Iridium Complex-Catalyzed Highly Selective Organic Synthesis
... This success prompted us to examine the allylic alkylation of enynyl acetates. Oxidative addition of (E)-22 or 23 gives an alkynyl group-substituted p-allyl iridium intermediate 15 (Scheme 9). We were interested in the reactivity of this intermediate. Enynyl acetate 23 was easily prepared by reactin ...
... This success prompted us to examine the allylic alkylation of enynyl acetates. Oxidative addition of (E)-22 or 23 gives an alkynyl group-substituted p-allyl iridium intermediate 15 (Scheme 9). We were interested in the reactivity of this intermediate. Enynyl acetate 23 was easily prepared by reactin ...
Low Temperature Precursors for SnOx Thin Films
... encouragement and useful discussions about the work presented within this thesis. I was fortunate to also have the wisdom and guidance of two other academic supervisors with Professor Kieran Molloy providing his wealth of knowledge and experience within the field of tin and materials chemistry and D ...
... encouragement and useful discussions about the work presented within this thesis. I was fortunate to also have the wisdom and guidance of two other academic supervisors with Professor Kieran Molloy providing his wealth of knowledge and experience within the field of tin and materials chemistry and D ...
Insulators
... through which the S.S interaction takes place. Generally, it was established that the S.S exchange interaction require R≤ 1.5 a, where a is the lattice parameter of host medium (Seo 2012). R could be estimated as radius of a sphere around each Co2+ ion. For a uniform distribution of Co2+ dopants wi ...
... through which the S.S interaction takes place. Generally, it was established that the S.S exchange interaction require R≤ 1.5 a, where a is the lattice parameter of host medium (Seo 2012). R could be estimated as radius of a sphere around each Co2+ ion. For a uniform distribution of Co2+ dopants wi ...
Ceria co-doping: Synergistic or average effect?
... respect to experiment for doped ceria should be in the order of 0.20% [54]. This is borne out by the results presented in Figure 1, which show an excellent agreement with the range of experimental data available in the literature and also with the values calculated using Hong and Virkar’s equation. ...
... respect to experiment for doped ceria should be in the order of 0.20% [54]. This is borne out by the results presented in Figure 1, which show an excellent agreement with the range of experimental data available in the literature and also with the values calculated using Hong and Virkar’s equation. ...
A Chapter 4 Organometallics
... d and f organometallic compounds are particularly sensitive to oxygen and water and this problem is more important for f-elements in view of their larger ionic radii and their lower propensity to form covalent bonds. For f-elements, relativistic effects (see Ch. 1) increase the complexity of theoret ...
... d and f organometallic compounds are particularly sensitive to oxygen and water and this problem is more important for f-elements in view of their larger ionic radii and their lower propensity to form covalent bonds. For f-elements, relativistic effects (see Ch. 1) increase the complexity of theoret ...
Design and Use of Nanostructured Single
... paying attention to the principles of sustainable and green chemistry [1]. Easy separation, easy recovery, no problems in solubility and miscibility are the strengths of a heterogeneous system in order to reduce the cost of production and to set up environmentally benign processes. However, further ...
... paying attention to the principles of sustainable and green chemistry [1]. Easy separation, easy recovery, no problems in solubility and miscibility are the strengths of a heterogeneous system in order to reduce the cost of production and to set up environmentally benign processes. However, further ...
Homogeneous Chromium Catalysts for Olefin Polymerization
... have resulted from many spectroscopic investigations of heterogeneous catalysts combined with extrapolations from the now extensive body of known organometallic structures. However, the relevance of this “deluge of conjecture”[8] is highly questionable. Most of the analytical work utilized IR spectr ...
... have resulted from many spectroscopic investigations of heterogeneous catalysts combined with extrapolations from the now extensive body of known organometallic structures. However, the relevance of this “deluge of conjecture”[8] is highly questionable. Most of the analytical work utilized IR spectr ...
enthalpy changes
... Calculate standard enthalpy changes using bond enthalpy values Calculate standard enthalpy changes using enthalpies of formation and combustion Know simple calorimetry methods for measuring enthalpy changes Calculate enthalpy changes from calorimetry measurements ...
