![4.LECTURE-Systems of the Earth [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014265275_1-c3f0353eb192762d4742baddbdbd9cf1-300x300.png)
4.LECTURE-Systems of the Earth [Compatibility Mode]
... pollutants from one area of the Earth to other regions and even their dispersion on a global scale. A large part of the processes taking place in the biosphere depend on the composition of the air that is used for maintaining life processes, especially in the case of organisms which are much more co ...
... pollutants from one area of the Earth to other regions and even their dispersion on a global scale. A large part of the processes taking place in the biosphere depend on the composition of the air that is used for maintaining life processes, especially in the case of organisms which are much more co ...
Power Point 1 - G. Holmes Braddock
... a variety of ways. Seasonal changes can drastically affect an ecosystem because since every seasonal change there are different resources that are being added and being removed from an ecosystem, and energy consumption and resources are depleted depending on the season drastically affecting the way ...
... a variety of ways. Seasonal changes can drastically affect an ecosystem because since every seasonal change there are different resources that are being added and being removed from an ecosystem, and energy consumption and resources are depleted depending on the season drastically affecting the way ...
abiotic Non-living factors like rain, sun, minerals in soil, and
... abiotic adaptation aquatic biodiversity biome biotic carnivore community consumer control decomposer ...
... abiotic adaptation aquatic biodiversity biome biotic carnivore community consumer control decomposer ...
REVIEW FOR ENV. SCIENCE FINAL 2015 *Environment
... *Environment, ecosystem, ecology, 5 levels of ecology (organism, population, community, ecosystem, biosphere), biomes (large geographic areas with similar climate), indicator species (trout in a stream) *Population, endangered, threatened, reasons for extinction, habitat destruction (number one caus ...
... *Environment, ecosystem, ecology, 5 levels of ecology (organism, population, community, ecosystem, biosphere), biomes (large geographic areas with similar climate), indicator species (trout in a stream) *Population, endangered, threatened, reasons for extinction, habitat destruction (number one caus ...
Ecological Interactions - Westhampton Beach Elementary School
... • Struggle between organisms to obtain things they need for survival (food, water, shelter, light) • Competition can be within a population or between populations of different species using the same resource • i.e. rabbits competing for food in a field or rabbits competing with squirrels for suitabl ...
... • Struggle between organisms to obtain things they need for survival (food, water, shelter, light) • Competition can be within a population or between populations of different species using the same resource • i.e. rabbits competing for food in a field or rabbits competing with squirrels for suitabl ...
Slide 1
... Conditions for Life on Earth Availability of water Physiological solvent, transport, coolant. The anomalous expansion on freezing (ice floats) prevents many water bodies from freezing solid. The high specific heat capacity of water moderates temperature change. Water provides aquatic habitats. ...
... Conditions for Life on Earth Availability of water Physiological solvent, transport, coolant. The anomalous expansion on freezing (ice floats) prevents many water bodies from freezing solid. The high specific heat capacity of water moderates temperature change. Water provides aquatic habitats. ...
German global warming PP
... about 0.8 °C (1.4 °F) with about two thirds of the increase occurring over just the last three decades. • Because the Earth has been gradually becoming warmer for so long there is debate about the validity of global warming and its existence. • Scientists are more than 90% certain most of it is caus ...
... about 0.8 °C (1.4 °F) with about two thirds of the increase occurring over just the last three decades. • Because the Earth has been gradually becoming warmer for so long there is debate about the validity of global warming and its existence. • Scientists are more than 90% certain most of it is caus ...
WS 2 - natural selection
... Use the example of anti-biotic resistant bacteria to explain the theory of natural selection. You may do this in words or with diagrams. ...
... Use the example of anti-biotic resistant bacteria to explain the theory of natural selection. You may do this in words or with diagrams. ...
Study Guide Exam Four
... Tundra like climate and vegetation conditions on a mountain is called what? What property of a community refers to the number of species making up the community? What property of a community refers to it being able to withstand minor disturbances? What does the term biotic stand for? What does the t ...
... Tundra like climate and vegetation conditions on a mountain is called what? What property of a community refers to the number of species making up the community? What property of a community refers to it being able to withstand minor disturbances? What does the term biotic stand for? What does the t ...
