Topological phases of matter
... Kosterlitz and Thouless, Long-range order and metastability in two-dimensional solids and superfluids, J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys. 5, L124 (1972); Ordering, Metastability, and phase transitions in two-dimensional systems, ibid. 6, 1181 (1973). ...
... Kosterlitz and Thouless, Long-range order and metastability in two-dimensional solids and superfluids, J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys. 5, L124 (1972); Ordering, Metastability, and phase transitions in two-dimensional systems, ibid. 6, 1181 (1973). ...
Semiclassical methods in solid state physics : two examples
... first study of such problems goes back to Landau in 1930 [58] for the motion of electrons approximation. It was soon followed by the work of Peierls metal, in the effective ...
... first study of such problems goes back to Landau in 1930 [58] for the motion of electrons approximation. It was soon followed by the work of Peierls metal, in the effective ...
Quantum anomalous Hall effect with cold atoms trapped in a square
... group [16] of rotating each lattice site around its own center [17]. In this work, we propose a distinct realization of QAHE in a two-dimensional (2D) anisotropic square optical lattice, which can be realized based on the double-well experiments performed at NIST [18], superposed with a periodic gau ...
... group [16] of rotating each lattice site around its own center [17]. In this work, we propose a distinct realization of QAHE in a two-dimensional (2D) anisotropic square optical lattice, which can be realized based on the double-well experiments performed at NIST [18], superposed with a periodic gau ...
Symplectic Geometry and Geometric Quantization
... classical system possesses a symmetry -represented by a hamiltonian action (to be defined later) of this group on the symplectic manifold modelling the classical phase space-, one would like the associated quantum system to form a unitary representation of this group. If the action is transitive, th ...
... classical system possesses a symmetry -represented by a hamiltonian action (to be defined later) of this group on the symplectic manifold modelling the classical phase space-, one would like the associated quantum system to form a unitary representation of this group. If the action is transitive, th ...
From Physics to Information Theory and Back - Philsci
... about possibilities of information processing and transmission—the results obtained, and the frameworks developed, have interest even for those of us who are not of that conviction. Indeed, much of the recent work echoes, and builds upon, work that predates the inception of quantum information theo ...
... about possibilities of information processing and transmission—the results obtained, and the frameworks developed, have interest even for those of us who are not of that conviction. Indeed, much of the recent work echoes, and builds upon, work that predates the inception of quantum information theo ...
On Water, Steam and String Theory
... plotted in a phase diagram (Fig. 1). Two points in this phase diagram catch one’s eye. The first one is the so-called triple point at 0o C and 0.006 atmospheres pressure. Below this pressure the liquid phase of water disappears, and ice directly evaporates when heated up. At the triple point, ice, w ...
... plotted in a phase diagram (Fig. 1). Two points in this phase diagram catch one’s eye. The first one is the so-called triple point at 0o C and 0.006 atmospheres pressure. Below this pressure the liquid phase of water disappears, and ice directly evaporates when heated up. At the triple point, ice, w ...
On the Dirac Scattering Problem
... Given that equations (11) and (15) are consistent with equation (7) we can exploit their simultaneity do develop a series solution. This is achieved by substituting equation (11) into the RHS of equation (15) and equation (15) into the RHS of equation (11) and then repeating this process ad infinitu ...
... Given that equations (11) and (15) are consistent with equation (7) we can exploit their simultaneity do develop a series solution. This is achieved by substituting equation (11) into the RHS of equation (15) and equation (15) into the RHS of equation (11) and then repeating this process ad infinitu ...
Fokker-Planck theory of superstatistics
... equilibrium state at a given value of the inverse temperature, ! , characterized by the conditional distribution, P (! i | " ) = Z !1 ( " ) exp(! " ! i ) with Z( ! ) = " i exp(! ! " i ) , is fast, but ! slowly varies according to some distribution, f ( ! ) . Therefore, B describes a randomness quenc ...
... equilibrium state at a given value of the inverse temperature, ! , characterized by the conditional distribution, P (! i | " ) = Z !1 ( " ) exp(! " ! i ) with Z( ! ) = " i exp(! ! " i ) , is fast, but ! slowly varies according to some distribution, f ( ! ) . Therefore, B describes a randomness quenc ...
Document
... • The Coulomb gauge is physical, expressions in Coulomb gauge, even with vector potential, are gauge invariant, including the hydrogen atomic Hamiltonian and multipole radiation. ...
... • The Coulomb gauge is physical, expressions in Coulomb gauge, even with vector potential, are gauge invariant, including the hydrogen atomic Hamiltonian and multipole radiation. ...
A Very Short Introduction to Quantum Field Theory
... is an imperfect analogy for an attractive potential. We could describe the attraction in one of two ways: we could say that there is an attractive potential between any pair of point-like masses, or we could introduce a continuous variable, φ(x, y) which describes the displacement of the sheet as a ...
