Applying Newton`s Laws
... • In static situation, the effect of a frictionless pulley is to re-direct the tension along the rope. (However, in dynamics, the tension of the rope on either sides of the pulley will be different unless the pulley is also massless. Rotational dynamics will discussed in Ch. 9 & 10). • Example bel ...
... • In static situation, the effect of a frictionless pulley is to re-direct the tension along the rope. (However, in dynamics, the tension of the rope on either sides of the pulley will be different unless the pulley is also massless. Rotational dynamics will discussed in Ch. 9 & 10). • Example bel ...
Chapter 14 - Simple Harmonic Motion
... forces provide the driving forces necessary for objects that oscillate with simple harmonic motion. ...
... forces provide the driving forces necessary for objects that oscillate with simple harmonic motion. ...
No Slide Title
... forces provide the driving forces necessary for objects that oscillate with simple harmonic motion. ...
... forces provide the driving forces necessary for objects that oscillate with simple harmonic motion. ...
Chapter 4 Motion
... You can tell the difference between a moving object and one that's still. But how would you define motion? An object is in motion when its position changes. Position is the location of an object in space, and it is always relative to a frame of reference. We use many words to express position, such ...
... You can tell the difference between a moving object and one that's still. But how would you define motion? An object is in motion when its position changes. Position is the location of an object in space, and it is always relative to a frame of reference. We use many words to express position, such ...
Tuesday, Sept. 16, 2014
... Galileo’s statement on natural states of matter: Any velocity once imparted to a moving body will be rigidly maintained as long as the external causes of retardation are removed!! Galileo’s statement is formulated by Newton into the 1st law of motion (Law of Inertia): In the absence of external forc ...
... Galileo’s statement on natural states of matter: Any velocity once imparted to a moving body will be rigidly maintained as long as the external causes of retardation are removed!! Galileo’s statement is formulated by Newton into the 1st law of motion (Law of Inertia): In the absence of external forc ...
Uniform Circular Motion
... motion the direction of velocity is always tangent to the circle. This means that as the object moves in a circle, the direction of the velocity is always changing. When we examine this motion, we shall see that the direction of change of the velocity is towards the center of the circle. This means ...
... motion the direction of velocity is always tangent to the circle. This means that as the object moves in a circle, the direction of the velocity is always changing. When we examine this motion, we shall see that the direction of change of the velocity is towards the center of the circle. This means ...
Exam 2013 with Answers File - QMplus
... v) What is the Proper Time between the creation and decay of the particle? 0.1ns, see (i), the particle may be considered to be a clock present at both events. [1] vi) What is the distance between the beamline and the detector in the particle’s frame of reference? 0.1ns 0.99995c ~ 3cm. ...
... v) What is the Proper Time between the creation and decay of the particle? 0.1ns, see (i), the particle may be considered to be a clock present at both events. [1] vi) What is the distance between the beamline and the detector in the particle’s frame of reference? 0.1ns 0.99995c ~ 3cm. ...
Unit 6 Powerpoint
... From the frame of the passenger (b), a force appears to push her toward the door From the frame of the Earth, the car applies a leftward force on the passenger The outward force is often called a centrifugal force ...
... From the frame of the passenger (b), a force appears to push her toward the door From the frame of the Earth, the car applies a leftward force on the passenger The outward force is often called a centrifugal force ...
Working with moving pulleys
... in direction. This is based on the fact that blocks are attached with a single string that passes over moving pulley. This simpli es analysis a great deal. On the other hand, if we refer accelerations to the ground, then we can not be sure of the directions of accelerations of the blocks as they dep ...
... in direction. This is based on the fact that blocks are attached with a single string that passes over moving pulley. This simpli es analysis a great deal. On the other hand, if we refer accelerations to the ground, then we can not be sure of the directions of accelerations of the blocks as they dep ...
Force and Motion
... 2. A(n)_____________ frame of reference is non-accelerating. 3. In a(n) ________________ frame of reference, fictitious forces arise. 4. The gravitational force on an object near Earth’s surface is called ________. 5. With no forces acting upon it, an object moves with constant ____________. 6. In a ...
... 2. A(n)_____________ frame of reference is non-accelerating. 3. In a(n) ________________ frame of reference, fictitious forces arise. 4. The gravitational force on an object near Earth’s surface is called ________. 5. With no forces acting upon it, an object moves with constant ____________. 6. In a ...
Force and Motion - Derry Area School District
... 2. A(n)_____________ frame of reference is non-accelerating. 3. In a(n) ________________ frame of reference, fictitious forces arise. 4. The gravitational force on an object near Earth’s surface is called ________. 5. With no forces acting upon it, an object moves with constant ____________. 6. In a ...
... 2. A(n)_____________ frame of reference is non-accelerating. 3. In a(n) ________________ frame of reference, fictitious forces arise. 4. The gravitational force on an object near Earth’s surface is called ________. 5. With no forces acting upon it, an object moves with constant ____________. 6. In a ...
Document
... Kinematics in Two Dimensions • Position, velocity, acceleration vectors • Constant acceleration in 2-D • Free fall in 2-D ...
... Kinematics in Two Dimensions • Position, velocity, acceleration vectors • Constant acceleration in 2-D • Free fall in 2-D ...
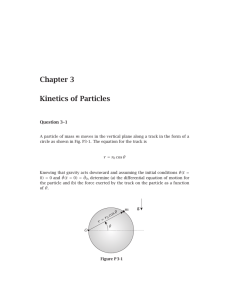
Chapter 3 Kinetics of Particles
... Observing that θ̇ ≠ 0 as a function of time, the differential equation of motion is obtained as p mgα mR 2 (1 + α2 )θ̈ + √ ...
... Observing that θ̇ ≠ 0 as a function of time, the differential equation of motion is obtained as p mgα mR 2 (1 + α2 )θ̈ + √ ...
CP Physics Chapter 7
... A car rounds a curve with a 50 m radius of curvature. If the coefficient of friction between the tires and road is 0.9, how fast can the car go without skidding? ...
... A car rounds a curve with a 50 m radius of curvature. If the coefficient of friction between the tires and road is 0.9, how fast can the car go without skidding? ...
Fictive forces
... this case the reference system is not accelerated but only rotated relative to an inertial system placed at the center of the Earth1 . We address each of the fictive forces separately: ~ = 0, and there is no fictive • Since the reference system is not accelerated, A force due to a linear acceleratio ...
... this case the reference system is not accelerated but only rotated relative to an inertial system placed at the center of the Earth1 . We address each of the fictive forces separately: ~ = 0, and there is no fictive • Since the reference system is not accelerated, A force due to a linear acceleratio ...
+x - SeyedAhmad.com
... Example 4: What is the maximum acceleration for the 2-kg mass in the previous problem? (A = 12 cm, k = 400 N/m) The maximum acceleration occurs when the restoring force is a maximum; i.e., when the stretch or compression of the spring is largest. ...
... Example 4: What is the maximum acceleration for the 2-kg mass in the previous problem? (A = 12 cm, k = 400 N/m) The maximum acceleration occurs when the restoring force is a maximum; i.e., when the stretch or compression of the spring is largest. ...