Ecosystems - funtastic physics
... If there are others of its kind, this is called a species. The number of this species is called the population. Populations interact to form habitats. Are there other organisms that live in this environment? If yes, what organisms? _______________________________________________. Add these organisms ...
... If there are others of its kind, this is called a species. The number of this species is called the population. Populations interact to form habitats. Are there other organisms that live in this environment? If yes, what organisms? _______________________________________________. Add these organisms ...
BIOTIC / ABIOTIC LIVING or NON-LIVING SYMBIOSIS ADAPTATION
... which one species benefits, while the other species does not benefit and is not harmed. Parasitism: A relationship in which one species benefits, while the other species is harmed. ...
... which one species benefits, while the other species does not benefit and is not harmed. Parasitism: A relationship in which one species benefits, while the other species is harmed. ...
Ch.1 - HCC Learning Web
... * To better understand the interaction between people and the environment we need information from many disciplines, such as Therefore… * Environmental Science is an interdisciplinary subject that includes scientific & social aspects of human impact on the world. ...
... * To better understand the interaction between people and the environment we need information from many disciplines, such as Therefore… * Environmental Science is an interdisciplinary subject that includes scientific & social aspects of human impact on the world. ...
Ecology Unit - Houston ISD
... Ecology = the study of the interactions between organisms and the living and nonliving components of their environment Levels of Organization 1) Biosphere = thin layer of Earth and atmosphere 2) Ecosystem = all organisms and nonliving components in a particular place 3) Community = all interacting o ...
... Ecology = the study of the interactions between organisms and the living and nonliving components of their environment Levels of Organization 1) Biosphere = thin layer of Earth and atmosphere 2) Ecosystem = all organisms and nonliving components in a particular place 3) Community = all interacting o ...
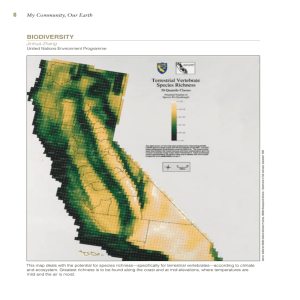
biodiversity - Association of American Geographers
... This map deals with the potential for species richness—specifically for terrestrial vertebrates—according to climate and ecosystem. Greatest richness is to be found along the coast and at mid-elevations, where temperatures are mild and the air is moist. ...
... This map deals with the potential for species richness—specifically for terrestrial vertebrates—according to climate and ecosystem. Greatest richness is to be found along the coast and at mid-elevations, where temperatures are mild and the air is moist. ...
Ch 2 powerpoint - Plain Local Schools
... each other, it is called coevolution Can be found between predator (enables them to find, subdue and capture prey) and prey (enables them to avoid, escape and fight off predators); ex: crabs (predator) and marine snails (prey); plants and herbivores ...
... each other, it is called coevolution Can be found between predator (enables them to find, subdue and capture prey) and prey (enables them to avoid, escape and fight off predators); ex: crabs (predator) and marine snails (prey); plants and herbivores ...
Ecology Unit Test Study Guide
... Plants produce their own food using carbon dioxide, water and sunlight (photosynthesis). This is different than ...
... Plants produce their own food using carbon dioxide, water and sunlight (photosynthesis). This is different than ...
An Introduction to Ecology and The Biosphere I
... c. Ecology was historically an observational science, often descriptive natural history. d. An organism’s environment has both abiotic and biotic components. - Abiotic components are nonliving chemical and physical factors such as temperature, light, water, and nutrients. - Biotic components are ...
... c. Ecology was historically an observational science, often descriptive natural history. d. An organism’s environment has both abiotic and biotic components. - Abiotic components are nonliving chemical and physical factors such as temperature, light, water, and nutrients. - Biotic components are ...
ecology
... F) Diverse ecosystems (with many different species) are more stable than those that are not diverse. G) As habitats are lost and species become extinct, biodiversity is reduced. This is considered bad because: 1. Ecosystems with low diversity are less stable than ecosystems with more diversity, 2. E ...
... F) Diverse ecosystems (with many different species) are more stable than those that are not diverse. G) As habitats are lost and species become extinct, biodiversity is reduced. This is considered bad because: 1. Ecosystems with low diversity are less stable than ecosystems with more diversity, 2. E ...
File
... c. Ecology was historically an observational science, often descriptive natural history. d. An organism’s environment has both abiotic and biotic components. - Abiotic components are nonliving chemical and physical factors such as temperature, light, water, and nutrients. - Biotic components are ...
