Inorganic Chemistry 2 (033021) - Inorganic Reaction
... The second reaction involves Co(III), d6, t2g and Co(II) d7 t2g eg ; so the electron is transferred from t2g on one metal ion to eg on the other. Since eg electrons are M-L σ-antibonding, the two species will have markedly different radii, so there will be a large contribution to the activation ener ...
... The second reaction involves Co(III), d6, t2g and Co(II) d7 t2g eg ; so the electron is transferred from t2g on one metal ion to eg on the other. Since eg electrons are M-L σ-antibonding, the two species will have markedly different radii, so there will be a large contribution to the activation ener ...
Under sulfur`s spell
... crown-shaped ring S8, but elemental sulfur also contains small amounts of the brightyellow S7 and tiny amounts of other rings. On heating, sulfur readily converts to a metastable one-dimensional elastomer, which quickly degrades at room temperature back to the S8 form. The tendency of sulfur to form ...
... crown-shaped ring S8, but elemental sulfur also contains small amounts of the brightyellow S7 and tiny amounts of other rings. On heating, sulfur readily converts to a metastable one-dimensional elastomer, which quickly degrades at room temperature back to the S8 form. The tendency of sulfur to form ...
Long-Living Light-Emitting Electrochemical Cells - Control
... the maximum luminance (t1/2), or as the total photon flux emitted up to the time the luminance reaches 1/5th of the maximum value (t1/5) for a cell area of 3 mm2.[6,15] In this particular device, due to the continuous increase of the luminance after the rapid switch-on up to 650 hours the first figu ...
... the maximum luminance (t1/2), or as the total photon flux emitted up to the time the luminance reaches 1/5th of the maximum value (t1/5) for a cell area of 3 mm2.[6,15] In this particular device, due to the continuous increase of the luminance after the rapid switch-on up to 650 hours the first figu ...
TERMS AND DEFINITIONS IN THERMOCHEMISTRY
... enthalpy change does not depend on the path chosen to accomplish the process, but only on the initial and final states involved. It is another statement of the law of conservation of energy. For example copper can be converted directly to copper(II) oxide by heating in oxygen. Copper(II) oxide may a ...
... enthalpy change does not depend on the path chosen to accomplish the process, but only on the initial and final states involved. It is another statement of the law of conservation of energy. For example copper can be converted directly to copper(II) oxide by heating in oxygen. Copper(II) oxide may a ...
01-43 chimica.qxd
... centre and favour reactions with olefins while blocking observed in the late 1950’s when chemists at DuPont, bimolecular decompositions. The design of tetrahedral Standard Oil, and Phillips Petroleum reported the Mo(VI) and W(VI) complexes that contain an alkylidene metathesis of propene with cataly ...
... centre and favour reactions with olefins while blocking observed in the late 1950’s when chemists at DuPont, bimolecular decompositions. The design of tetrahedral Standard Oil, and Phillips Petroleum reported the Mo(VI) and W(VI) complexes that contain an alkylidene metathesis of propene with cataly ...
1. General introduction 1.1 Organometallic chemistry and homogeneous catalysis
... claimed to be the most appropriate because of its combination of bulkiness and low coordinating ability.40,76 For this anion, multinuclear NMR studies showed the weakest contacts with the cationic part of the catalysts.76 Preformed catalysts containing one40 or two molecules of chelating ligand77 ha ...
... claimed to be the most appropriate because of its combination of bulkiness and low coordinating ability.40,76 For this anion, multinuclear NMR studies showed the weakest contacts with the cationic part of the catalysts.76 Preformed catalysts containing one40 or two molecules of chelating ligand77 ha ...
1 - American Chemical Society
... pendicular, have a some what lower ground state and/or higher excited state. On the other hand, the excited state of Cu(c) with two neighboring sulfur atoms, which have their aryl groups parallel, is lower (and/or the ground state is higher) because the electron rmulsion is changed into an attractin ...
... pendicular, have a some what lower ground state and/or higher excited state. On the other hand, the excited state of Cu(c) with two neighboring sulfur atoms, which have their aryl groups parallel, is lower (and/or the ground state is higher) because the electron rmulsion is changed into an attractin ...
Therapeutic iron chelators and their potential side
... Unfortunately many ligands which possess a high affinity for iron(II1) also have high affinities for other metals. Aminocarboxylate ligands such as DTPA, used in patients who develop toxic side-effects with D F O due to its relative lack of selectivity for iron(III), lead t o zinc depletion. In an a ...
