reaction force.
... The cart system: the cart will accelerate because there is an external force being place on it by the horse. There is also an external force of friction but this can be discounted because the wheels are smooth and shiny. The horse system: there is a reaction force from the cart that is external to ...
... The cart system: the cart will accelerate because there is an external force being place on it by the horse. There is also an external force of friction but this can be discounted because the wheels are smooth and shiny. The horse system: there is a reaction force from the cart that is external to ...
Force = Mass x Acceleration - GZ @ Science Class Online
... When sky divers reach terminal velocity they are traveling at a constant speed. The forces of gravity accelerating the skydiver towards earth are matched exactly by the force of friction from the air particles pushing against the skydiver. If the person wears a more aerodynamic suit or points their ...
... When sky divers reach terminal velocity they are traveling at a constant speed. The forces of gravity accelerating the skydiver towards earth are matched exactly by the force of friction from the air particles pushing against the skydiver. If the person wears a more aerodynamic suit or points their ...
Interaction Forces - juan
... •This might suggest that one causes the other; however, this is not true. ...
... •This might suggest that one causes the other; however, this is not true. ...
solutions for chapter 21 problems 4, 12, 19, 25, 33, 40, 50, 75, 89, 96.
... (This analysis is very similar to that used in Chapter 3 for projectile motion, except that here the acceleration is upward rather than downward.) This acceleration must be produced by the electric-field force: eE ma E ...
... (This analysis is very similar to that used in Chapter 3 for projectile motion, except that here the acceleration is upward rather than downward.) This acceleration must be produced by the electric-field force: eE ma E ...
Assignment #3 - Long Branch Public Schools
... Include all forces and draw them to relative scale. Draw the expected direction of acceleration next to each free-body diagram. b. Use Newton’s Second Law to write an equation for the 500 g mass. c. Use Newton’s Second Law to write an equation for the 300 g mass. d. Find the acceleration of the syst ...
... Include all forces and draw them to relative scale. Draw the expected direction of acceleration next to each free-body diagram. b. Use Newton’s Second Law to write an equation for the 500 g mass. c. Use Newton’s Second Law to write an equation for the 300 g mass. d. Find the acceleration of the syst ...
Lessons 45-47
... which runs parallel to the ramp and over a pulley at the top of the ramp. After passing over the pulley the other end of the rope is attached to a counterweight which hangs straight down. In your design the mass of the counterweight is always adjusted to be twice the mass of the package. Your boss i ...
... which runs parallel to the ramp and over a pulley at the top of the ramp. After passing over the pulley the other end of the rope is attached to a counterweight which hangs straight down. In your design the mass of the counterweight is always adjusted to be twice the mass of the package. Your boss i ...
Chapter 6 - TeacherWeb
... Free fall: An object is in free fall only if _________________ gravity is the only force vacuum acting on it. This can only occur in a _________________ (where there is no air resistance). Orbiting: An object is orbiting when it is traveling in a _______________ circular path around another object. ...
... Free fall: An object is in free fall only if _________________ gravity is the only force vacuum acting on it. This can only occur in a _________________ (where there is no air resistance). Orbiting: An object is orbiting when it is traveling in a _______________ circular path around another object. ...
Worksheet #1 Free Body or Force diagrams…
... 5. What changes depending on location in the universe, mass or weight? Explain. ...
... 5. What changes depending on location in the universe, mass or weight? Explain. ...
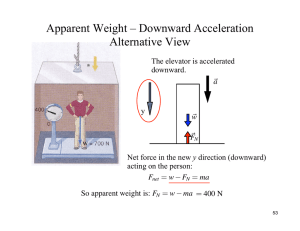
Apparent Weight – Downward Acceleration Alternative View
... much like a tread of a tire. Its strength comes from tough fibers called collagen. The joint surface cartilage is well lubricated - more slippery than well-manufactured ball bearings... Its living cells are nourished by joint fluid, called synovial fluid which is also extremely good lubrication. ...
... much like a tread of a tire. Its strength comes from tough fibers called collagen. The joint surface cartilage is well lubricated - more slippery than well-manufactured ball bearings... Its living cells are nourished by joint fluid, called synovial fluid which is also extremely good lubrication. ...
Ch 3 test
... speed of the ball will be: a. 10 m/sec. b. 15 m/sec. c. 30 m/sec. d. 45 m/sec. A cart is rolling down a special ramp where there is no friction at all. What will happen if the amount of mass on the cart is increased? a. The cart will accelerate less. b. The cart's acceleration will not be affected. ...
... speed of the ball will be: a. 10 m/sec. b. 15 m/sec. c. 30 m/sec. d. 45 m/sec. A cart is rolling down a special ramp where there is no friction at all. What will happen if the amount of mass on the cart is increased? a. The cart will accelerate less. b. The cart's acceleration will not be affected. ...
