Transition metal complexes
... to be coordinated with the ion. Simple ligands like water or chlorine form only one link with the central atom and are said to be monodentate. The process of binding to the metal ion with more than one coordination site per ligand is called chelation. Compounds that bind avidly to form complexes are ...
... to be coordinated with the ion. Simple ligands like water or chlorine form only one link with the central atom and are said to be monodentate. The process of binding to the metal ion with more than one coordination site per ligand is called chelation. Compounds that bind avidly to form complexes are ...
Different types of ligands form different bond stabilities with transition
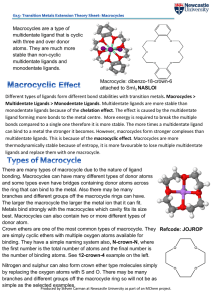
... the ring that can bind to the metal. Also there may be many branches and different groups off the macrocycle rings can have. The larger the macrocycle the larger the metal ion that it can fit. Metals bind strongly with the macrocycles which cavity fits its size best. Macrocycles can also contain two ...
... the ring that can bind to the metal. Also there may be many branches and different groups off the macrocycle rings can have. The larger the macrocycle the larger the metal ion that it can fit. Metals bind strongly with the macrocycles which cavity fits its size best. Macrocycles can also contain two ...
In situ Raman Spectroscopic Study of Supported Molten Salt
... under gas and temperature conditions of practical importance has been a long-sought goal in catalysis (1). In the present study, in-situ Raman spectroscopy at temperatures up to 500oC is used for the first time to identify vanadium species on the surface of a vanadium oxide based supported molten sa ...
... under gas and temperature conditions of practical importance has been a long-sought goal in catalysis (1). In the present study, in-situ Raman spectroscopy at temperatures up to 500oC is used for the first time to identify vanadium species on the surface of a vanadium oxide based supported molten sa ...
Lewis Structures
... The molecules or ions that surround the metal in a complex ion are called ligands. The ligands act like a Lewis Base in that they donate a pair of electrons. A ligand must therefore have at least one unshared pair of electrons. The type of bond between the metal and the ligand is a coordinate covale ...
... The molecules or ions that surround the metal in a complex ion are called ligands. The ligands act like a Lewis Base in that they donate a pair of electrons. A ligand must therefore have at least one unshared pair of electrons. The type of bond between the metal and the ligand is a coordinate covale ...
Lecture 12
... mining operations by grinding up the ore and then suspending it in a dilute solution of CN-, which dissolves the Au on bubbling air through the solution: ...
... mining operations by grinding up the ore and then suspending it in a dilute solution of CN-, which dissolves the Au on bubbling air through the solution: ...
Unit 10 The d-Block Elements
... 12 nearest neighbours. The atomic radius of these elements is relatively small. The d-block metals have therefore much higher melting points than s-block metals, since these small sized atoms are closely-packed in the metal lattice, with 3d and 4s electrons participating in metallic bonding by deloc ...
... 12 nearest neighbours. The atomic radius of these elements is relatively small. The d-block metals have therefore much higher melting points than s-block metals, since these small sized atoms are closely-packed in the metal lattice, with 3d and 4s electrons participating in metallic bonding by deloc ...
Lecture 12 –Octahedral Substitution Reactions
... in a substitution reaction is the change in d-orbital energy on going from the ground state of the complex to the transition state. ...
... in a substitution reaction is the change in d-orbital energy on going from the ground state of the complex to the transition state. ...
1 " A Mixed-Metal Nitrido Carbonyl Cluster Compound. Synthesis
... C O groups are 2.01 and 1.18 A, respectively. Crystals of the mixed salt [PtRhloN(CO),,](Cs)[N(CH3)4]2 The anion possesses 150 valence electrons, corresponding to 75 which are well suited for X-ray analysis7 were obtained together cluster valence molecular orbitals. The hcp cluster illustrated in wi ...
... C O groups are 2.01 and 1.18 A, respectively. Crystals of the mixed salt [PtRhloN(CO),,](Cs)[N(CH3)4]2 The anion possesses 150 valence electrons, corresponding to 75 which are well suited for X-ray analysis7 were obtained together cluster valence molecular orbitals. The hcp cluster illustrated in wi ...
CHM 423 Coordination Chemistry
... chemical bond called coordinate covalent bond involves donation of electron pair(s) by a molecule or negatively charged ion, a Lewis base, to a neutral metal or positively charged ion, a Lewis acid. These compounds are known, from spectroscopic studies, to exist in various structures based on the nu ...
... chemical bond called coordinate covalent bond involves donation of electron pair(s) by a molecule or negatively charged ion, a Lewis base, to a neutral metal or positively charged ion, a Lewis acid. These compounds are known, from spectroscopic studies, to exist in various structures based on the nu ...
Surface Facet of Palladium Nanocrystals
... standing on the generation process of singlet O2 with metal nanoparticles and lead to the capability of designing optimal nanocatalysts for related organic reactions. In this article, we first employ single-facet palladium (Pd) nanocrystals as a model system to investigate the detailed mechanisms. We ...
