is most of the energy found (top or bottom)? What is found at the bottom? 18. What range in the range of tolerance would you find organisms thriving and reproducing? (Look at graph) 19. What is the hydrologic cycle? 20. What are the two ways in which humans have most ...
... 17. In an energy pyramid, where is most of the energy found (top or bottom)? What is found at the bottom? 18. What range in the range of tolerance would you find organisms thriving and reproducing? (Look at graph) 19. What is the hydrologic cycle? 20. What are the two ways in which humans have most ...
Natural environment

The natural environment encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally on Earth or some region thereof. It is an environment that encompasses the interaction of all living species. Climate, weather, and natural resources that affect human survival and economic activity.The concept of the natural environment can be distinguished by components: Complete ecological units that function as natural systems without massive civilized human intervention, including all vegetation, microorganisms, soil, rocks, atmosphere, and natural phenomena that occur within their boundaries Universal natural resources and physical phenomena that lack clear-cut boundaries, such as air, water, and climate, as well as energy, radiation, electric charge, and magnetism, not originating from civilized human activityIn contrast to the natural environment is the built environment. In such areas where man has fundamentally transformed landscapes such as urban settings and agricultural land conversion, the natural environment is greatly modified and diminished, with a much more simplified human environment largely replacing it. Even events which seem less extreme such as hydroelectric dam construction, or photovoltaic system construction in the desert, the natural environment is substantially altered.It is difficult to find absolutely natural environments, and it is common that the naturalness varies in a continuum, from ideally 100% natural in one extreme to 0% natural in the other. More precisely, we can consider the different aspects or components of an environment, and see that their degree of naturalness is not uniform. If, for instance, we take an agricultural field, and consider the mineralogic composition and the structure of its soil, we will find that whereas the first is quite similar to that of an undisturbed forest soil, the structure is quite different.Natural environment is often used as a synonym for habitat. For instance, when we say that the natural environment of giraffes is the savanna.