Predation in Ecosystems
... 2. Predatory interactions occur between organisms within an ecosystem. 3. Mutually beneficial interactions occur between organisms within an ecosystem. Organisms involved in these mutually beneficial interactions can become so dependent upon one another that they cannot survive alone. 4. Resource av ...
... 2. Predatory interactions occur between organisms within an ecosystem. 3. Mutually beneficial interactions occur between organisms within an ecosystem. Organisms involved in these mutually beneficial interactions can become so dependent upon one another that they cannot survive alone. 4. Resource av ...
Ecology Unit
... The term symbiosis commonly describes close and often long-term interactions between different species, in which at least one species benefits. The symbiotic relationship may be characterized as being mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasitic. In mutualism, both species benefit; in commensalism, one ...
... The term symbiosis commonly describes close and often long-term interactions between different species, in which at least one species benefits. The symbiotic relationship may be characterized as being mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasitic. In mutualism, both species benefit; in commensalism, one ...
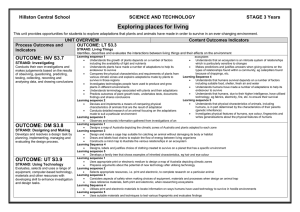
Exploring places for living
... Living things depend on other living things and non-living things such as water, soil, and a suitable temperature, for their survival Living things have adaptations such as structures and behaviours that enable them to live in their particular habitat, eg size colour, shape, habits Every organism ha ...
... Living things depend on other living things and non-living things such as water, soil, and a suitable temperature, for their survival Living things have adaptations such as structures and behaviours that enable them to live in their particular habitat, eg size colour, shape, habits Every organism ha ...
Themes of Biology
... mean to be alive? While most people are capable of distinguishing between living and nonliving, actually defining life can be quite difficult. Perhaps you consider movement, sensitivity, development, and even death as characteristics of living organisms. While present in all living things, these pro ...
... mean to be alive? While most people are capable of distinguishing between living and nonliving, actually defining life can be quite difficult. Perhaps you consider movement, sensitivity, development, and even death as characteristics of living organisms. While present in all living things, these pro ...
5-4 Wildlife Conservation and Management by Other System ~ 5
... system serves to commemorate nature in Japan and protect the natural assets, which are the setting for the indigenous culture of the nation. National monuments, designated by taking into consideration the climatic zones and different forest and vegetation types, as well as secondary nature made by m ...
... system serves to commemorate nature in Japan and protect the natural assets, which are the setting for the indigenous culture of the nation. National monuments, designated by taking into consideration the climatic zones and different forest and vegetation types, as well as secondary nature made by m ...
Section 2: Forest Biomes
... Describe how plants determine the name of a biome. Explain how temperature and precipitation determine which plants grow in an area. Explain how latitude and altitude affect which plants grow in an area. ...
... Describe how plants determine the name of a biome. Explain how temperature and precipitation determine which plants grow in an area. Explain how latitude and altitude affect which plants grow in an area. ...
The Earth’s Ecosystems
... The mountain biome is one of the coldest biomes on Earth. It is cold, snowy and windy. It is usually below freezing at night. Alpine biomes are located on mountains. They are below the snow line. The altitude is high. The word alpine comes from the word “alps." Alps mean high mountains. The temperat ...
... The mountain biome is one of the coldest biomes on Earth. It is cold, snowy and windy. It is usually below freezing at night. Alpine biomes are located on mountains. They are below the snow line. The altitude is high. The word alpine comes from the word “alps." Alps mean high mountains. The temperat ...
File
... 1) How do scientist classify organisms? Scientist classify similar organisms in one group, and an organism that is very different from other known organisms is placed in a new. 2) Describe one advantage of having a classification system: A classification system makes it easier to communicate clearly ...
... 1) How do scientist classify organisms? Scientist classify similar organisms in one group, and an organism that is very different from other known organisms is placed in a new. 2) Describe one advantage of having a classification system: A classification system makes it easier to communicate clearly ...