... is an imperfect analogy for an attractive potential. We could describe the attraction in one of two ways: we could say that there is an attractive potential between any pair of point-like masses, or we could introduce a continuous variable, φ(x, y) which describes the displacement of the sheet as a ...
PDF
... of a selected group. For topological groups, where the underlying vector space consists of continuous complex valued functions, this product requires the availability of some structure of measure and of measurable functions, with the sum replaced by an integral. Notice also that this algebra has an ...
... of a selected group. For topological groups, where the underlying vector space consists of continuous complex valued functions, this product requires the availability of some structure of measure and of measurable functions, with the sum replaced by an integral. Notice also that this algebra has an ...
Part 1 - SCIPP
... p3 be the momenta of masses m1 , m2 and m3 respectively. Since we are in the center of mass frame, p1 = 0. Therefore, p1 = p2 + p3 = 0 and thus, p2 = −p3 . We can rotate our problem such that p2 and p3 are in the x̂ direction. To determine the energies of masses m2 and m3 , we will use both momentum ...
... p3 be the momenta of masses m1 , m2 and m3 respectively. Since we are in the center of mass frame, p1 = 0. Therefore, p1 = p2 + p3 = 0 and thus, p2 = −p3 . We can rotate our problem such that p2 and p3 are in the x̂ direction. To determine the energies of masses m2 and m3 , we will use both momentum ...
Exotic path integrals and dualities
... elegant: supersymmetric path integrals simplify significantly as they can be evaluated by only considering certain fixed points of the supersymmetric theory. Topological field theories are theories that are independent of the metric on the space-time on which they are defined. We shall discuss the t ...
... elegant: supersymmetric path integrals simplify significantly as they can be evaluated by only considering certain fixed points of the supersymmetric theory. Topological field theories are theories that are independent of the metric on the space-time on which they are defined. We shall discuss the t ...
$doc.title
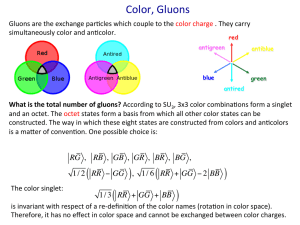
... mass. On the other hand, the QCD gluons are massless, and their strong interac1on is not damped by a small parameter. As a result, the QCD vacuum polariza1on effect is extremely strong, and the empt ...
... mass. On the other hand, the QCD gluons are massless, and their strong interac1on is not damped by a small parameter. As a result, the QCD vacuum polariza1on effect is extremely strong, and the empt ...
Classical calculation of radiative lifetimes of atomic hydrogen in a
... of the magnetic field. For moderate B field magnitudes, the quadratic terms lead to a number of perturbing effects. First, the angle of this plane relative to B oscillates in time at a slow frequency of approximately ⍀2 / , where is the orbital frequency of the Kepler orbit. Second, the eccentric ...
... of the magnetic field. For moderate B field magnitudes, the quadratic terms lead to a number of perturbing effects. First, the angle of this plane relative to B oscillates in time at a slow frequency of approximately ⍀2 / , where is the orbital frequency of the Kepler orbit. Second, the eccentric ...
CHAPTER 6: Quantum Mechanics II
... Consider a particle passing through a potential well region rather than through a potential barrier. Classically, the particle would speed up passing the well region, because K = mv2 / 2 = E + V0. According to quantum mechanics, reflection and transmission may occur, but the wavelength inside the po ...
... Consider a particle passing through a potential well region rather than through a potential barrier. Classically, the particle would speed up passing the well region, because K = mv2 / 2 = E + V0. According to quantum mechanics, reflection and transmission may occur, but the wavelength inside the po ...
Can Molecules Have Permanent Electric Dipole Moments?
... The Stark effect measures the interaction of a molecular dipole moment with an electric field, while the Zeeman effect measures the interaction of a molecular magnetic moment with a magnetic field. While both electric and magnetic dipoles are rank one tensor quantities, they have quite different sym ...
... The Stark effect measures the interaction of a molecular dipole moment with an electric field, while the Zeeman effect measures the interaction of a molecular magnetic moment with a magnetic field. While both electric and magnetic dipoles are rank one tensor quantities, they have quite different sym ...
ELECTROGRAVITATION AS A UNIFIED FIELD
... but is a terminated field. (The field vector is connected to a conjugate vector field.) This would include neutrons, bosons, and particles exhibiting zero charge in general. Mass would then be the result of standing wave fields. The source for all this energy would come from the same place as the en ...
... but is a terminated field. (The field vector is connected to a conjugate vector field.) This would include neutrons, bosons, and particles exhibiting zero charge in general. Mass would then be the result of standing wave fields. The source for all this energy would come from the same place as the en ...