HonorsReview
... 26.A 100-kg fullback makes a turn on the football field. The fullback sweeps out a path that is a portion of a circle with a radius of 10-meters. The fullback makes a half of a turn around the circle in 5.0 seconds. A. Determine the speed? b. Determine the acceleration? c. Determine net force acting ...
... 26.A 100-kg fullback makes a turn on the football field. The fullback sweeps out a path that is a portion of a circle with a radius of 10-meters. The fullback makes a half of a turn around the circle in 5.0 seconds. A. Determine the speed? b. Determine the acceleration? c. Determine net force acting ...
Sem 2 Course Review
... What are ways that human activity has contributed to the pollution that causes smog and acid rain? What are some effects of smog and acid rain on the environment? What has been done or is being done to reduce the pollution that causes smog and acid rain? What are ways that human activity has affecte ...
... What are ways that human activity has contributed to the pollution that causes smog and acid rain? What are some effects of smog and acid rain on the environment? What has been done or is being done to reduce the pollution that causes smog and acid rain? What are ways that human activity has affecte ...
ATLAST Force and Motion Benchmark Clarification for Student
... into a net force; they either balance each other out (net force is zero), or act like an unbalanced force (net force is not zero). If the sum of forces exerted on an object in one direction is the same strength as the sum of forces exerted on the object in the opposite direction, then the forces o ...
... into a net force; they either balance each other out (net force is zero), or act like an unbalanced force (net force is not zero). If the sum of forces exerted on an object in one direction is the same strength as the sum of forces exerted on the object in the opposite direction, then the forces o ...
What you need to be able to do
... (c) Both pucks speed up at the same rate. 8) After the steel puck slides across the ice for several seconds, it gradually slows down and stops. Why does the puck slow down and stop? (a) The force on the puck gets smaller and smaller. (b) No force is needed; moving objects tend to slow down. (c) The ...
... (c) Both pucks speed up at the same rate. 8) After the steel puck slides across the ice for several seconds, it gradually slows down and stops. Why does the puck slow down and stop? (a) The force on the puck gets smaller and smaller. (b) No force is needed; moving objects tend to slow down. (c) The ...
Summary of the unit on force, motion, and energy
... accomplish this; it’s bigger for a concrete block than it is for a cell phone, because the block weighs more. In some cases we can ignore both this response force and any other forces that would cause the system being studied to do something that is being prevented. Thus a ball on a level table in e ...
... accomplish this; it’s bigger for a concrete block than it is for a cell phone, because the block weighs more. In some cases we can ignore both this response force and any other forces that would cause the system being studied to do something that is being prevented. Thus a ball on a level table in e ...
1 - Manhasset Public Schools
... 11. The diagram shows the top view of a 65-kilogram student at point A on an amusement park ride. The ride spins the student in a horizontal circle of radius 2.5 meters, at a constant speed of 8.6 meters per second. The floor is lowered and the student remains against the wall without falling to the ...
... 11. The diagram shows the top view of a 65-kilogram student at point A on an amusement park ride. The ride spins the student in a horizontal circle of radius 2.5 meters, at a constant speed of 8.6 meters per second. The floor is lowered and the student remains against the wall without falling to the ...
Document
... A 60.-kilogram adult and 30.-kilogram child are passengers on a rotor ride at an amusement park. When the rotating hollow cylinder reaches a certain constant speed, v, the floor moves downward. Both passengers stay "pinned" against the wall of the rotor, as shown in the diagram. The magnitude of the ...
... A 60.-kilogram adult and 30.-kilogram child are passengers on a rotor ride at an amusement park. When the rotating hollow cylinder reaches a certain constant speed, v, the floor moves downward. Both passengers stay "pinned" against the wall of the rotor, as shown in the diagram. The magnitude of the ...
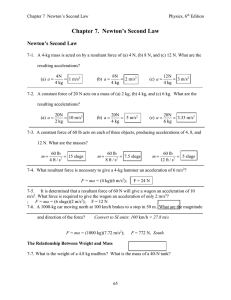
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... Only motion in a straight line is motion that is not changing its direction. Movement in a circle is actually a continuous changing of directions. Therefore, it must be undergoing an acceleration. Ask what force is acting on the yo-yo to change its direction. In an open discussion, explain to stude ...
... Only motion in a straight line is motion that is not changing its direction. Movement in a circle is actually a continuous changing of directions. Therefore, it must be undergoing an acceleration. Ask what force is acting on the yo-yo to change its direction. In an open discussion, explain to stude ...
Chapter 2 - unefa virtual
... Acceleration exists only while a force is applied, once the force is removed, both astronaut and solar panel move in opposite directions at the speeds obtained when contact is broken.. 7-45. A 400-lb sled slides down a hill (k = 0.2) inclined at an angle of 600. What is the normal force on the sled ...
... Acceleration exists only while a force is applied, once the force is removed, both astronaut and solar panel move in opposite directions at the speeds obtained when contact is broken.. 7-45. A 400-lb sled slides down a hill (k = 0.2) inclined at an angle of 600. What is the normal force on the sled ...
