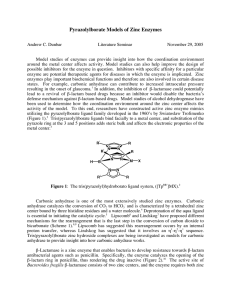
Full text - SG
... solvatochromic behavior of the metal-to ligand charge transfer transitions. Atomic orbital contributions to molecular orbitals can be used very effectively to probe the nature of electronic transitions and determine their charge transfer character. Keywords: Time-dependent density-functional respons ...
... solvatochromic behavior of the metal-to ligand charge transfer transitions. Atomic orbital contributions to molecular orbitals can be used very effectively to probe the nature of electronic transitions and determine their charge transfer character. Keywords: Time-dependent density-functional respons ...
The 16 and 18 Electron Rule in Organometallic Chemistry and
... joined. With less electronegative olefins, such as C,H4 or C2F4, it may be more convenient to regard their co-ordination as a Lewis base addition rather than as an oxidative addition. The real extent of electron transfer must be determined by ESCA or some other means. The count of metal valence elec ...
... joined. With less electronegative olefins, such as C,H4 or C2F4, it may be more convenient to regard their co-ordination as a Lewis base addition rather than as an oxidative addition. The real extent of electron transfer must be determined by ESCA or some other means. The count of metal valence elec ...
Orbitals - faculty at Chemeketa
... Atoms are most stable if they have a filled or empty outer layer of electrons. Except for H and He, a filled layer contains 8 electrons - an octet. Atoms gain, lose or share electrons to make a filled or empty outer layer. Atoms gain, lose or share electrons based ...
... Atoms are most stable if they have a filled or empty outer layer of electrons. Except for H and He, a filled layer contains 8 electrons - an octet. Atoms gain, lose or share electrons to make a filled or empty outer layer. Atoms gain, lose or share electrons based ...
Complex Ion Equilibria - South Kingstown High School
... Fractional precipitation is the technique of ...
... Fractional precipitation is the technique of ...
Phage display - Miltenyi Biotec
... filamentous bacteriophages, "phage display", has become a cornerstone of techniques to investigate molecular interactions. Phage display is used: - to identify and analyze features of surface proteins that interact with other proteins. - to isolate new ligand that bind to particular amino acid sequen ...
... filamentous bacteriophages, "phage display", has become a cornerstone of techniques to investigate molecular interactions. Phage display is used: - to identify and analyze features of surface proteins that interact with other proteins. - to isolate new ligand that bind to particular amino acid sequen ...
Substituent Effect in the γ–Position of Acetylacetonate on the
... the d-d absorption band of the complexes to lower wave numbers with increasing its values. The statistical evaluations of the data (R, S. E., F-test, Q2 and PRESS/SSY) also confirm the suggested parameter. All complexes show good crossvalidation values (Q2 > 0.70; Q2 = 0.72 - 0. 92). This phenomenon ...
... the d-d absorption band of the complexes to lower wave numbers with increasing its values. The statistical evaluations of the data (R, S. E., F-test, Q2 and PRESS/SSY) also confirm the suggested parameter. All complexes show good crossvalidation values (Q2 > 0.70; Q2 = 0.72 - 0. 92). This phenomenon ...
Complexes of the Group 5 Elements
... the red-brown, diamagnetic V2 complex is transformed to a dark-green, paramagnetic complex with a V23+ core. The compound is extremely air-sensitive and must be crystallized quickly at temperatures below -10 °C. Otherwise it reverts to the triply-bonded diamagnetic species. An X-ray study reveals th ...
... the red-brown, diamagnetic V2 complex is transformed to a dark-green, paramagnetic complex with a V23+ core. The compound is extremely air-sensitive and must be crystallized quickly at temperatures below -10 °C. Otherwise it reverts to the triply-bonded diamagnetic species. An X-ray study reveals th ...
Introduction - University of Pretoria
... form LnM+-CR2¯ can explain the experimental observations that these compounds react mostly as nucleophiles. A partial negative charge resides on the carbene carbon atom as a result of polarization of shared electrons between an electropositive metal and a more electronegative carbene carbon atom. Th ...
... form LnM+-CR2¯ can explain the experimental observations that these compounds react mostly as nucleophiles. A partial negative charge resides on the carbene carbon atom as a result of polarization of shared electrons between an electropositive metal and a more electronegative carbene carbon atom. Th ...
Sabina4_V10 - Universidade de Vigo
... spectroscopic studies (vide infra) suggest that the replacement of the water present in the as-synthesized compounds by DMSO in the single crystals did not lead to significant modifications in the coordinative characteristics of the metal-ligand core. The IR spectra of the complexes provide informat ...
... spectroscopic studies (vide infra) suggest that the replacement of the water present in the as-synthesized compounds by DMSO in the single crystals did not lead to significant modifications in the coordinative characteristics of the metal-ligand core. The IR spectra of the complexes provide informat ...
Theoretical Study of Structural and Optical Properties of
... model for the description of the extended MgO environment. As model peptide we have chosen CysTrp since the cysteine residue interacts strongly with metal particles through the sulphur atom and tryptophan is the most important chromophoric aminoacid. Our results show that in the case of CysTrp bound ...
... model for the description of the extended MgO environment. As model peptide we have chosen CysTrp since the cysteine residue interacts strongly with metal particles through the sulphur atom and tryptophan is the most important chromophoric aminoacid. Our results show that in the case of CysTrp bound ...
Degradation of bidentate coordinated platinum(II)
... phenanthroline)(ethylenediamine)platinum(II)]2+), with reduced L-glutathione and L-methionine. Both ...
