
Supporting Information - Royal Society of Chemistry
... Figure S2. Changes in the absorption maxima are plotted against the ratio of enzyme to complex 3. The dotted line is connecting the data points; it is not a fitted curve. Inhibition data for the complexes: For determining the Ki values of complexes 2-4, the concentrations of different compounds requ ...
... Figure S2. Changes in the absorption maxima are plotted against the ratio of enzyme to complex 3. The dotted line is connecting the data points; it is not a fitted curve. Inhibition data for the complexes: For determining the Ki values of complexes 2-4, the concentrations of different compounds requ ...
Document
... [(arene)RuCl2]2 and pta [13-15]. Half-sandwich Ru(II)-pta complexes with the general name RAPTA are subject to scrutiny not only because of their catalytic effect but also of their anticancer activity [16]. N-Alkyl derivatives of pta can also be used as ligands in half-sandwich Ru-complexes [15, 17] ...
... [(arene)RuCl2]2 and pta [13-15]. Half-sandwich Ru(II)-pta complexes with the general name RAPTA are subject to scrutiny not only because of their catalytic effect but also of their anticancer activity [16]. N-Alkyl derivatives of pta can also be used as ligands in half-sandwich Ru-complexes [15, 17] ...
M.Sc. Chemistry - Manonmaniam Sundaranar University
... diagrams – Electronic spectra of Ist row transition metal complexes -Evaluation of 10 Dq, β and B‟ for octahedral d2 and d8 systems. - Charge transfer spectra - types - difference from d-d spectra- Tetragonal distortion (Jahn-Teller distortion) from octahedral symmetry and its effect on Page 5 of 15 ...
... diagrams – Electronic spectra of Ist row transition metal complexes -Evaluation of 10 Dq, β and B‟ for octahedral d2 and d8 systems. - Charge transfer spectra - types - difference from d-d spectra- Tetragonal distortion (Jahn-Teller distortion) from octahedral symmetry and its effect on Page 5 of 15 ...
Hydrogen bonding in thiobenzamide synthon and its Cadmium
... The environment around the metal atoms may be described as distorted octahedral geometry with four chloride atoms (Cl2, Cl2i , Cl1ii and Cl1iii ) in the equatorial plane and sulfur atom of the TBA ligand and another chloride atom (Cl1) in the axial position (equivalent position code: i = x-1, y, z; ...
... The environment around the metal atoms may be described as distorted octahedral geometry with four chloride atoms (Cl2, Cl2i , Cl1ii and Cl1iii ) in the equatorial plane and sulfur atom of the TBA ligand and another chloride atom (Cl1) in the axial position (equivalent position code: i = x-1, y, z; ...
view - The Long Group - University of California, Berkeley
... determined by single-crystal X-ray analysis. The former consists of an expanded Prussian blue type framework with [Re6S8]2+ and [Co2(µ-OH2)2]4+ cluster cores occupying alternate metal ion sites, and features cubelike cages enclosing water-filled cavities approximately 258 Å3 in volume. The latter st ...
... determined by single-crystal X-ray analysis. The former consists of an expanded Prussian blue type framework with [Re6S8]2+ and [Co2(µ-OH2)2]4+ cluster cores occupying alternate metal ion sites, and features cubelike cages enclosing water-filled cavities approximately 258 Å3 in volume. The latter st ...
From the Metal to the Molecule
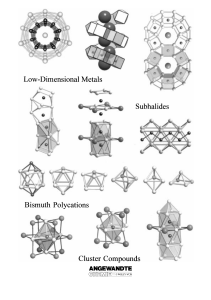
... Mostly, it is found to be more convenient to use intermetallic phases or metal halides as starting materials. In some cases, it is necessary to add auxiliary reagents, such as niobium halides, which modify the partial pressures in the gas phase through various equilibrium processes but are not incor ...
... Mostly, it is found to be more convenient to use intermetallic phases or metal halides as starting materials. In some cases, it is necessary to add auxiliary reagents, such as niobium halides, which modify the partial pressures in the gas phase through various equilibrium processes but are not incor ...
