Full Article - Berkeley Global Science Institute
... metal sequence arrangements. These were cleaved from the resin, and their character was confirmed by mass spectrometry. ...
... metal sequence arrangements. These were cleaved from the resin, and their character was confirmed by mass spectrometry. ...
Observation of back-donation in 3d metal cyanide complexes
... K 3 Mn(CN) 6 , K 3 Fe(CN) 6 , and K 3 Co(CN) 6 have been measured by detecting the total electron yield. The N K spectra of the complexes are very similar and differ only in intensity of the lowest-energy absorption band. The intensity of this feature systematically decreases and its energy position ...
... K 3 Mn(CN) 6 , K 3 Fe(CN) 6 , and K 3 Co(CN) 6 have been measured by detecting the total electron yield. The N K spectra of the complexes are very similar and differ only in intensity of the lowest-energy absorption band. The intensity of this feature systematically decreases and its energy position ...
Preparation, Identification and Biological Activity of a New Ligand
... Schiff bases are condensation products of primary amines with carbonyl compounds and they were first reported by Schiff [1] in 1864. The common structural feature of these compounds is the azomethine group with a general formula RHC=NR1, where R and R1 are alkyl, aryl, cyclo alkyl or heterocyclic gr ...
... Schiff bases are condensation products of primary amines with carbonyl compounds and they were first reported by Schiff [1] in 1864. The common structural feature of these compounds is the azomethine group with a general formula RHC=NR1, where R and R1 are alkyl, aryl, cyclo alkyl or heterocyclic gr ...
Information regarding naming of Complex Ions Reference Sources: Naming Complex Ions
... For splitting of d orbitals due to ligands around central metal ion see: http://www.chemguide.co.uk/inorganic/complexions/colour2.html ...
... For splitting of d orbitals due to ligands around central metal ion see: http://www.chemguide.co.uk/inorganic/complexions/colour2.html ...
Transition Metals and Coordination Chem
... M with empty d- orbitals Ligand with e- pair Combine to form LA-LB (Compound) In general, the complex is more stable than the separated compound. ...
... M with empty d- orbitals Ligand with e- pair Combine to form LA-LB (Compound) In general, the complex is more stable than the separated compound. ...
NaI/CuI–II heterometallic cages interconnected by unusual linear 2
... Gutenberg – University of Mainz, Institute of Inorganic and Analytical Chemistry, Mainz It is well known that the cyanate ion can link a pair of metal centers in end-on (u1,1-OCN, u1,1--NCO and the most rare u4-NCO1a) or end-to-end (u1,3--NCO) bonded fashion (Scheme 1). In contrast to the end-on cya ...
... Gutenberg – University of Mainz, Institute of Inorganic and Analytical Chemistry, Mainz It is well known that the cyanate ion can link a pair of metal centers in end-on (u1,1-OCN, u1,1--NCO and the most rare u4-NCO1a) or end-to-end (u1,3--NCO) bonded fashion (Scheme 1). In contrast to the end-on cya ...
Pigments The Visible Spectrum
... • The deep blue color the gemstone sapphire is also based on impurity doping into Al2O3. The color arises from the following charge transfer excitation: Fe2+ + Ti4+ → Fe3+ + Ti3+ (λmax ~ 2.2 eV, 570 nm) • The transition is facilitated by the geometry of the corundum structure where the two ions shar ...
... • The deep blue color the gemstone sapphire is also based on impurity doping into Al2O3. The color arises from the following charge transfer excitation: Fe2+ + Ti4+ → Fe3+ + Ti3+ (λmax ~ 2.2 eV, 570 nm) • The transition is facilitated by the geometry of the corundum structure where the two ions shar ...
L"" "`L
... complexes of period 5 and period 6 metal ions are almost always square-planar, and [RhH(CO)(PR3)2] is no exception. The bulky PR 3 ligands are cis to one another. This compound has Cs symmetry, with the mirror plane coincident with the rhodium atom and the four ligand atoms bound to it. A planar com ...
... complexes of period 5 and period 6 metal ions are almost always square-planar, and [RhH(CO)(PR3)2] is no exception. The bulky PR 3 ligands are cis to one another. This compound has Cs symmetry, with the mirror plane coincident with the rhodium atom and the four ligand atoms bound to it. A planar com ...
Cu(NH3)4 - Granite Bay High School / Granite Bay High School
... (2) a prefix must precede ligand names designating the number of molecules or ions present (di-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, etc.) (3) central atom is named second (Latin stems used for many of the metals) ...
... (2) a prefix must precede ligand names designating the number of molecules or ions present (di-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, etc.) (3) central atom is named second (Latin stems used for many of the metals) ...
Photoredox Reactions: Energy Storage and Halocarbon Degradation
... M = Mo indicates that the equatorial carboxylate ligands in the diruthenium species also experience x-contact shifts. Variable-temperature studies and calculated estimates of dipolar shifts (using structural parameters taken from solid-state structures) indicate a significant zerofield splitting con ...
... M = Mo indicates that the equatorial carboxylate ligands in the diruthenium species also experience x-contact shifts. Variable-temperature studies and calculated estimates of dipolar shifts (using structural parameters taken from solid-state structures) indicate a significant zerofield splitting con ...
