INTRODUCTION Macrocycles are important and powerful ligands
... under oxidative aqueous conditions to give rust (Fe2O3) or MnO2, respectively. This transformation not only destroys the catalyst, but also creates other undesirable effects, such as staining or surface oxidations caused by the insoluble metal oxides.23 The knowledge of modern coordination chemistry ...
... under oxidative aqueous conditions to give rust (Fe2O3) or MnO2, respectively. This transformation not only destroys the catalyst, but also creates other undesirable effects, such as staining or surface oxidations caused by the insoluble metal oxides.23 The knowledge of modern coordination chemistry ...
Molecular Symmetry Chem 332.3 Fall 2005 Inorganic Chemistry II
... ¾Diamagnetic - pushed out of a magnetic field. Indicates that all electrons are paired. ...
... ¾Diamagnetic - pushed out of a magnetic field. Indicates that all electrons are paired. ...
(i) Coordination entity
... Coordination isomerism: It arises from the interchange of ligands between cationic and anionic entities of different metal ions present in a complex . Example [Co(NH3)6][Cr(CN)6] & [Cr(NH3)6][Co(CN)6] STEREOISOMERISM: Stereo isomers have the same chemical formula and chemical bonds but they have dif ...
... Coordination isomerism: It arises from the interchange of ligands between cationic and anionic entities of different metal ions present in a complex . Example [Co(NH3)6][Cr(CN)6] & [Cr(NH3)6][Co(CN)6] STEREOISOMERISM: Stereo isomers have the same chemical formula and chemical bonds but they have dif ...
Axial Ligation Equilibria as Probes of the Effective Steric Bulk of
... Recently, we used octasubstituted tetraarylporphyrins to establish that the alkyl exchange reaction of alkyl-cobalt(III) porphyrin complexes with cobalt(II) porphyrin complexes proceeds via a bimolecular, SH2 mechanism. However, our results suggested that the relationship between the effective steri ...
... Recently, we used octasubstituted tetraarylporphyrins to establish that the alkyl exchange reaction of alkyl-cobalt(III) porphyrin complexes with cobalt(II) porphyrin complexes proceeds via a bimolecular, SH2 mechanism. However, our results suggested that the relationship between the effective steri ...
Presentation
... 8. What is the relationship of bond order with stability of the molecule and bond length? Higher the bond order order, greater is the stability of the molecule and lesser is the bond length ...
... 8. What is the relationship of bond order with stability of the molecule and bond length? Higher the bond order order, greater is the stability of the molecule and lesser is the bond length ...
Investigation of atomic level patterns in protein
... PISCES server, are characterized by the following: 1) the chains share sequence identity of below 25%; 2) the resolution of the protein-ligand complex structure is below 2.0Å; and 3) the R factor is below 0.25. These criteria, which resulted in selection of 2320 chains, assure that the selected prot ...
... PISCES server, are characterized by the following: 1) the chains share sequence identity of below 25%; 2) the resolution of the protein-ligand complex structure is below 2.0Å; and 3) the R factor is below 0.25. These criteria, which resulted in selection of 2320 chains, assure that the selected prot ...
TransitionMetals - Lesmahagow High School
... differing stability. Transition metals exhibit variable oxidation states because they can not only lose their 4s electrons but some or all of their 3d electrons. Sometimes electron configurations can be used to explain why one oxidation state is more stable. For example, during rusting Fe2+ ions are ...
... differing stability. Transition metals exhibit variable oxidation states because they can not only lose their 4s electrons but some or all of their 3d electrons. Sometimes electron configurations can be used to explain why one oxidation state is more stable. For example, during rusting Fe2+ ions are ...
Coordination Chemistry III: Tanabe
... ligand-based orbitals and metal d-orbitals are possible. - called charge transfer transitions since an electron is transferred from the metal to the ligand or vice versa - very intense transitions since they are Laporte and spin allowed (ε ~50,000 compared to <20 L mol-1 cm-1 for d-d transitions) - ...
... ligand-based orbitals and metal d-orbitals are possible. - called charge transfer transitions since an electron is transferred from the metal to the ligand or vice versa - very intense transitions since they are Laporte and spin allowed (ε ~50,000 compared to <20 L mol-1 cm-1 for d-d transitions) - ...
Chapter 10 Homework Problem Molecular Orbital Diagram for Cr
... You may discuss ideas about this assignment with your classmates, but the answers you hand in should be your own work. You are also encouraged to discuss any of this material with me. Preliminary Considerations 1. (5 pts) What is the oxidation state of Cr in this complex? How many valence electrons ...