Metal clusters inside out
... As long as the closed electronic configuration is preserved, the compounds are still semiconducting; however, electron deficiency may lead to electronic delocalization between clusters and metallic properties via charge transfer through appropriate ligands. Chevrel phases and the various phases based ...
... As long as the closed electronic configuration is preserved, the compounds are still semiconducting; however, electron deficiency may lead to electronic delocalization between clusters and metallic properties via charge transfer through appropriate ligands. Chevrel phases and the various phases based ...
Extremely Bulky Amido d-Block Metal(II) Halide Complexes
... valent amido iron(II) chloride complex [FeCl{N(R)(Ar#)}(tmeda)] [5] 2-01 (R = C (CD3)2CH3, Ar# = 2,5-FMeC6H3). The complex is stabilized by a bulky amide ligand, along with a molecule of chelating tetramethylethylenediamine (tmeda) coordinating to the iron centre. Complex 2-01 was prepared by a salt ...
... valent amido iron(II) chloride complex [FeCl{N(R)(Ar#)}(tmeda)] [5] 2-01 (R = C (CD3)2CH3, Ar# = 2,5-FMeC6H3). The complex is stabilized by a bulky amide ligand, along with a molecule of chelating tetramethylethylenediamine (tmeda) coordinating to the iron centre. Complex 2-01 was prepared by a salt ...
The role of bivalent metals in hydroxyapatite structures as revealed
... stretching vibrations and it is presumed that the surface of expansion exerts a destructive effect on the symmetry and structure of growing crystals.22 Expansion takes place near the surface of the polarized layer containing deformed channels with OH⫺ groups and deformed tetrahedral molecules of pho ...
... stretching vibrations and it is presumed that the surface of expansion exerts a destructive effect on the symmetry and structure of growing crystals.22 Expansion takes place near the surface of the polarized layer containing deformed channels with OH⫺ groups and deformed tetrahedral molecules of pho ...
P/S ligands derived from carbohydrates in Rh-catalyzed
... three decades, there are still significant problems which remain unresolved, so reducing its impact in the arena of fine chemicals synthesis.6 One of the main reasons for this scenario is that the catalyst precursors are generally relatively expensive complex molecules obtained through a multistep syn ...
... three decades, there are still significant problems which remain unresolved, so reducing its impact in the arena of fine chemicals synthesis.6 One of the main reasons for this scenario is that the catalyst precursors are generally relatively expensive complex molecules obtained through a multistep syn ...
c00kieee - Ritter Illustration
... containing this highly radioactive material is isolated and analyzed by X-ray analysis, the intensity of the diffraction from the crystal has been observed to decrease with time, presumably as the crystal lattice is damaged. In the extreme, a visible change can occur where an originally clear crysta ...
... containing this highly radioactive material is isolated and analyzed by X-ray analysis, the intensity of the diffraction from the crystal has been observed to decrease with time, presumably as the crystal lattice is damaged. In the extreme, a visible change can occur where an originally clear crysta ...
Imidazole-Based [2 + 1] Re(I)/99mTc(I
... bipyridine and a series of imidazole derivatives were investigated as a means of identifying complexes suitable for creating targeted isostructural optical/nuclear molecular imaging probes. To prepare the desired complexes, [Re(CO)3(H2O)3]Br was combined with 2,2′-bipyridine (bipy) to give [Re(CO)3( ...
... bipyridine and a series of imidazole derivatives were investigated as a means of identifying complexes suitable for creating targeted isostructural optical/nuclear molecular imaging probes. To prepare the desired complexes, [Re(CO)3(H2O)3]Br was combined with 2,2′-bipyridine (bipy) to give [Re(CO)3( ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC)
... DMSO.The complexes were insoluble in alcohol, water and DMF. All the complexes showed a non-electrolytic nature with a molar conductance in the range 1-2ohm-1 cm-2 mol -1.The elemental analysis confirm the proposed composition Table-1. The abbreviations gly, ala, phenala, met, tyr and cys represent ...
... DMSO.The complexes were insoluble in alcohol, water and DMF. All the complexes showed a non-electrolytic nature with a molar conductance in the range 1-2ohm-1 cm-2 mol -1.The elemental analysis confirm the proposed composition Table-1. The abbreviations gly, ala, phenala, met, tyr and cys represent ...
