Chapter 5 Lecture
... Any reference frame that moves with constant velocity relative to an inertial frame is itself an inertial frame. If you accelerate relative to an object in an inertial frame, you are observing the object from a non-inertial reference frame. A reference frame that moves with constant velocity relativ ...
... Any reference frame that moves with constant velocity relative to an inertial frame is itself an inertial frame. If you accelerate relative to an object in an inertial frame, you are observing the object from a non-inertial reference frame. A reference frame that moves with constant velocity relativ ...
Lecture notes - University of Oxford
... For many problems there may be a natural or convenient choice of reference frame, although this is not always the case. However, an important assumption in Newtonian mechanics is that any two observers, using any choice of reference frames, agree on their measurements of distances – provided they us ...
... For many problems there may be a natural or convenient choice of reference frame, although this is not always the case. However, an important assumption in Newtonian mechanics is that any two observers, using any choice of reference frames, agree on their measurements of distances – provided they us ...
Physics 201 Analytical Mechanics
... momentum imparted to the mass, m, in the time interval ∆t = t − t o . Definition of impulsive force: A force that acts such a short time that the mass does not move while the force is acting. The momentum is changed, in ...
... momentum imparted to the mass, m, in the time interval ∆t = t − t o . Definition of impulsive force: A force that acts such a short time that the mass does not move while the force is acting. The momentum is changed, in ...
ME451 Kinematics and Dynamics of Machine Systems
... alternative for solving complicated systems described by non-linear differential equations ...
... alternative for solving complicated systems described by non-linear differential equations ...
Physics 207: Lecture 2 Notes
... 1.2 g Normal elevator acceleration (up). 1.5-2g Walking down stairs. 2-3 g Hopping down stairs. 1.5 g Commercial airliner during takeoff run. 2 g Commercial airliner at rotation 3.5 g Maximum acceleration in amusement park rides (design guidelines). 4 g Indy cars in the second turn at Disney World ( ...
... 1.2 g Normal elevator acceleration (up). 1.5-2g Walking down stairs. 2-3 g Hopping down stairs. 1.5 g Commercial airliner during takeoff run. 2 g Commercial airliner at rotation 3.5 g Maximum acceleration in amusement park rides (design guidelines). 4 g Indy cars in the second turn at Disney World ( ...
Physics 18 Spring 2011 Homework 4
... Consider the forces acting on your foot, when your feet are spread apart at an angle θ, as shown in the figure to the right. The frictional force, F~f , preventing you from sliding points to the right, the normal force F~N points vertically, while the force of your weight, F~W , points at an angle, ...
... Consider the forces acting on your foot, when your feet are spread apart at an angle θ, as shown in the figure to the right. The frictional force, F~f , preventing you from sliding points to the right, the normal force F~N points vertically, while the force of your weight, F~W , points at an angle, ...
Tuesday, June 3, 2008
... Newton’s First Law Aristotle (384-322BC): A natural state of a body is rest. Thus force is required to move an object. To move faster, ones needs larger forces. Galileo’s statement on natural states of matter: Any velocity once imparted to a moving body will be rigidly maintained as long as the ext ...
... Newton’s First Law Aristotle (384-322BC): A natural state of a body is rest. Thus force is required to move an object. To move faster, ones needs larger forces. Galileo’s statement on natural states of matter: Any velocity once imparted to a moving body will be rigidly maintained as long as the ext ...
Exam 1 Solutions Kinematics and Newton’s laws of motion
... Can you feel gravity? We previously determined that you can’t. 1) Hanging from a 100 m high diving board – your arms feel stretched by the bending of the board. 2) Standing on a bed – your legs feel compressed by the springs in the mattress. The bent diving board or the compressed springs provide th ...
... Can you feel gravity? We previously determined that you can’t. 1) Hanging from a 100 m high diving board – your arms feel stretched by the bending of the board. 2) Standing on a bed – your legs feel compressed by the springs in the mattress. The bent diving board or the compressed springs provide th ...
Lecture 10 - Purdue Physics
... – Note: If vx is negative, the displacement is also negative. So, we count the area as negative. Lecture 10 ...
... – Note: If vx is negative, the displacement is also negative. So, we count the area as negative. Lecture 10 ...
Semester Exam REVIEW PACKET KEY
... iii. During the time the ball is in the air, what never changes, acceleration or velocity? Why? Acceleration, because the surface gravity on Earth stays the consistent ...
... iii. During the time the ball is in the air, what never changes, acceleration or velocity? Why? Acceleration, because the surface gravity on Earth stays the consistent ...
PreAP Physics Extra Practice Unit 1: Uniform Motion and Graphing
... 2. Two physics teachers challenge each other to a 100 m race across the football field. The loser will grade the winner’s physics labs for one month. Mrs. Jensen runs the race in 10.4 seconds. Mr. Avis runs the first 25 m with an average speed of 10 m/s, the next 50 meters with an average speed of 9 ...