Class Notes Forces
... always acts in the direction opposite to the object's motion. Friction can prevent an object from moving (static friction) as when a block of wood rests on an inclined board. Friction can also change an object's acceleration (kinetic friction) such as when the brakes are applied on a moving car. The ...
... always acts in the direction opposite to the object's motion. Friction can prevent an object from moving (static friction) as when a block of wood rests on an inclined board. Friction can also change an object's acceleration (kinetic friction) such as when the brakes are applied on a moving car. The ...
Name
... Which force will change? Which force remains the same? If the upwards acceleration is 3 m/s2, then what is the magnitude of each force? ...
... Which force will change? Which force remains the same? If the upwards acceleration is 3 m/s2, then what is the magnitude of each force? ...
Document
... the body will stop moving. the body will move in the direction of the force. the body’s velocity will increase in magnitude but not change direction. the body will gradually change direction more and more toward that of the force while speeding up. the body will first stop moving and then move in th ...
... the body will stop moving. the body will move in the direction of the force. the body’s velocity will increase in magnitude but not change direction. the body will gradually change direction more and more toward that of the force while speeding up. the body will first stop moving and then move in th ...
Newton`s Law Answers
... E) From part C, how much would the velocity decrease by in 0.1 second. F) For the times 0 to 1.7 seconds, express the acceleration as a number in m/s/s. a = _____ m/s/s G) Comment on what the data and analysis tell you about net force in the first 1.7 seconds. Does it change with time? What could be ...
... E) From part C, how much would the velocity decrease by in 0.1 second. F) For the times 0 to 1.7 seconds, express the acceleration as a number in m/s/s. a = _____ m/s/s G) Comment on what the data and analysis tell you about net force in the first 1.7 seconds. Does it change with time? What could be ...
Document
... force and use terms properly. 3. Explain the effect of changes in magnitude, direction, and point of application of force have on the motion state of a body. 4. Define and give examples of linear forces, concurrent forces, and parallel forces. 5. Determine magnitude, direction, and point of applicat ...
... force and use terms properly. 3. Explain the effect of changes in magnitude, direction, and point of application of force have on the motion state of a body. 4. Define and give examples of linear forces, concurrent forces, and parallel forces. 5. Determine magnitude, direction, and point of applicat ...
G-force

g-force (with g from gravitational) is a measurement of the type of acceleration that causes weight. Despite the name, it is incorrect to consider g-force a fundamental force, as ""g-force"" (lower case character) is a type of acceleration that can be measured with an accelerometer. Since g-force accelerations indirectly produce weight, any g-force can be described as a ""weight per unit mass"" (see the synonym specific weight). When the g-force acceleration is produced by the surface of one object being pushed by the surface of another object, the reaction-force to this push produces an equal and opposite weight for every unit of an object's mass. The types of forces involved are transmitted through objects by interior mechanical stresses. The g-force acceleration (save for certain electromagnetic force influences) is the cause of an object's acceleration in relation to free-fall.The g-force acceleration experienced by an object is due to the vector sum of all non-gravitational and non-electromagnetic forces acting on an object's freedom to move. In practice, as noted, these are surface-contact forces between objects. Such forces cause stresses and strains on objects, since they must be transmitted from an object surface. Because of these strains, large g-forces may be destructive.Gravitation acting alone does not produce a g-force, even though g-forces are expressed in multiples of the acceleration of a standard gravity. Thus, the standard gravitational acceleration at the Earth's surface produces g-force only indirectly, as a result of resistance to it by mechanical forces. These mechanical forces actually produce the g-force acceleration on a mass. For example, the 1 g force on an object sitting on the Earth's surface is caused by mechanical force exerted in the upward direction by the ground, keeping the object from going into free-fall. The upward contact-force from the ground ensures that an object at rest on the Earth's surface is accelerating relative to the free-fall condition (Free fall is the path that the object would follow when falling freely toward the Earth's center). Stress inside the object is ensured from the fact that the ground contact forces are transmitted only from the point of contact with the ground.Objects allowed to free-fall in an inertial trajectory under the influence of gravitation-only, feel no g-force acceleration, a condition known as zero-g (which means zero g-force). This is demonstrated by the ""zero-g"" conditions inside a freely falling elevator falling toward the Earth's center (in vacuum), or (to good approximation) conditions inside a spacecraft in Earth orbit. These are examples of coordinate acceleration (a change in velocity) without a sensation of weight. The experience of no g-force (zero-g), however it is produced, is synonymous with weightlessness.In the absence of gravitational fields, or in directions at right angles to them, proper and coordinate accelerations are the same, and any coordinate acceleration must be produced by a corresponding g-force acceleration. An example here is a rocket in free space, in which simple changes in velocity are produced by the engines, and produce g-forces on the rocket and passengers.