Chapter 8 - scecinascience
... The Earth’s resources were determined when the planet formed. •Earth was formed roughyly 4.6 billion years ...
... The Earth’s resources were determined when the planet formed. •Earth was formed roughyly 4.6 billion years ...
Click here for Final Jeopardy
... Nitrogen gas from the air and converts it into usable forms for plants. ...
... Nitrogen gas from the air and converts it into usable forms for plants. ...
Outline
... vitamins, etc. active transported out of the tubule and back to blood vessels C. Secretion at the proximal tubule region a very selective process. (e.g. controlled secretion of H+ ions helps maintain body fluid pH.) NH3, H+, drugs, poisons ...
... vitamins, etc. active transported out of the tubule and back to blood vessels C. Secretion at the proximal tubule region a very selective process. (e.g. controlled secretion of H+ ions helps maintain body fluid pH.) NH3, H+, drugs, poisons ...
Chp 13 Ecology
... • Biodiversity is the assortment, or variety, of living things in an ecosystem. • Rain forests have more biodiversity than other locations in the world, but are threatened by human activities. ...
... • Biodiversity is the assortment, or variety, of living things in an ecosystem. • Rain forests have more biodiversity than other locations in the world, but are threatened by human activities. ...
carbon cycle
... vapor absorb some infrared energy and radiate a portion of it back toward earth. ...
... vapor absorb some infrared energy and radiate a portion of it back toward earth. ...
Section 1: What Is an Ecosystem?
... • The variety of organisms in a given area is called biodiversity. • Physical factors can have a big influence on biodiversity. High or low temperatures, or limited food or water can lower biodiversity. • Ecosystems with high biodiversity are often more able to resist damage. ...
... • The variety of organisms in a given area is called biodiversity. • Physical factors can have a big influence on biodiversity. High or low temperatures, or limited food or water can lower biodiversity. • Ecosystems with high biodiversity are often more able to resist damage. ...
What Is an Ecosystem?
... • The variety of organisms in a given area is called biodiversity. • Physical factors can have a big influence on biodiversity. High or low temperatures, or limited food or water can lower biodiversity. • Ecosystems with high biodiversity are often more able to resist damage. ...
... • The variety of organisms in a given area is called biodiversity. • Physical factors can have a big influence on biodiversity. High or low temperatures, or limited food or water can lower biodiversity. • Ecosystems with high biodiversity are often more able to resist damage. ...
GASTANDARDSPractice 1st
... 5. What 2 gases are cycled through photosynthesis and respiration? Carbon Dioxide & Oxygen 6. What is the form of energy used to do work? ATP SB3b. Compare how structures and function vary between the six kingdoms (Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Protists, Fungi, Plants, and Animals). Alondra & Olivia 1 ...
... 5. What 2 gases are cycled through photosynthesis and respiration? Carbon Dioxide & Oxygen 6. What is the form of energy used to do work? ATP SB3b. Compare how structures and function vary between the six kingdoms (Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Protists, Fungi, Plants, and Animals). Alondra & Olivia 1 ...
Detailed information about common freshwater invertebrates
... Children are fascinated by water, and a pond teeming with life is ideal for exploring. Ponds are an important component of wetland habitat, supporting a diverse animal and plant population-- everything from moose to water lilies, from ducks to dragonflies. Wetlands are areas where the ground is wet ...
... Children are fascinated by water, and a pond teeming with life is ideal for exploring. Ponds are an important component of wetland habitat, supporting a diverse animal and plant population-- everything from moose to water lilies, from ducks to dragonflies. Wetlands are areas where the ground is wet ...
APES Semester 1 Review Packet
... 7. What organisms change radiant energy to chemical energy? Why is this important? 8. Why is symbiosis an important consideration when trying to understand any species? 9. How has natural selection led to biodiversity? What other mechanisms lead to speciation? 10. How and why has the Tree of Life be ...