... standing on the generation process of singlet O2 with metal nanoparticles and lead to the capability of designing optimal nanocatalysts for related organic reactions. In this article, we first employ single-facet palladium (Pd) nanocrystals as a model system to investigate the detailed mechanisms. We ...
Roshal, A.V. Grigorovich, A.O. Doroshenko, V.G. Pivovarenko, A.P.
... presence of water. In the studies of complex formation we used the anhydrous barium perchlorate from Aldrich and dehydrated magnesium perchlorate obtained by roasting of trihydrate sample at 215 °C and 0.15 mmHg pressure during 3 h.18 The quality of dehydration was controlled gravimetrically. Spectr ...
... presence of water. In the studies of complex formation we used the anhydrous barium perchlorate from Aldrich and dehydrated magnesium perchlorate obtained by roasting of trihydrate sample at 215 °C and 0.15 mmHg pressure during 3 h.18 The quality of dehydration was controlled gravimetrically. Spectr ...
Lewis Base Ligands
... One possible exception to the 2e- donor “rule” when they are coordinating to a single metal center is for iodide. It is the least electronegative of the common halides (not counting astatine) and is the best donor group. This is some evidence that iodide is a good enough donor and has enough orbital ...
... One possible exception to the 2e- donor “rule” when they are coordinating to a single metal center is for iodide. It is the least electronegative of the common halides (not counting astatine) and is the best donor group. This is some evidence that iodide is a good enough donor and has enough orbital ...
Compounds
... ▫ Have to look at __________________ ▫ Remember most atoms are stable with ___ ▫ Common exceptions H, He, Li, and Be can be stable with 2 B is stable with 6 Elements with d orbitals (can have more than 8) ...
... ▫ Have to look at __________________ ▫ Remember most atoms are stable with ___ ▫ Common exceptions H, He, Li, and Be can be stable with 2 B is stable with 6 Elements with d orbitals (can have more than 8) ...
Spin crossover

Spin Crossover (SCO), sometimes referred to as spin transition or spin equilibrium behavior, is a phenomenon that occurs in some metal complexes wherein the spin state of the complex changes due to external stimuli such as a variation of temperature, pressure, light irradiation or an influence of a magnetic field.With regard to a ligand field and ligand field theory, the change in spin state is a transition from a low spin (LS) ground state electron configuration to a high spin (HS) ground state electron configuration of the metal’s d atomic orbitals (AOs), or vice versa. The magnitude of the ligand field splitting along with the pairing energy of the complex determines whether it will have a LS or HS electron configuration. A LS state occurs because the ligand field splitting (Δ) is greater than the pairing energy of the complex (which is an unfavorable process).Figure 1 is a simplified illustration of the metal’s d orbital splitting in the presence of an octahedral ligand field. A large splitting between the t2g and eg AOs requires a substantial amount of energy for the electrons to overcome the energy gap (Δ) to comply with Hund’s Rule. Therefore, electrons will fill the lower energy t2g orbitals completely before populating the higher energy eg orbitals. Conversely, a HS state occurs with weaker ligand fields and smaller orbital splitting. In this case the energy required to populate the higher levels is substantially less than the pairing energy and the electrons fill the orbitals according to Hund’s Rule by populating the higher energy orbitals before pairing with electrons in the lower lying orbitals. An example of a metal ion that can exist in either a LS or HS state is Fe3+ in an octahedral ligand field. Depending on the ligands that are coordinated to this complex the Fe3+ can attain a LS or a HS state, as in Figure 1.Spin crossover refers to the transitions between high to low, or low to high, spin states. This phenomenon is commonly observed with some first row transition metal complexes with a d4 through d7 electron configuration in an octahedral ligand geometry. Spin transition curves are a common representation of SCO phenomenon with the most commonly observed types depicted in Figure 2 in which γHS (the high-spin molar fraction) is plotted vs. T. The figure shows a gradual spin transition (left), an abrupt transition with hysteresis (middle) and a two-step transition (right). For a transition to be considered gradual, it typically takes place over a large temperature range, even up to several hundred K, whereas for a transition to be considered abrupt, it should take place within 10 K or less.These curves indicate that a spin transition has occurred in a metal complex as temperature changed. The gradual transition curve is an indication that not all metal centers within the complex are undergoing the transition at the same temperature. The abrupt spin change with hysteresis indicates a strong cooperativity, or “communication”, between neighboring metal complexes. In the latter case, the material is bistable and can exist in the two different spin states with a different range of external stimuli (temperature in this case) for the two phenomena, namely LS → HS and HS → LS. The two-step transition is relatively rare but is observed, for example, with dinuclear SCO complexes for which the spin transition in one metal center renders the transition in the second metal center less favorable.There are several types of spin crossover that can occur in a complex; some of them are light induced excited state spin trapping (LIESST), ligand-driven light induced spin change (LD-LISC), and charge transfer induced spin transition (CTIST).