... Calculate standard enthalpy changes using bond enthalpy values Calculate standard enthalpy changes using enthalpies of formation and combustion Know simple calorimetry methods for measuring enthalpy changes Calculate enthalpy changes from calorimetry measurements ...
DELTAHPP
... Calculate standard enthalpy changes using bond enthalpy values Calculate standard enthalpy changes using enthalpies of formation and combustion Know simple calorimetry methods for measuring enthalpy changes Calculate enthalpy changes from calorimetry measurements ...
... Calculate standard enthalpy changes using bond enthalpy values Calculate standard enthalpy changes using enthalpies of formation and combustion Know simple calorimetry methods for measuring enthalpy changes Calculate enthalpy changes from calorimetry measurements ...
deltahpps
... Calculate standard enthalpy changes using bond enthalpy values Calculate standard enthalpy changes using enthalpies of formation and combustion Know simple calorimetry methods for measuring enthalpy changes Calculate enthalpy changes from calorimetry measurements ...
... Calculate standard enthalpy changes using bond enthalpy values Calculate standard enthalpy changes using enthalpies of formation and combustion Know simple calorimetry methods for measuring enthalpy changes Calculate enthalpy changes from calorimetry measurements ...
PDF File
... specificity; reactions with sulfur- or nitrogen-substituted substrates were severely compromised in Mg2⫹ but were stimulated by addition of softer metal ions such as Mn2⫹ (3, 5, 7, 9). A fundamental question that remains unanswered, however, is whether these interactions are mediated by the same or ...
... specificity; reactions with sulfur- or nitrogen-substituted substrates were severely compromised in Mg2⫹ but were stimulated by addition of softer metal ions such as Mn2⫹ (3, 5, 7, 9). A fundamental question that remains unanswered, however, is whether these interactions are mediated by the same or ...
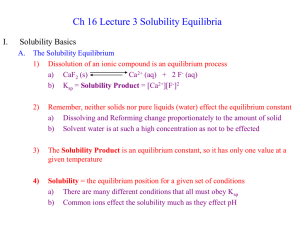
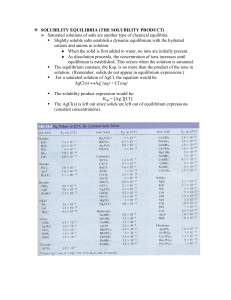
SOLUBILITY EQUILIBRIA
... When a metal ion (a Lewis acid) reacts with a Lewis base, a complex ion can form. The formation of complex ions represents a reversible equilibria situation. A complex ion is a charged species consisting of a metal ion surrounded by ligands. A ligand is typically an anion or neutral molecule ...
... When a metal ion (a Lewis acid) reacts with a Lewis base, a complex ion can form. The formation of complex ions represents a reversible equilibria situation. A complex ion is a charged species consisting of a metal ion surrounded by ligands. A ligand is typically an anion or neutral molecule ...
Preparation and structural characterization of group 1 metal
... resonances at 1.61 and 1.32 ppm with equal intensity in the 1H NMR spectrum, consistent with Cs symmetry for this molecule in solution. The phosphorus donor appears as a broad singlet resonance at 33.80 ppm with the peak-width at half height (Dm1/2) being 68 Hz in toluened8 at room temperature. A va ...
... resonances at 1.61 and 1.32 ppm with equal intensity in the 1H NMR spectrum, consistent with Cs symmetry for this molecule in solution. The phosphorus donor appears as a broad singlet resonance at 33.80 ppm with the peak-width at half height (Dm1/2) being 68 Hz in toluened8 at room temperature. A va ...