... 2. Two physics teachers challenge each other to a 100 m race across the football field. The loser will grade the winner’s physics labs for one month. Mrs. Jensen runs the race in 10.4 seconds. Mr. Avis runs the first 25 m with an average speed of 10 m/s, the next 50 meters with an average speed of 9 ...
0.1 Exponents 0.2 Scientific Notation and Powers of 10 0.3 Algebra
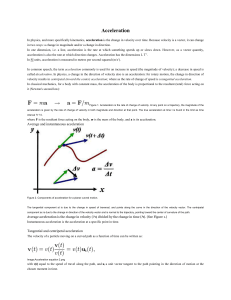
... The average acceleration aav of an object as it moves from x1 (at time t1 ) to x2 (at time t2 ) is a vector quantity whose x component is the ratio of the change in the x component of velocity, ∆vx = v2x − v1x , to the time ...
... The average acceleration aav of an object as it moves from x1 (at time t1 ) to x2 (at time t2 ) is a vector quantity whose x component is the ratio of the change in the x component of velocity, ∆vx = v2x − v1x , to the time ...
Thursday Aug 27 1-d Motion/Kinematics • Goal: Describe Motion
... Scalars add, subtract, multiply the way we're used to. Vectors need to account for direction – may need trig. If parallel or antiparallel, then can treat more simply. If not – need to use trig. Magnitude of vector is its ‘size’ (ignore direction) The magnitude of a vector “3 m to the left” is 3 m Bo ...
... Scalars add, subtract, multiply the way we're used to. Vectors need to account for direction – may need trig. If parallel or antiparallel, then can treat more simply. If not – need to use trig. Magnitude of vector is its ‘size’ (ignore direction) The magnitude of a vector “3 m to the left” is 3 m Bo ...
Physics 207: Lecture 2 Notes
... MP Problem Set 2 due tonight(!) MP Problem Set 3 due next week Physics 207: Lecture 5, Pg 1 ...
... MP Problem Set 2 due tonight(!) MP Problem Set 3 due next week Physics 207: Lecture 5, Pg 1 ...
Velocity and Acceleration PowerPoint
... Force and Motion Standards • S8P5 Students will recognize characteristics of gravity, electricity, and magnetism as major kinds of forces acting in nature. • a. Recognize that every object exerts gravitational force on every other object and that the force exerted depends on how much mass the objec ...
... Force and Motion Standards • S8P5 Students will recognize characteristics of gravity, electricity, and magnetism as major kinds of forces acting in nature. • a. Recognize that every object exerts gravitational force on every other object and that the force exerted depends on how much mass the objec ...
if on the Internet, Press on your browser to
... Now, things are going to be very very weird. I’m sure you were astonished when you discovered time dilation. But Einstein also discovered another strange consequence of his postulates. The World in which we live is not Euclidean (in most cases). This means that circles are not round; that parallel l ...
... Now, things are going to be very very weird. I’m sure you were astonished when you discovered time dilation. But Einstein also discovered another strange consequence of his postulates. The World in which we live is not Euclidean (in most cases). This means that circles are not round; that parallel l ...
Acceleration
... where un is the unit (outward) normal vector to the particle's trajectory, and Ris its instantaneous radius of curvature based upon the osculating circle at time t. These components are called thetangential acceleration at and the radial acceleration, respectively. The negative of the radial acceler ...
... where un is the unit (outward) normal vector to the particle's trajectory, and Ris its instantaneous radius of curvature based upon the osculating circle at time t. These components are called thetangential acceleration at and the radial acceleration, respectively. The negative of the radial acceler ...
Relativity
... Given this unsatisfactory consequence of classical electromagnetism, as well as the lack of evidence for the ether, Einstein decided to address the problem in the most fundamental and straightforward way possible. He began with the basic assumption that electromagnetism, like Newtonian mechanics, di ...
... Given this unsatisfactory consequence of classical electromagnetism, as well as the lack of evidence for the ether, Einstein decided to address the problem in the most fundamental and straightforward way possible. He began with the basic assumption that electromagnetism, like Newtonian mechanics, di ...
Classical mechanics
... opportunity to learn to use many of the mathematical techniques needed in so many other branches of physics - vectors, vector calculus, differential equations, complex numbers, Taylor series, Fourier series, calculus of variations, and matrices. I have tried to give at least a minimal review or intr ...
... opportunity to learn to use many of the mathematical techniques needed in so many other branches of physics - vectors, vector calculus, differential equations, complex numbers, Taylor series, Fourier series, calculus of variations, and matrices. I have tried to give at least a minimal review or intr ...
Introduction to Classical Mechanics 1 HISTORY
... A Comment on Vectors. For two- or three-dimensional motion, the position, velocity, and accleration are all vectors— mathematical quantities with both magnitude and direction. We will denote vectors by boldface symbols, e.g., x for position, v for velocity, and a for acceleration. In hand-written eq ...
... A Comment on Vectors. For two- or three-dimensional motion, the position, velocity, and accleration are all vectors— mathematical quantities with both magnitude and direction. We will denote vectors by boldface symbols, e.g., x for position, v for velocity, and a for acceleration. In hand-written eq ...