Aron Janine 1986
... coenzyme, adenosylcobalamin, and in methyl, ethyl and cyclobutylcobalamins have been determined in aqueous solution at 96 °C. The t!£ values increase (rates decrease) in the following ligand order: ethyl (ca. 9 min) < cyclobutyl (ca. 75 min) < adeno^yl (c*». '80 min) < methy) (ca. 80 hrs). These val ...
... coenzyme, adenosylcobalamin, and in methyl, ethyl and cyclobutylcobalamins have been determined in aqueous solution at 96 °C. The t!£ values increase (rates decrease) in the following ligand order: ethyl (ca. 9 min) < cyclobutyl (ca. 75 min) < adeno^yl (c*». '80 min) < methy) (ca. 80 hrs). These val ...
Spin crossover

Spin Crossover (SCO), sometimes referred to as spin transition or spin equilibrium behavior, is a phenomenon that occurs in some metal complexes wherein the spin state of the complex changes due to external stimuli such as a variation of temperature, pressure, light irradiation or an influence of a magnetic field.With regard to a ligand field and ligand field theory, the change in spin state is a transition from a low spin (LS) ground state electron configuration to a high spin (HS) ground state electron configuration of the metal’s d atomic orbitals (AOs), or vice versa. The magnitude of the ligand field splitting along with the pairing energy of the complex determines whether it will have a LS or HS electron configuration. A LS state occurs because the ligand field splitting (Δ) is greater than the pairing energy of the complex (which is an unfavorable process).Figure 1 is a simplified illustration of the metal’s d orbital splitting in the presence of an octahedral ligand field. A large splitting between the t2g and eg AOs requires a substantial amount of energy for the electrons to overcome the energy gap (Δ) to comply with Hund’s Rule. Therefore, electrons will fill the lower energy t2g orbitals completely before populating the higher energy eg orbitals. Conversely, a HS state occurs with weaker ligand fields and smaller orbital splitting. In this case the energy required to populate the higher levels is substantially less than the pairing energy and the electrons fill the orbitals according to Hund’s Rule by populating the higher energy orbitals before pairing with electrons in the lower lying orbitals. An example of a metal ion that can exist in either a LS or HS state is Fe3+ in an octahedral ligand field. Depending on the ligands that are coordinated to this complex the Fe3+ can attain a LS or a HS state, as in Figure 1.Spin crossover refers to the transitions between high to low, or low to high, spin states. This phenomenon is commonly observed with some first row transition metal complexes with a d4 through d7 electron configuration in an octahedral ligand geometry. Spin transition curves are a common representation of SCO phenomenon with the most commonly observed types depicted in Figure 2 in which γHS (the high-spin molar fraction) is plotted vs. T. The figure shows a gradual spin transition (left), an abrupt transition with hysteresis (middle) and a two-step transition (right). For a transition to be considered gradual, it typically takes place over a large temperature range, even up to several hundred K, whereas for a transition to be considered abrupt, it should take place within 10 K or less.These curves indicate that a spin transition has occurred in a metal complex as temperature changed. The gradual transition curve is an indication that not all metal centers within the complex are undergoing the transition at the same temperature. The abrupt spin change with hysteresis indicates a strong cooperativity, or “communication”, between neighboring metal complexes. In the latter case, the material is bistable and can exist in the two different spin states with a different range of external stimuli (temperature in this case) for the two phenomena, namely LS → HS and HS → LS. The two-step transition is relatively rare but is observed, for example, with dinuclear SCO complexes for which the spin transition in one metal center renders the transition in the second metal center less favorable.There are several types of spin crossover that can occur in a complex; some of them are light induced excited state spin trapping (LIESST), ligand-driven light induced spin change (LD-LISC), and charge transfer induced spin transition (CTIST).



















![Imidazole-Based [2 + 1] Re(I)/99mTc(I](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016453198_1-7284afe0756f420c3d5e168652a9a305-300x300.png)