... phenanthroline)(ethylenediamine)platinum(II)]2+), with reduced L-glutathione and L-methionine. Both ...
Material properties and microstructure from
... volatiles, Cu-chloride complexes are predicted to be dominant, with the exception of sulfur-rich alkaline magmas. In silicate melts, Cu dissolves into the oxide matrix and its solubility is only moderately increased by the presence of S and Cl in concentrations typical of natural systems. Both incre ...
... volatiles, Cu-chloride complexes are predicted to be dominant, with the exception of sulfur-rich alkaline magmas. In silicate melts, Cu dissolves into the oxide matrix and its solubility is only moderately increased by the presence of S and Cl in concentrations typical of natural systems. Both incre ...
Design and Synthesis of a Thermally Stable Organic Electride
... serve to isolate the cations from electrons trapped in intermolecular cavities and channels.1-7 Electrides provide unique examples of low-density electron gases confined to cavities and channels of known geometry, which makes them related to both salts and plasmas. Therefore, they are of interest in ...
... serve to isolate the cations from electrons trapped in intermolecular cavities and channels.1-7 Electrides provide unique examples of low-density electron gases confined to cavities and channels of known geometry, which makes them related to both salts and plasmas. Therefore, they are of interest in ...
Speciation in Metal Toxicity and Metal-Based Therapeutics
... ion is found in a number of foods and beverages. Thus, accidental ingestion of up to 2.5 g Ni2+ as NiCl2 and NiSO4 in drinking water produced only mild and transient effects [3]. Solid evidence that ingestion of these salts leads to cancer is lacking. On the other hand, in experimental animals, -tr ...
... ion is found in a number of foods and beverages. Thus, accidental ingestion of up to 2.5 g Ni2+ as NiCl2 and NiSO4 in drinking water produced only mild and transient effects [3]. Solid evidence that ingestion of these salts leads to cancer is lacking. On the other hand, in experimental animals, -tr ...
module 1: metal carbonyls
... Figure: Formation of M → CO bond by back donation in metal carbonyls. Bridging CO groups: In addition to the linear M-C-O groups, the carbon monoxide ligand is also known to form bridges. This type of bonding is observed in some binuclear and polynuclear carbonyls. It is denoted by µn–CO, where n ...
... Figure: Formation of M → CO bond by back donation in metal carbonyls. Bridging CO groups: In addition to the linear M-C-O groups, the carbon monoxide ligand is also known to form bridges. This type of bonding is observed in some binuclear and polynuclear carbonyls. It is denoted by µn–CO, where n ...
Spin crossover

Spin Crossover (SCO), sometimes referred to as spin transition or spin equilibrium behavior, is a phenomenon that occurs in some metal complexes wherein the spin state of the complex changes due to external stimuli such as a variation of temperature, pressure, light irradiation or an influence of a magnetic field.With regard to a ligand field and ligand field theory, the change in spin state is a transition from a low spin (LS) ground state electron configuration to a high spin (HS) ground state electron configuration of the metal’s d atomic orbitals (AOs), or vice versa. The magnitude of the ligand field splitting along with the pairing energy of the complex determines whether it will have a LS or HS electron configuration. A LS state occurs because the ligand field splitting (Δ) is greater than the pairing energy of the complex (which is an unfavorable process).Figure 1 is a simplified illustration of the metal’s d orbital splitting in the presence of an octahedral ligand field. A large splitting between the t2g and eg AOs requires a substantial amount of energy for the electrons to overcome the energy gap (Δ) to comply with Hund’s Rule. Therefore, electrons will fill the lower energy t2g orbitals completely before populating the higher energy eg orbitals. Conversely, a HS state occurs with weaker ligand fields and smaller orbital splitting. In this case the energy required to populate the higher levels is substantially less than the pairing energy and the electrons fill the orbitals according to Hund’s Rule by populating the higher energy orbitals before pairing with electrons in the lower lying orbitals. An example of a metal ion that can exist in either a LS or HS state is Fe3+ in an octahedral ligand field. Depending on the ligands that are coordinated to this complex the Fe3+ can attain a LS or a HS state, as in Figure 1.Spin crossover refers to the transitions between high to low, or low to high, spin states. This phenomenon is commonly observed with some first row transition metal complexes with a d4 through d7 electron configuration in an octahedral ligand geometry. Spin transition curves are a common representation of SCO phenomenon with the most commonly observed types depicted in Figure 2 in which γHS (the high-spin molar fraction) is plotted vs. T. The figure shows a gradual spin transition (left), an abrupt transition with hysteresis (middle) and a two-step transition (right). For a transition to be considered gradual, it typically takes place over a large temperature range, even up to several hundred K, whereas for a transition to be considered abrupt, it should take place within 10 K or less.These curves indicate that a spin transition has occurred in a metal complex as temperature changed. The gradual transition curve is an indication that not all metal centers within the complex are undergoing the transition at the same temperature. The abrupt spin change with hysteresis indicates a strong cooperativity, or “communication”, between neighboring metal complexes. In the latter case, the material is bistable and can exist in the two different spin states with a different range of external stimuli (temperature in this case) for the two phenomena, namely LS → HS and HS → LS. The two-step transition is relatively rare but is observed, for example, with dinuclear SCO complexes for which the spin transition in one metal center renders the transition in the second metal center less favorable.There are several types of spin crossover that can occur in a complex; some of them are light induced excited state spin trapping (LIESST), ligand-driven light induced spin change (LD-LISC), and charge transfer induced spin transition (CTIST).