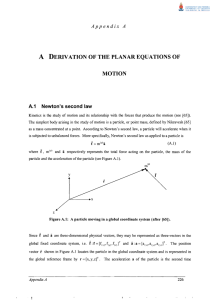
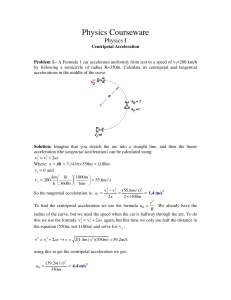
here.
... V(x m In effect we have solved Newton’s second order equation of motion in two steps. Energy is the constant of integration in the first step and x0 is the second constant of integration. Our answer expresses t as a function of x. We must invert it to find trajectories x(t) with energy E and initial ...
... V(x m In effect we have solved Newton’s second order equation of motion in two steps. Energy is the constant of integration in the first step and x0 is the second constant of integration. Our answer expresses t as a function of x. We must invert it to find trajectories x(t) with energy E and initial ...
Newton`s Laws of. Motion
... Or the two frames may have the same origins of space and time, but have different orientations of the three spatial axes. By carefully choosing your reference frame, taking advantage of these different possibilities, you can sometimes simplify your work. For example, in problems involving blocks sli ...
... Or the two frames may have the same origins of space and time, but have different orientations of the three spatial axes. By carefully choosing your reference frame, taking advantage of these different possibilities, you can sometimes simplify your work. For example, in problems involving blocks sli ...
Chapter-5 (Newton's laws of motion)
... A free body diagram is a diagram showing the chosen body by itself, “free” of its surroundings, with vectors drawn to show the magnitudes and directions of all the forces applied to the body by the various other bodies that interact with it. Be careful to include all the forces acting on the body, b ...
... A free body diagram is a diagram showing the chosen body by itself, “free” of its surroundings, with vectors drawn to show the magnitudes and directions of all the forces applied to the body by the various other bodies that interact with it. Be careful to include all the forces acting on the body, b ...
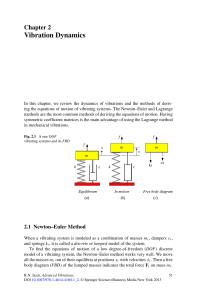
Vibration Dynamics
... in which, x is a column array of describing coordinates of the system, and f is a column array of the associated applied forces. The square matrices [m], [c], [k] are the mass, damping, and stiffness matrices. Example 30 (The one, two, and three DOF model of vehicles) The one, two, and three DOF mod ...
... in which, x is a column array of describing coordinates of the system, and f is a column array of the associated applied forces. The square matrices [m], [c], [k] are the mass, damping, and stiffness matrices. Example 30 (The one, two, and three DOF model of vehicles) The one, two, and three DOF mod ...
Global Kinematics in the Deep Vs Shallow
... at the lithosphere-asthenosphere decoupling zone and lateral mantle compositional variations. All these models could be valid, but applied to different cases. Therefore we disagree in using uncritically all so-called hotspots because their different origin can corrupt the calculation of lithosphere- ...
... at the lithosphere-asthenosphere decoupling zone and lateral mantle compositional variations. All these models could be valid, but applied to different cases. Therefore we disagree in using uncritically all so-called hotspots because their different origin can corrupt the calculation of lithosphere- ...
Rigid Body Dynamics
... So far we have formulated classical mechanics in inertial frames of reference, i.e., those vector bases in which Newton’s second law holds (we have also allowed general coordinates, in which the Euler-Lagrange equations hold). However, it is sometimes useful to use non-inertial frames, and particula ...
... So far we have formulated classical mechanics in inertial frames of reference, i.e., those vector bases in which Newton’s second law holds (we have also allowed general coordinates, in which the Euler-Lagrange equations hold). However, it is sometimes useful to use non-inertial frames, and particula ...
Lagrangian and Hamiltonian Dynamics
... • One then describes the system as having 3n-m degrees of freedom. ...
... • One then describes the system as having 3n-m degrees of freedom. ...
SOLUTION:
... seen from an inertial system was given above: it is an effect of being in a rotating system, wherein points that are farther from the rotation axis have higher linear speeds. On the other hand, when viewed from the rotating system, we can describe the motion using Newton’s second law, ...
... seen from an inertial system was given above: it is an effect of being in a rotating system, wherein points that are farther from the rotation axis have higher linear speeds. On the other hand, when viewed from the rotating system, we can describe the motion using Newton’s second law, ...
Motion in Two Dimensions
... that is tossed straight up in the air. If you were watching the softball from a hot-air balloon high above the field, what motion would you see then? You would see the ball move from one player to the other at a constant speed, just like any object that is given an initial horizontal velocity, such ...
... that is tossed straight up in the air. If you were watching the softball from a hot-air balloon high above the field, what motion would you see then? You would see the ball move from one player to the other at a constant speed, just like any object that is given an initial horizontal velocity, such ...
ppt - SBEL
... Finding an exact solution within pen/paper framework impossible even for the swinging motion of a pendulum in gravitational field We need to resort to numerical methods (algorithms) to produce an approximation of the solution We’ll continue this discussion on Th when we focus on an ME451 ...
... Finding an exact solution within pen/paper framework impossible even for the swinging motion of a pendulum in gravitational field We need to resort to numerical methods (algorithms) to produce an approximation of the solution We’ll continue this discussion on Th when we focus on an ME451 ...
AP centripetal accelerations
... According to the problem there are only two forces acting on the car: air resistance and r r friction force, but the sum of these two forces has to be F = ma due to Newton’s second law, so the vector diagram will be: ...
... According to the problem there are only two forces acting on the car: air resistance and r r friction force, but the sum of these two forces has to be F = ma due to Newton’s second law, so the vector diagram will be: ...
week 1
... The text shows the details, but for a system of particles: F = m aG where F is the sum of the external forces acting on the entire system. Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics, 13th SI Edition R. C. Hibbeler and Kai Beng Yap ...
... The text shows the details, but for a system of particles: F = m aG where F is the sum of the external forces acting on the entire system. Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics, 13th SI Edition R. C. Hibbeler and Kai Beng Yap ...
Calculating Acceleration
... Earth's atmosphere. One of the other by-products is sodium hyxdroxide. This is commonly known as Lye, which is a caustic compound. The quantities produced are very small and present a very small risk of burns. The white powder residue seen after inflation is common corn starch, used as a lubricant f ...
... Earth's atmosphere. One of the other by-products is sodium hyxdroxide. This is commonly known as Lye, which is a caustic compound. The quantities produced are very small and present a very small risk of burns. The white powder residue seen after inflation is common corn starch, used as a lubricant f ...
physics 220 - Purdue Physics
... - This is a vector equation - The direction of the net force is the same as the direction of the acceleration - In 3 dimensions Fx = max Fy = may Fz = maz ...
... - This is a vector equation - The direction of the net force is the same as the direction of the acceleration - In 3 dimensions Fx = max Fy = may Fz = maz ...
Noninertial Reference Frames
... The Coriolis force is given by FCor = −2m ω × ṙ. According to (12.18), the acceleration of a free particle (F 0 = 0) isn’t along ge – an orthogonal component is generated by the Coriolis force. To actually solve the coupled equations of motion is difficult because the unit vectors {r̂, θ̂, φ̂} chan ...
... The Coriolis force is given by FCor = −2m ω × ṙ. According to (12.18), the acceleration of a free particle (F 0 = 0) isn’t along ge – an orthogonal component is generated by the Coriolis force. To actually solve the coupled equations of motion is difficult because the unit vectors {r̂, θ̂, φ̂} chan ...