Cyanide Geochemistry - University of Manitoba
... • Most often used as it measures the cyanide which would be easily leached in mildly acidic conditions including free cyanide and weakly complexed cyanide (with Cd and Ni). • The WAD technique is least susceptible to interference and overestimation. • There are two methods of analysis: • a) Reflux d ...
... • Most often used as it measures the cyanide which would be easily leached in mildly acidic conditions including free cyanide and weakly complexed cyanide (with Cd and Ni). • The WAD technique is least susceptible to interference and overestimation. • There are two methods of analysis: • a) Reflux d ...
The solid state and solution structures of tin(IV)
... that have been prepared, their physical properties, and molecular complexities are given in Table 1. It is noteworthy that the molecular complexities determined in solution may have been measured under different conditions and therefore may not be strictly comparable. There are also some contradicto ...
... that have been prepared, their physical properties, and molecular complexities are given in Table 1. It is noteworthy that the molecular complexities determined in solution may have been measured under different conditions and therefore may not be strictly comparable. There are also some contradicto ...
Spin crossover

Spin Crossover (SCO), sometimes referred to as spin transition or spin equilibrium behavior, is a phenomenon that occurs in some metal complexes wherein the spin state of the complex changes due to external stimuli such as a variation of temperature, pressure, light irradiation or an influence of a magnetic field.With regard to a ligand field and ligand field theory, the change in spin state is a transition from a low spin (LS) ground state electron configuration to a high spin (HS) ground state electron configuration of the metal’s d atomic orbitals (AOs), or vice versa. The magnitude of the ligand field splitting along with the pairing energy of the complex determines whether it will have a LS or HS electron configuration. A LS state occurs because the ligand field splitting (Δ) is greater than the pairing energy of the complex (which is an unfavorable process).Figure 1 is a simplified illustration of the metal’s d orbital splitting in the presence of an octahedral ligand field. A large splitting between the t2g and eg AOs requires a substantial amount of energy for the electrons to overcome the energy gap (Δ) to comply with Hund’s Rule. Therefore, electrons will fill the lower energy t2g orbitals completely before populating the higher energy eg orbitals. Conversely, a HS state occurs with weaker ligand fields and smaller orbital splitting. In this case the energy required to populate the higher levels is substantially less than the pairing energy and the electrons fill the orbitals according to Hund’s Rule by populating the higher energy orbitals before pairing with electrons in the lower lying orbitals. An example of a metal ion that can exist in either a LS or HS state is Fe3+ in an octahedral ligand field. Depending on the ligands that are coordinated to this complex the Fe3+ can attain a LS or a HS state, as in Figure 1.Spin crossover refers to the transitions between high to low, or low to high, spin states. This phenomenon is commonly observed with some first row transition metal complexes with a d4 through d7 electron configuration in an octahedral ligand geometry. Spin transition curves are a common representation of SCO phenomenon with the most commonly observed types depicted in Figure 2 in which γHS (the high-spin molar fraction) is plotted vs. T. The figure shows a gradual spin transition (left), an abrupt transition with hysteresis (middle) and a two-step transition (right). For a transition to be considered gradual, it typically takes place over a large temperature range, even up to several hundred K, whereas for a transition to be considered abrupt, it should take place within 10 K or less.These curves indicate that a spin transition has occurred in a metal complex as temperature changed. The gradual transition curve is an indication that not all metal centers within the complex are undergoing the transition at the same temperature. The abrupt spin change with hysteresis indicates a strong cooperativity, or “communication”, between neighboring metal complexes. In the latter case, the material is bistable and can exist in the two different spin states with a different range of external stimuli (temperature in this case) for the two phenomena, namely LS → HS and HS → LS. The two-step transition is relatively rare but is observed, for example, with dinuclear SCO complexes for which the spin transition in one metal center renders the transition in the second metal center less favorable.There are several types of spin crossover that can occur in a complex; some of them are light induced excited state spin trapping (LIESST), ligand-driven light induced spin change (LD-LISC), and charge transfer induced spin transition (CTIST).