... Unfortunately many ligands which possess a high affinity for iron(II1) also have high affinities for other metals. Aminocarboxylate ligands such as DTPA, used in patients who develop toxic side-effects with D F O due to its relative lack of selectivity for iron(III), lead t o zinc depletion. In an a ...
Metal Fluorides: Tools for Structural and Computational Analysis of
... monoester, illustrated for adenosine 50 -phosphate, AMP. The addition of a second phosphoryl group to a terminal oxygen generates a pyrophosphate monoester, illustrated for adenosine 50 -diphosphate, ADP; and capture of a third phosphoryl group gives adenosine 50 -triphosphate, ATP (Scheme 2). Strin ...
... monoester, illustrated for adenosine 50 -phosphate, AMP. The addition of a second phosphoryl group to a terminal oxygen generates a pyrophosphate monoester, illustrated for adenosine 50 -diphosphate, ADP; and capture of a third phosphoryl group gives adenosine 50 -triphosphate, ATP (Scheme 2). Strin ...
glossary of terms used in theoretical organic chemistry
... consistence. Although theoretical organic chemistry cannot be separated from theoretical chemistry itself, it constitutes a signi®cant part of the latter representing the domain of physical organic chemistry associated with theoretical modeling of reaction mechanisms, computational studies of struct ...
... consistence. Although theoretical organic chemistry cannot be separated from theoretical chemistry itself, it constitutes a signi®cant part of the latter representing the domain of physical organic chemistry associated with theoretical modeling of reaction mechanisms, computational studies of struct ...
Advances in f-element cyanide chemistry
... revealed by 1H NMR spectroscopy.58 Comparison of the crystal structures of [NnBu4]2[MIII(Cp*)2(CN)3] (M = Ce, U) shows that the U–C(Cp*) and U–C(CN) distances are shorter, by 0.02–0.03 Å, than the Ce–C(Cp*) and Ce–C(CN) distances, while the ionic radius of uranium(III) is ∼0.02 Å larger than that of ...
... revealed by 1H NMR spectroscopy.58 Comparison of the crystal structures of [NnBu4]2[MIII(Cp*)2(CN)3] (M = Ce, U) shows that the U–C(Cp*) and U–C(CN) distances are shorter, by 0.02–0.03 Å, than the Ce–C(Cp*) and Ce–C(CN) distances, while the ionic radius of uranium(III) is ∼0.02 Å larger than that of ...
Naphtyl-imidazo-anthraquinones as novel colorimetric
... Compound 1 exhibited an absorption band at 422 nm and a yellow colour in acetonitrile solution. Upon addition of increasing amount of fluoride, this band progressively decreased while a new absorption band at 493 nm increased in intensity (Δλ= 71 nm) (Figure 2A). A clearly visible colour modulation ...
... Compound 1 exhibited an absorption band at 422 nm and a yellow colour in acetonitrile solution. Upon addition of increasing amount of fluoride, this band progressively decreased while a new absorption band at 493 nm increased in intensity (Δλ= 71 nm) (Figure 2A). A clearly visible colour modulation ...
6149.pdf
... When complex formation is performed starting from nitrate, it is called complexation. When complexation is carried out using oxide as feed, it involves ionisation in addition to complexation and is referred as direct in situ complexation. The procedure for dissolution of TTA is established first as S ...
... When complex formation is performed starting from nitrate, it is called complexation. When complexation is carried out using oxide as feed, it involves ionisation in addition to complexation and is referred as direct in situ complexation. The procedure for dissolution of TTA is established first as S ...
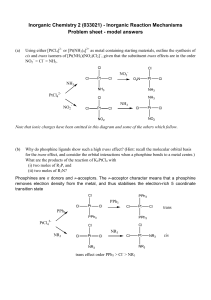
-108- Chapter 7 Answers to Problems 7.1 In I all d orbitals transform
... orbitals in the CFT model (cf. problem 7.2 a). Electron pairs contributed by ligands are sufficient to fill all lower levels. Therefore, any electrons contributed by the metal ion result in filling in the upper three levels in the same manner as predicted in the CFT model. ...
... orbitals in the CFT model (cf. problem 7.2 a). Electron pairs contributed by ligands are sufficient to fill all lower levels. Therefore, any electrons contributed by the metal ion result in filling in the upper three levels in the same manner as predicted in the CFT model. ...
Polyamide from lactams by reactive rotational molding via anionic
... went up. In-situ monitoring of polymerization and crystallization by rheology and DSC The monitoring of the change in crystallinity of the APA6 material during the reaction is shown in Figures 6 and 7. By combining the curves obtained from isothermal DSC and rheological measurements, it could be con ...
