CircularMotion&Gravitation
... Newton and Satellite Motion Newton’s Law of Gravitation predicts artificial satellites can orbit the earth with centripetal acceleration. Satellites have acceleration towards the center of Earth, but they also have tangential speed to keep them in orbit! Astronauts in orbit are often described as “ ...
... Newton and Satellite Motion Newton’s Law of Gravitation predicts artificial satellites can orbit the earth with centripetal acceleration. Satellites have acceleration towards the center of Earth, but they also have tangential speed to keep them in orbit! Astronauts in orbit are often described as “ ...
Lecture 6
... Newton’s Laws of Motion • The ancient (& wrong!) view (of Aristotle): – A force is needed to keep an object in motion. In the 21st Century, this is still a common – The “natural” state of an object is at rest. ...
... Newton’s Laws of Motion • The ancient (& wrong!) view (of Aristotle): – A force is needed to keep an object in motion. In the 21st Century, this is still a common – The “natural” state of an object is at rest. ...
Unit 6: Motion and Forces
... makes an object harder to stop or change direction as it increases ...
... makes an object harder to stop or change direction as it increases ...
Momentum - Brock physics
... it’s more or less obvious that the two bodies just trade velocities. Setting m1=m 2 in the second solution, we indeed find w1=v2. Second, suppose that one of the bodies, say number 2, had zero velocity and were very massive. Then it’s as though the first body were hitting a brick wall. It would just ...
... it’s more or less obvious that the two bodies just trade velocities. Setting m1=m 2 in the second solution, we indeed find w1=v2. Second, suppose that one of the bodies, say number 2, had zero velocity and were very massive. Then it’s as though the first body were hitting a brick wall. It would just ...
Systems of Particles
... 1. One part in which the system is treated as though it were a single particle (with the total mass of the system) located at a special point called the center of mass. This part is often called the CM motion. 2. Another part describing the internal motion of the system, as seen by an observer locat ...
... 1. One part in which the system is treated as though it were a single particle (with the total mass of the system) located at a special point called the center of mass. This part is often called the CM motion. 2. Another part describing the internal motion of the system, as seen by an observer locat ...
BuildingTypes
... • When the building is multistory, the parts from the joists up is repeated. • In platform construction, the process repeats for each floor. • Joists are placed to form the ceiling for the first story and the floor for the second story. ...
... • When the building is multistory, the parts from the joists up is repeated. • In platform construction, the process repeats for each floor. • Joists are placed to form the ceiling for the first story and the floor for the second story. ...
Circular Motion Notes
... Example 5. The coefficient of static friction between a car’s tire and a certain concrete road is 1.0 when the road is dry and 0.7 when the road is wet. If the car can safely make the turn at 25 mi/h on a dry day, what is the maximum velocity on a rainy day? ...
... Example 5. The coefficient of static friction between a car’s tire and a certain concrete road is 1.0 when the road is dry and 0.7 when the road is wet. If the car can safely make the turn at 25 mi/h on a dry day, what is the maximum velocity on a rainy day? ...
1st Semester Final Exam Review
... What is the speed and acceleration of the rock at its peak and when the rock returns back to its initial position? 4) A rock and leaf are dropped at the same time. Describe and Explain what happens on Earth and in a vacuum. EARTH ...
... What is the speed and acceleration of the rock at its peak and when the rock returns back to its initial position? 4) A rock and leaf are dropped at the same time. Describe and Explain what happens on Earth and in a vacuum. EARTH ...
Ezio Fornero, Space and Motion as Problems of
... considerations (significant by themselves but not yet sufficient), a fundamental reason exists in favour of Newton’s theory or every other theory which, although disagreeing with the Newton’s one in some point, preserve some a distinction between correct and incorrect descriptions, i.e. between vali ...
... considerations (significant by themselves but not yet sufficient), a fundamental reason exists in favour of Newton’s theory or every other theory which, although disagreeing with the Newton’s one in some point, preserve some a distinction between correct and incorrect descriptions, i.e. between vali ...
Origin of Inertial Mass
... Gravitational mass and inertial mass are distinct properties of matter that originate by fundamentally different mechanisms and relate to different forces. The force of gravity is an attraction of two bodies for each other. This article is concerned with inertial mass only and does not deal with gr ...
... Gravitational mass and inertial mass are distinct properties of matter that originate by fundamentally different mechanisms and relate to different forces. The force of gravity is an attraction of two bodies for each other. This article is concerned with inertial mass only and does not deal with gr ...
Lecture_1 - National University of Singapore
... related if they both use the same reference point (ie a point that has height zero) ? Question: What happens if A’s reference point is d (B-sticks) above B’s reference point ? Question: Let a point have height u (A-sticks) in A’s world and v (B-sticks) in B’s world. Derive an equation that expresses ...
... related if they both use the same reference point (ie a point that has height zero) ? Question: What happens if A’s reference point is d (B-sticks) above B’s reference point ? Question: Let a point have height u (A-sticks) in A’s world and v (B-sticks) in B’s world. Derive an equation that expresses ...
Sections 13.1-13.4 - University of Mary Hardin–Baylor
... motor attached to a cable and pulley system as shown. How can we determine the tension force in the cable required to lift the elevator and load at a given acceleration? This is needed to decide what size cable should be used. Is the tension force in the cable greater than the weight of the elevator ...
... motor attached to a cable and pulley system as shown. How can we determine the tension force in the cable required to lift the elevator and load at a given acceleration? This is needed to decide what size cable should be used. Is the tension force in the cable greater than the weight of the elevator ...
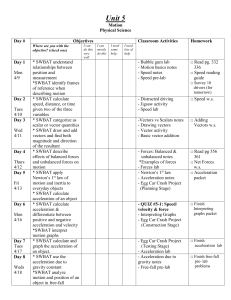
Physics
... • How is a frame of reference used to describe motion? • What is the difference between speed and velocity? • What do you need to know to find the speed of an object? • How can you study speed by using graphs? ...
... • How is a frame of reference used to describe motion? • What is the difference between speed and velocity? • What do you need to know to find the speed of an object? • How can you study speed by using graphs? ...
Monday, Sept. 16, 2002 - UTA HEP WWW Home Page
... Results of Physical measurements in different reference frames could be different Observations of the same motion in a stationary frame would be different than the ones made in the frame moving together with the moving object. Consider that you are driving a car. To you, the objects in the car do no ...
... Results of Physical measurements in different reference frames could be different Observations of the same motion in a stationary frame would be different than the ones made in the frame moving together with the moving object. Consider that you are driving a car. To you, the objects in the car do no ...
General Relativity - UF Physics
... prediction of General Relativity. However, we may soon be on the verge of direct detection of gravitational waves. An experiment called LIGO (Laser Interferometer Gravitational Observatory) is under construction in the U.S., as are a couple of experiments in Europe. LIGO is a pair of interferometers ...
... prediction of General Relativity. However, we may soon be on the verge of direct detection of gravitational waves. An experiment called LIGO (Laser Interferometer Gravitational Observatory) is under construction in the U.S., as are a couple of experiments in Europe. LIGO is a pair of interferometers ...
General Relativity The Equivalence Principle
... prediction of General Relativity. However, we may soon be on the verge of direct detection of gravitational waves. An experiment called LIGO (Laser Interferometer Gravitational Observatory) is under construction in the U.S., as are a couple of experiments in Europe. LIGO is a pair of interferometers ...
... prediction of General Relativity. However, we may soon be on the verge of direct detection of gravitational waves. An experiment called LIGO (Laser Interferometer Gravitational Observatory) is under construction in the U.S., as are a couple of experiments in Europe. LIGO is a pair of interferometers ...