... You may discuss ideas about this assignment with your classmates, but the answers you hand in should be your own work. You are also encouraged to discuss any of this material with me. Preliminary Considerations 1. (5 pts) What is the oxidation state of Cr in this complex? How many valence electrons ...
Ligand Field Theory www.AssignmentPoint.com Ligand field theory
... orbital theory and crystal field theory, which describes the loss of degeneracy of metal d orbitals in transition metal complexes. Griffith and Orgel championed ligand field theory as a more accurate description of such complexes. They used the electrostatic principles established in crystal field t ...
... orbital theory and crystal field theory, which describes the loss of degeneracy of metal d orbitals in transition metal complexes. Griffith and Orgel championed ligand field theory as a more accurate description of such complexes. They used the electrostatic principles established in crystal field t ...
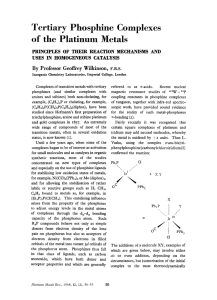
Tertiary Phosphine Complexes of the Platinum Metals
... labile or reactive groups such as H, CH,, C,H, bound to metals as, for example, in (Et,P),PtCl(CH,). This stabilising influence arises from the property of the phosphines to adjust energy levels in the metal atoms of complexes through the d,-d, bonding capacity of the phosphorus atom. Such R,P compo ...
... labile or reactive groups such as H, CH,, C,H, bound to metals as, for example, in (Et,P),PtCl(CH,). This stabilising influence arises from the property of the phosphines to adjust energy levels in the metal atoms of complexes through the d,-d, bonding capacity of the phosphorus atom. Such R,P compo ...
Coordination Chemistry: Bonding, Spectra, and Magnetism
... there is more overlap with larger d-orbitals. (Note that this trend is opposite to what occurs for main group elements.) Number and Geometry of Ligands - increases with increasing number of ligands - as discussed previously Nature of Ligands - memorize the basic outline of the spectrochemical seri ...
... there is more overlap with larger d-orbitals. (Note that this trend is opposite to what occurs for main group elements.) Number and Geometry of Ligands - increases with increasing number of ligands - as discussed previously Nature of Ligands - memorize the basic outline of the spectrochemical seri ...
2Cu 2+ + O 2 2
... Hr and sMMO share the main features: a four-helix-bundle surrounding a Fe-(carboxylato)2-Fe core but differ in the particular environment of the Fe centers: -Hr coordination sphere is more histidine rich -Hr permits only terminal O2-coordination to a single iron, while sMMO diiron center presents op ...
... Hr and sMMO share the main features: a four-helix-bundle surrounding a Fe-(carboxylato)2-Fe core but differ in the particular environment of the Fe centers: -Hr coordination sphere is more histidine rich -Hr permits only terminal O2-coordination to a single iron, while sMMO diiron center presents op ...
d- Block Elements - Sakshieducation.com
... 12. What is meant by chelating effect? Give example? A: A bidentate (or) a poly dentate ligand is known as chelating ligand if on coordination it results in the formation of a closed (or) cyclic structure.Chelating ligands form more stable complexes than the monodentate ligands. This is called chela ...
... 12. What is meant by chelating effect? Give example? A: A bidentate (or) a poly dentate ligand is known as chelating ligand if on coordination it results in the formation of a closed (or) cyclic structure.Chelating ligands form more stable complexes than the monodentate ligands. This is called chela ...
Sample 3 - University of Puget Sound
... for the chemical industry.1 The need to reduce energy consumption is driving many chemistry related fields to develop sustainable methods of synthesizing chemical compounds. For example, the pharmaceutical industry has a particularly significant energy footprint due to the excessive production of wa ...
... for the chemical industry.1 The need to reduce energy consumption is driving many chemistry related fields to develop sustainable methods of synthesizing chemical compounds. For example, the pharmaceutical industry has a particularly significant energy footprint due to the excessive production of wa ...
Outer-sphere Ligand to Ligand Charge Transfer of Metal Complexes
... the metal to the ligand (CTML),2 from one metal to another metal (CTMM),2 or from one ligand to another ligand (CTLL).3-7 In principle it should be possible to observe all these optical CT transitions also as outer-sphere processes. Although intermolecular CT excitation of metal complexes becomes in ...
... the metal to the ligand (CTML),2 from one metal to another metal (CTMM),2 or from one ligand to another ligand (CTLL).3-7 In principle it should be possible to observe all these optical CT transitions also as outer-sphere processes. Although intermolecular CT excitation of metal complexes becomes in ...