... went up. In-situ monitoring of polymerization and crystallization by rheology and DSC The monitoring of the change in crystallinity of the APA6 material during the reaction is shown in Figures 6 and 7. By combining the curves obtained from isothermal DSC and rheological measurements, it could be con ...
DNA polymerase going in reverse: Requirement for transient metal
... Two closely spaced divalent metal ions (catalytic and nucleotide-binding metals) provide the scaffold for these reactions. The catalytic metal lowers the pKa of O3′ of the growing primer terminus, and the nucleotide-binding metal facilitates substrate binding. Recent time-lapse crystallographic stud ...
... Two closely spaced divalent metal ions (catalytic and nucleotide-binding metals) provide the scaffold for these reactions. The catalytic metal lowers the pKa of O3′ of the growing primer terminus, and the nucleotide-binding metal facilitates substrate binding. Recent time-lapse crystallographic stud ...
pyrimidin-7(4H)-one against Leishmani
... HmtpO {5-methyl-1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7(4H)-one} is a triazolopyrimidine derivative considered to be an analogue of the naturally occurring nucleobase hypoxanthine, which is ideally suited for the study of metal –metal interactions due to its multiple donor positions. In this respect, the s ...
... HmtpO {5-methyl-1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7(4H)-one} is a triazolopyrimidine derivative considered to be an analogue of the naturally occurring nucleobase hypoxanthine, which is ideally suited for the study of metal –metal interactions due to its multiple donor positions. In this respect, the s ...
Spin crossover

Spin Crossover (SCO), sometimes referred to as spin transition or spin equilibrium behavior, is a phenomenon that occurs in some metal complexes wherein the spin state of the complex changes due to external stimuli such as a variation of temperature, pressure, light irradiation or an influence of a magnetic field.With regard to a ligand field and ligand field theory, the change in spin state is a transition from a low spin (LS) ground state electron configuration to a high spin (HS) ground state electron configuration of the metal’s d atomic orbitals (AOs), or vice versa. The magnitude of the ligand field splitting along with the pairing energy of the complex determines whether it will have a LS or HS electron configuration. A LS state occurs because the ligand field splitting (Δ) is greater than the pairing energy of the complex (which is an unfavorable process).Figure 1 is a simplified illustration of the metal’s d orbital splitting in the presence of an octahedral ligand field. A large splitting between the t2g and eg AOs requires a substantial amount of energy for the electrons to overcome the energy gap (Δ) to comply with Hund’s Rule. Therefore, electrons will fill the lower energy t2g orbitals completely before populating the higher energy eg orbitals. Conversely, a HS state occurs with weaker ligand fields and smaller orbital splitting. In this case the energy required to populate the higher levels is substantially less than the pairing energy and the electrons fill the orbitals according to Hund’s Rule by populating the higher energy orbitals before pairing with electrons in the lower lying orbitals. An example of a metal ion that can exist in either a LS or HS state is Fe3+ in an octahedral ligand field. Depending on the ligands that are coordinated to this complex the Fe3+ can attain a LS or a HS state, as in Figure 1.Spin crossover refers to the transitions between high to low, or low to high, spin states. This phenomenon is commonly observed with some first row transition metal complexes with a d4 through d7 electron configuration in an octahedral ligand geometry. Spin transition curves are a common representation of SCO phenomenon with the most commonly observed types depicted in Figure 2 in which γHS (the high-spin molar fraction) is plotted vs. T. The figure shows a gradual spin transition (left), an abrupt transition with hysteresis (middle) and a two-step transition (right). For a transition to be considered gradual, it typically takes place over a large temperature range, even up to several hundred K, whereas for a transition to be considered abrupt, it should take place within 10 K or less.These curves indicate that a spin transition has occurred in a metal complex as temperature changed. The gradual transition curve is an indication that not all metal centers within the complex are undergoing the transition at the same temperature. The abrupt spin change with hysteresis indicates a strong cooperativity, or “communication”, between neighboring metal complexes. In the latter case, the material is bistable and can exist in the two different spin states with a different range of external stimuli (temperature in this case) for the two phenomena, namely LS → HS and HS → LS. The two-step transition is relatively rare but is observed, for example, with dinuclear SCO complexes for which the spin transition in one metal center renders the transition in the second metal center less favorable.There are several types of spin crossover that can occur in a complex; some of them are light induced excited state spin trapping (LIESST), ligand-driven light induced spin change (LD-LISC), and charge transfer induced spin transition (CTIST).






![f-Element Disiloxanediolates: Novel Si[minus]O](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014304880_1-eb67bfb0c3fc05ae875f0048d30df664-300x300.png)
















