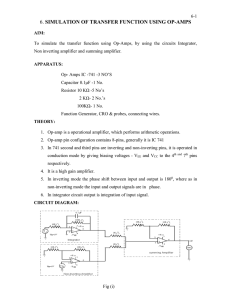
EXPERIMENT 1 (ELECTRO-TECHNIQUE)
... Figure 5.6: Circuit diagram of a series RLC circuit 2. Set the function generator to produce a sine wave input signal of amplitude 8Vp-p and frequency 5 kHz. Use this input voltage as the reference signal. 3. Obtain the Vs and VR traces on the scope. Make sure you have done the correct settings as i ...
... Figure 5.6: Circuit diagram of a series RLC circuit 2. Set the function generator to produce a sine wave input signal of amplitude 8Vp-p and frequency 5 kHz. Use this input voltage as the reference signal. 3. Obtain the Vs and VR traces on the scope. Make sure you have done the correct settings as i ...
Placing a Digital Meter in Circuits - Cleveland Institute of Electronics
... You can place the meter on either side of the resistor. Notice the polarity of the meter leads are opposite from where they would be measuring voltage. 3Ω ...
... You can place the meter on either side of the resistor. Notice the polarity of the meter leads are opposite from where they would be measuring voltage. 3Ω ...
NATG 1100 DC Circuit Fundamentals - Description
... students learn, what they know, and what they can do with their knowledge. Results from these various activities guide Barton, as a learning college, in finding ways to improve student learning. Course Outcomes Upon completion of this course, the student should be able to: 1. Define the conductive a ...
... students learn, what they know, and what they can do with their knowledge. Results from these various activities guide Barton, as a learning college, in finding ways to improve student learning. Course Outcomes Upon completion of this course, the student should be able to: 1. Define the conductive a ...
Parallel Circuits
... individual branch resistances. d. For the student to determine, for a parallel circuit, the effects of changing a single resistor value, upon total resistance, total current and the distribution of branch currents. ...
... individual branch resistances. d. For the student to determine, for a parallel circuit, the effects of changing a single resistor value, upon total resistance, total current and the distribution of branch currents. ...
ET8017_Exam_Nov_2012_Solutions
... B) In the auto-zeroing phase the settling is limited by one R and the two capacitors in series, while in the amplification phase the settling is limited by 2R and two capacitors in series. So the worst-case settling time constant occurs during the amplification phase and is equal to RC. Exponential ...
... B) In the auto-zeroing phase the settling is limited by one R and the two capacitors in series, while in the amplification phase the settling is limited by 2R and two capacitors in series. So the worst-case settling time constant occurs during the amplification phase and is equal to RC. Exponential ...
Electronics Technology Fundamentals
... Current Characteristics – the current through any element in a series circuit must equal the current through every other element in the circuit ...
... Current Characteristics – the current through any element in a series circuit must equal the current through every other element in the circuit ...
Lab 3 – Finding the value of an unknown capacitor By Henry Lin
... ohms 5. Do this for both small capacitors. F. Finding the capacitance from the physical characteristics The capacitance can also be found by the equation ...
... ohms 5. Do this for both small capacitors. F. Finding the capacitance from the physical characteristics The capacitance can also be found by the equation ...
Instruction manual
... Do not measure Frequency on high voltage (>1000V) to avoid electrical shock hazard and/or damage to the instrument. Frequency is the number of cycles a voltage or current signal completes each second. The Meter can measure Frequency or Duty Cycle while making either an AC Voltage or AC Current measu ...
... Do not measure Frequency on high voltage (>1000V) to avoid electrical shock hazard and/or damage to the instrument. Frequency is the number of cycles a voltage or current signal completes each second. The Meter can measure Frequency or Duty Cycle while making either an AC Voltage or AC Current measu ...
Ch19CT
... and current have all decreased by a factor of e. After two time constants, everything has fallen by e2. The initial current is 1A. So after two time constants, the current is 1/e2 A = 0.135A. None of these. ...
... and current have all decreased by a factor of e. After two time constants, everything has fallen by e2. The initial current is 1A. So after two time constants, the current is 1/e2 A = 0.135A. None of these. ...
Series Circuits
... least one branch not shared by any other independent loops. • Two or more elements are in series if they share a single node and thus carry the same current. • Two or more elements are in parallel if they are connected to the same two nodes and thus have the same voltage. ...
... least one branch not shared by any other independent loops. • Two or more elements are in series if they share a single node and thus carry the same current. • Two or more elements are in parallel if they are connected to the same two nodes and thus have the same voltage. ...
Test probe
A test probe (test lead, test prod, or scope probe) is a physical device used to connect electronic test equipment to a device under test (DUT). They range from very simple, robust devices to complex probes that are sophisticated, expensive, and fragile.