Exam practice answers 6
... (any suitable example will get the marks e.g. cis–trans platin) has two different isomeric forms with the ammonia molecules or chloride ions either being on opposite sides of the complex ion (the trans form) or alongside each other (the cis form). The bidentate ligand 1,2-diaminoethane (en) can be ...
... (any suitable example will get the marks e.g. cis–trans platin) has two different isomeric forms with the ammonia molecules or chloride ions either being on opposite sides of the complex ion (the trans form) or alongside each other (the cis form). The bidentate ligand 1,2-diaminoethane (en) can be ...
The Transition Elements and Their Coordination Compounds
... When solid complex dissolves in water, the complex ion and the counter ions separate, but ligands remain bound to central atom Coordination Numbers, Geometries, and Ligands Coordination Number (CN) - the number of ligand atoms that are bonded directly to the central metal ion. The coordination numbe ...
... When solid complex dissolves in water, the complex ion and the counter ions separate, but ligands remain bound to central atom Coordination Numbers, Geometries, and Ligands Coordination Number (CN) - the number of ligand atoms that are bonded directly to the central metal ion. The coordination numbe ...
Chapter 20: Reactions of Complexes (Mechanisms)
... You should review Petrucci 9E Chapter 14 (Kinetics) & Ch 24 (Coord. Chem.) The generalized rate‐law for any reaction is (where [A] = conc’n of A): ...
... You should review Petrucci 9E Chapter 14 (Kinetics) & Ch 24 (Coord. Chem.) The generalized rate‐law for any reaction is (where [A] = conc’n of A): ...
The Synthesis and Color of Cr Complexes
... form the Co(NH3)63+ complex cation. When precipitated from an aqueous solution, this 3+ cation combines with 3 Cl- anions to form the [Co(NH3)6]Cl3 coordination compound; much like the Na+ cation combines with the Cl- anion to form the compound NaCl. (Note the use of [ ]’s around the Complex Ion Co( ...
... form the Co(NH3)63+ complex cation. When precipitated from an aqueous solution, this 3+ cation combines with 3 Cl- anions to form the [Co(NH3)6]Cl3 coordination compound; much like the Na+ cation combines with the Cl- anion to form the compound NaCl. (Note the use of [ ]’s around the Complex Ion Co( ...
112 ex iii lec outline f 04
... Structural Isomers: Different Sequences of Atoms a. Coordination Isomers differ in that the ligands that are directly bonded to the metal, would be instead outside of the complex ion and be the counter ions. ...
... Structural Isomers: Different Sequences of Atoms a. Coordination Isomers differ in that the ligands that are directly bonded to the metal, would be instead outside of the complex ion and be the counter ions. ...
HL Periodicity
... As the d-block fills, there are electrons available for other functions (create colors). The atomic radii are curious, also. Based on electron config. ...
... As the d-block fills, there are electrons available for other functions (create colors). The atomic radii are curious, also. Based on electron config. ...
Chiral-Auxiliary-Mediated Asymmetric Synthesis of Tris
... As molecular recognition involving metal complexes continues to gain importance, for example, in the design of nucleic acid probes or enzyme inhibitors, so does the demand for efficient syntheses of enantiopure chiral-at-metal coordination compounds. However, compared with the availability of highly ...
... As molecular recognition involving metal complexes continues to gain importance, for example, in the design of nucleic acid probes or enzyme inhibitors, so does the demand for efficient syntheses of enantiopure chiral-at-metal coordination compounds. However, compared with the availability of highly ...
Ligand
4-3D-balls.png?width=300)
In coordination chemistry, a ligand (/lɪɡənd/) is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs. The nature of metal-ligand bonding can range from covalent to ionic. Furthermore, the metal-ligand bond order can range from one to three. Ligands are viewed as Lewis bases, although rare cases are known to involve Lewis acidic ""ligand.""Metals and metalloids are bound to ligands in virtually all circumstances, although gaseous ""naked"" metal ions can be generated in high vacuum. Ligands in a complex dictate the reactivity of the central atom, including ligand substitution rates, the reactivity of the ligands themselves, and redox. Ligand selection is a critical consideration in many practical areas, including bioinorganic and medicinal chemistry, homogeneous catalysis, and environmental chemistry.Ligands are classified in many ways like : their charge, their size (bulk), the identity of the coordinating atom(s), and the number of electrons donated to the metal (denticity or hapticity). The size of a ligand is indicated by its cone angle.