Worksheet 9 Notes - Oregon State chemistry
... [Fe(NO2)6]4-? [(NO2) is the NO2- ion]. Low spin due to the NO2- ion being strong field: CN- > NO2- > en > NH3 > NCS- > H2O > F- > ClThe iron ion in [Fe(NO2)6]4- is 2+. This is because each of the six NO2- ions carries a charge of –1 and the charge on the entire complex is 4-. Fe is in Group 8 (it ha ...
... [Fe(NO2)6]4-? [(NO2) is the NO2- ion]. Low spin due to the NO2- ion being strong field: CN- > NO2- > en > NH3 > NCS- > H2O > F- > ClThe iron ion in [Fe(NO2)6]4- is 2+. This is because each of the six NO2- ions carries a charge of –1 and the charge on the entire complex is 4-. Fe is in Group 8 (it ha ...
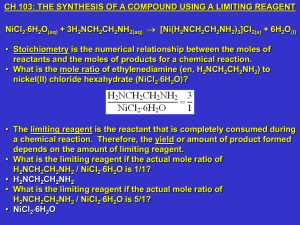
Week #10: The Synthesis of a Compound using a Limiting Reagent
... cation bonded (or coordinated) to 1 or more groups of atoms. These groups of atoms are called ligands. • Coordination number is the number of ligand atoms that bond to the central metal of a complex ion. • What is the metal atom in this complex ion? • Ni2+ • What is the ligand? ...
... cation bonded (or coordinated) to 1 or more groups of atoms. These groups of atoms are called ligands. • Coordination number is the number of ligand atoms that bond to the central metal of a complex ion. • What is the metal atom in this complex ion? • Ni2+ • What is the ligand? ...
Document
... cation bonded (or coordinated) to 1 or more groups of atoms. These groups of atoms are called ligands. • Coordination number is the number of ligand atoms that bond to the central metal of a complex ion. • What is the metal atom in this complex ion? • Ni2+ • What is the ligand? ...
... cation bonded (or coordinated) to 1 or more groups of atoms. These groups of atoms are called ligands. • Coordination number is the number of ligand atoms that bond to the central metal of a complex ion. • What is the metal atom in this complex ion? • Ni2+ • What is the ligand? ...
Spin crossover

Spin Crossover (SCO), sometimes referred to as spin transition or spin equilibrium behavior, is a phenomenon that occurs in some metal complexes wherein the spin state of the complex changes due to external stimuli such as a variation of temperature, pressure, light irradiation or an influence of a magnetic field.With regard to a ligand field and ligand field theory, the change in spin state is a transition from a low spin (LS) ground state electron configuration to a high spin (HS) ground state electron configuration of the metal’s d atomic orbitals (AOs), or vice versa. The magnitude of the ligand field splitting along with the pairing energy of the complex determines whether it will have a LS or HS electron configuration. A LS state occurs because the ligand field splitting (Δ) is greater than the pairing energy of the complex (which is an unfavorable process).Figure 1 is a simplified illustration of the metal’s d orbital splitting in the presence of an octahedral ligand field. A large splitting between the t2g and eg AOs requires a substantial amount of energy for the electrons to overcome the energy gap (Δ) to comply with Hund’s Rule. Therefore, electrons will fill the lower energy t2g orbitals completely before populating the higher energy eg orbitals. Conversely, a HS state occurs with weaker ligand fields and smaller orbital splitting. In this case the energy required to populate the higher levels is substantially less than the pairing energy and the electrons fill the orbitals according to Hund’s Rule by populating the higher energy orbitals before pairing with electrons in the lower lying orbitals. An example of a metal ion that can exist in either a LS or HS state is Fe3+ in an octahedral ligand field. Depending on the ligands that are coordinated to this complex the Fe3+ can attain a LS or a HS state, as in Figure 1.Spin crossover refers to the transitions between high to low, or low to high, spin states. This phenomenon is commonly observed with some first row transition metal complexes with a d4 through d7 electron configuration in an octahedral ligand geometry. Spin transition curves are a common representation of SCO phenomenon with the most commonly observed types depicted in Figure 2 in which γHS (the high-spin molar fraction) is plotted vs. T. The figure shows a gradual spin transition (left), an abrupt transition with hysteresis (middle) and a two-step transition (right). For a transition to be considered gradual, it typically takes place over a large temperature range, even up to several hundred K, whereas for a transition to be considered abrupt, it should take place within 10 K or less.These curves indicate that a spin transition has occurred in a metal complex as temperature changed. The gradual transition curve is an indication that not all metal centers within the complex are undergoing the transition at the same temperature. The abrupt spin change with hysteresis indicates a strong cooperativity, or “communication”, between neighboring metal complexes. In the latter case, the material is bistable and can exist in the two different spin states with a different range of external stimuli (temperature in this case) for the two phenomena, namely LS → HS and HS → LS. The two-step transition is relatively rare but is observed, for example, with dinuclear SCO complexes for which the spin transition in one metal center renders the transition in the second metal center less favorable.There are several types of spin crossover that can occur in a complex; some of them are light induced excited state spin trapping (LIESST), ligand-driven light induced spin change (LD-LISC), and charge transfer induced spin transition (CTIST).