... 7. What organisms change radiant energy to chemical energy? Why is this important? 8. Why is symbiosis an important consideration when trying to understand any species? 9. How has natural selection led to biodiversity? What other mechanisms lead to speciation? 10. How and why has the Tree of Life be ...
Religion, Ethics, and Ecology
... religious standards. For its author asserts that the problem of global warming boils down to us distinguishing what is right from what is wrong and acting accordingly. At the same time, we should question Gore’s categorization of the climate crisis as “a moral issue.” Why does he not use the phrase ...
... religious standards. For its author asserts that the problem of global warming boils down to us distinguishing what is right from what is wrong and acting accordingly. At the same time, we should question Gore’s categorization of the climate crisis as “a moral issue.” Why does he not use the phrase ...
Organismal Interactions and Ecology
... LO 3.41 The student is able to create a representation that describes how organisms exchange information in response to internal changes and external cues, and which can result in changes in behavior. [See SP 1.1] LO 3.42 The student is able to describe how organisms exchange information in response ...
... LO 3.41 The student is able to create a representation that describes how organisms exchange information in response to internal changes and external cues, and which can result in changes in behavior. [See SP 1.1] LO 3.42 The student is able to describe how organisms exchange information in response ...
Ecology: Flow of Energy
... • An ecosystem refers to all the animals and plants found in one place, and the way they all live together. • Different plants and animals live in different ecosystems. • Different ecosystems can be close together. • Some animals belong to several ecosystems. ...
... • An ecosystem refers to all the animals and plants found in one place, and the way they all live together. • Different plants and animals live in different ecosystems. • Different ecosystems can be close together. • Some animals belong to several ecosystems. ...
No Slide Title
... 4) Large cerebrum, resulting in development of complex tools, languages, culture & man’s dominance ...
... 4) Large cerebrum, resulting in development of complex tools, languages, culture & man’s dominance ...
Powerpoint: Chapter 5 notes
... These occur in areas of exposed ground that are subject to intense freeze and thaw cycles Over thousands of years, repeated freezing and thawing of groundwater in loose gravel and mud slowly pushes the larger rocks away from the pressure centre of finer grained material where the water is retained. ...
... These occur in areas of exposed ground that are subject to intense freeze and thaw cycles Over thousands of years, repeated freezing and thawing of groundwater in loose gravel and mud slowly pushes the larger rocks away from the pressure centre of finer grained material where the water is retained. ...
Natural environment

The natural environment encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally on Earth or some region thereof. It is an environment that encompasses the interaction of all living species. Climate, weather, and natural resources that affect human survival and economic activity.The concept of the natural environment can be distinguished by components: Complete ecological units that function as natural systems without massive civilized human intervention, including all vegetation, microorganisms, soil, rocks, atmosphere, and natural phenomena that occur within their boundaries Universal natural resources and physical phenomena that lack clear-cut boundaries, such as air, water, and climate, as well as energy, radiation, electric charge, and magnetism, not originating from civilized human activityIn contrast to the natural environment is the built environment. In such areas where man has fundamentally transformed landscapes such as urban settings and agricultural land conversion, the natural environment is greatly modified and diminished, with a much more simplified human environment largely replacing it. Even events which seem less extreme such as hydroelectric dam construction, or photovoltaic system construction in the desert, the natural environment is substantially altered.It is difficult to find absolutely natural environments, and it is common that the naturalness varies in a continuum, from ideally 100% natural in one extreme to 0% natural in the other. More precisely, we can consider the different aspects or components of an environment, and see that their degree of naturalness is not uniform. If, for instance, we take an agricultural field, and consider the mineralogic composition and the structure of its soil, we will find that whereas the first is quite similar to that of an undisturbed forest soil, the structure is quite different.Natural environment is often used as a synonym for habitat. For instance, when we say that the natural environment of giraffes is the savanna.