4-3 - mrhsluniewskiscience
... Newton’s 3rd Law • The thing to do would be to take one of the tools from your tool belt and throw it is hard as you can directly away from the shuttle. Then, with the help of Newton's second and third laws, you will accelerate back towards the shuttle. As you throw the tool, you push against it, c ...
... Newton’s 3rd Law • The thing to do would be to take one of the tools from your tool belt and throw it is hard as you can directly away from the shuttle. Then, with the help of Newton's second and third laws, you will accelerate back towards the shuttle. As you throw the tool, you push against it, c ...
Terminal Velocity Lab
... time, which caused it to hit the ground first. The coffee filter did not experience as great of a jump in velocity and took much longer to fall because of its mass. 3. Yes, the book reached terminal velocity. I know this because the velocity graph of the book shows that it peaked and flat lined at t ...
... time, which caused it to hit the ground first. The coffee filter did not experience as great of a jump in velocity and took much longer to fall because of its mass. 3. Yes, the book reached terminal velocity. I know this because the velocity graph of the book shows that it peaked and flat lined at t ...
AP Physics – The Physics Little AP Test Review Helper
... using proper symbols. Ask yourself these questions: What is going on in the problem? What do you have to find out? What kind of problem is it? Is it an electric problem? Is it a projectile motion problem? Is it a motion problem? Is it a force problem? &tc. Many of the problems will sneakily require ...
... using proper symbols. Ask yourself these questions: What is going on in the problem? What do you have to find out? What kind of problem is it? Is it an electric problem? Is it a projectile motion problem? Is it a motion problem? Is it a force problem? &tc. Many of the problems will sneakily require ...
12: Forces
... • Inertia is related to an object’s mass. – inertia: the tendency of an object to resist a change in motion unless an outside force acts on the object • Seat belts and car seats provide protection. – When a car comes to a stop, your seat belt and the friction between you and the seat provide the unb ...
... • Inertia is related to an object’s mass. – inertia: the tendency of an object to resist a change in motion unless an outside force acts on the object • Seat belts and car seats provide protection. – When a car comes to a stop, your seat belt and the friction between you and the seat provide the unb ...
document
... direction of the net force acting on it, there must be a net force toward the center of the circle. This force can be provided by any number of agents ...
... direction of the net force acting on it, there must be a net force toward the center of the circle. This force can be provided by any number of agents ...
6 Newton`s Second Law of Motion–Force and Acceleration
... How much force, or thrust, must a 30,000-kg jet plane develop to achieve an acceleration of 1.5 m/s2? ...
... How much force, or thrust, must a 30,000-kg jet plane develop to achieve an acceleration of 1.5 m/s2? ...
G-force

g-force (with g from gravitational) is a measurement of the type of acceleration that causes weight. Despite the name, it is incorrect to consider g-force a fundamental force, as ""g-force"" (lower case character) is a type of acceleration that can be measured with an accelerometer. Since g-force accelerations indirectly produce weight, any g-force can be described as a ""weight per unit mass"" (see the synonym specific weight). When the g-force acceleration is produced by the surface of one object being pushed by the surface of another object, the reaction-force to this push produces an equal and opposite weight for every unit of an object's mass. The types of forces involved are transmitted through objects by interior mechanical stresses. The g-force acceleration (save for certain electromagnetic force influences) is the cause of an object's acceleration in relation to free-fall.The g-force acceleration experienced by an object is due to the vector sum of all non-gravitational and non-electromagnetic forces acting on an object's freedom to move. In practice, as noted, these are surface-contact forces between objects. Such forces cause stresses and strains on objects, since they must be transmitted from an object surface. Because of these strains, large g-forces may be destructive.Gravitation acting alone does not produce a g-force, even though g-forces are expressed in multiples of the acceleration of a standard gravity. Thus, the standard gravitational acceleration at the Earth's surface produces g-force only indirectly, as a result of resistance to it by mechanical forces. These mechanical forces actually produce the g-force acceleration on a mass. For example, the 1 g force on an object sitting on the Earth's surface is caused by mechanical force exerted in the upward direction by the ground, keeping the object from going into free-fall. The upward contact-force from the ground ensures that an object at rest on the Earth's surface is accelerating relative to the free-fall condition (Free fall is the path that the object would follow when falling freely toward the Earth's center). Stress inside the object is ensured from the fact that the ground contact forces are transmitted only from the point of contact with the ground.Objects allowed to free-fall in an inertial trajectory under the influence of gravitation-only, feel no g-force acceleration, a condition known as zero-g (which means zero g-force). This is demonstrated by the ""zero-g"" conditions inside a freely falling elevator falling toward the Earth's center (in vacuum), or (to good approximation) conditions inside a spacecraft in Earth orbit. These are examples of coordinate acceleration (a change in velocity) without a sensation of weight. The experience of no g-force (zero-g), however it is produced, is synonymous with weightlessness.In the absence of gravitational fields, or in directions at right angles to them, proper and coordinate accelerations are the same, and any coordinate acceleration must be produced by a corresponding g-force acceleration. An example here is a rocket in free space, in which simple changes in velocity are produced by the engines, and produce g-forces on the rocket and passengers.