... c. Ecology was historically an observational science, often descriptive natural history. d. An organism’s environment has both abiotic and biotic components. - Abiotic components are nonliving chemical and physical factors such as temperature, light, water, and nutrients. - Biotic components are ...
What is an ecosystem
... number of species found in an ecosystem. Some ecosystems, such as a tropical rainforest, have a greater biodiversity than others. Write the term from the passage above that best matches the description. Some terms will be used more than once. _________________________ 1. All living organisms in an e ...
... number of species found in an ecosystem. Some ecosystems, such as a tropical rainforest, have a greater biodiversity than others. Write the term from the passage above that best matches the description. Some terms will be used more than once. _________________________ 1. All living organisms in an e ...
Bhawalkar Ecological Research Institute
... Institute), Pune, India. It converts any polluted, dead water into “living/bio-water” that becomes a resource for its intended use in home, agriculture and industries. Bio-water resists scaling, corrosion, algal growth, biofouling, chemical contamination and growth of pathogens/pests. Bio-water nour ...
... Institute), Pune, India. It converts any polluted, dead water into “living/bio-water” that becomes a resource for its intended use in home, agriculture and industries. Bio-water resists scaling, corrosion, algal growth, biofouling, chemical contamination and growth of pathogens/pests. Bio-water nour ...
Ecosystems and Interdependence
... Students will take part in pond dipping and bug hunting to explore a variety of different habitats and species adaptations. They will use equipment to carefully catch creatures and use keys to identify what they’ve found. Students will look at the different features of each animal and think about ho ...
... Students will take part in pond dipping and bug hunting to explore a variety of different habitats and species adaptations. They will use equipment to carefully catch creatures and use keys to identify what they’ve found. Students will look at the different features of each animal and think about ho ...
APES Review Worksheet #1
... 19. Sketch and/or label the following on the map of the world below: a. the equator b. two lines showing where our planet’s deserts are concentrated c. the general location facing the highest rate of ozone depletion d. a continent containing large quantities of developing countries that face a high ...
... 19. Sketch and/or label the following on the map of the world below: a. the equator b. two lines showing where our planet’s deserts are concentrated c. the general location facing the highest rate of ozone depletion d. a continent containing large quantities of developing countries that face a high ...
Formulář inovovaného předmětu
... Environmental issues are a concern for everyone. Global warming is becoming a huge problem, and those in the developed nations are contributing to, and will be affected by, climate change. Cutting down trees, too many cars on the roads, companies that pollute the air and water with chemicals, a cons ...
... Environmental issues are a concern for everyone. Global warming is becoming a huge problem, and those in the developed nations are contributing to, and will be affected by, climate change. Cutting down trees, too many cars on the roads, companies that pollute the air and water with chemicals, a cons ...
Natural environment

The natural environment encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally on Earth or some region thereof. It is an environment that encompasses the interaction of all living species. Climate, weather, and natural resources that affect human survival and economic activity.The concept of the natural environment can be distinguished by components: Complete ecological units that function as natural systems without massive civilized human intervention, including all vegetation, microorganisms, soil, rocks, atmosphere, and natural phenomena that occur within their boundaries Universal natural resources and physical phenomena that lack clear-cut boundaries, such as air, water, and climate, as well as energy, radiation, electric charge, and magnetism, not originating from civilized human activityIn contrast to the natural environment is the built environment. In such areas where man has fundamentally transformed landscapes such as urban settings and agricultural land conversion, the natural environment is greatly modified and diminished, with a much more simplified human environment largely replacing it. Even events which seem less extreme such as hydroelectric dam construction, or photovoltaic system construction in the desert, the natural environment is substantially altered.It is difficult to find absolutely natural environments, and it is common that the naturalness varies in a continuum, from ideally 100% natural in one extreme to 0% natural in the other. More precisely, we can consider the different aspects or components of an environment, and see that their degree of naturalness is not uniform. If, for instance, we take an agricultural field, and consider the mineralogic composition and the structure of its soil, we will find that whereas the first is quite similar to that of an undisturbed forest soil, the structure is quite different.Natural environment is often used as a synonym for habitat. For instance, when we say that the natural environment of giraffes is the savanna.