– Simple turn-off description of Trench- Field-stop IGBT IGBT
... A further stored charge influence on the switching behavior can be shown by variation of the gate turn-off resistance. Fig. 5 illustrates the turn-off under different gate resistors. For gate resistors ranging from 1 to 30 Ohm, the dV/dt of the collector voltage is constant. The dV/dt is intrinsical ...
... A further stored charge influence on the switching behavior can be shown by variation of the gate turn-off resistance. Fig. 5 illustrates the turn-off under different gate resistors. For gate resistors ranging from 1 to 30 Ohm, the dV/dt of the collector voltage is constant. The dV/dt is intrinsical ...
Experiment 7: DC Measurements and Meter Loading
... Experiment 7: DC Measurements and Meter Loading Introduction Meters used to measure voltage or current have an internal resistance. Since the meter must be connected to the circuit to make a measurement, the circuit is changed by the resistance of the meter. This is referred to as the meter's "loadi ...
... Experiment 7: DC Measurements and Meter Loading Introduction Meters used to measure voltage or current have an internal resistance. Since the meter must be connected to the circuit to make a measurement, the circuit is changed by the resistance of the meter. This is referred to as the meter's "loadi ...
circuits worksheet
... 21) I = 23.6 A so fuse will melt 22a) 17 22b) I35 = 1.0 A; I55 = 0.64 A; I85 = 0.41 A 23b) 6.0 23c) 0.75 A 23d) 2.3 V 24b) 20.0 24c) 6.0 A 24d) 3.0 A 24e) 90. V ...
... 21) I = 23.6 A so fuse will melt 22a) 17 22b) I35 = 1.0 A; I55 = 0.64 A; I85 = 0.41 A 23b) 6.0 23c) 0.75 A 23d) 2.3 V 24b) 20.0 24c) 6.0 A 24d) 3.0 A 24e) 90. V ...
CIRCUITS WORKSHEET
... 21) I = 23.6 A so fuse will melt 22a) 17 22b) I35 = 1.0 A; I55 = 0.64 A; I85 = 0.41 A 23b) 6.0 23c) 0.75 A 23d) 2.3 V 24b) 20.0 24c) 6.0 A 24d) 3.0 A 24e) 90. V ...
... 21) I = 23.6 A so fuse will melt 22a) 17 22b) I35 = 1.0 A; I55 = 0.64 A; I85 = 0.41 A 23b) 6.0 23c) 0.75 A 23d) 2.3 V 24b) 20.0 24c) 6.0 A 24d) 3.0 A 24e) 90. V ...
How to Use a Multimeter
... The first thing we’ll need is an extra piece of wire. As mentioned, we’ll need to physically interrupt the circuit to measure the current. Said another way, pull out the VCC wire going to the resistor, add a wire where that wire was connected, and then probe from the power pin on the power supply t ...
... The first thing we’ll need is an extra piece of wire. As mentioned, we’ll need to physically interrupt the circuit to measure the current. Said another way, pull out the VCC wire going to the resistor, add a wire where that wire was connected, and then probe from the power pin on the power supply t ...
12. Transformers, Impedance Matching and Maximum Power Transfer
... Maximum Power Transfer Introduction The transformer is a device that takes AC at one voltage and transforms it into another voltage either higher or lower than the original voltage. Alternatively, a transformer can be used to do the same thing with current. Transformers only work with AC (and they d ...
... Maximum Power Transfer Introduction The transformer is a device that takes AC at one voltage and transforms it into another voltage either higher or lower than the original voltage. Alternatively, a transformer can be used to do the same thing with current. Transformers only work with AC (and they d ...
MY-64 Digital Multimeter use
... Adjust the meter for maximum accuracy, and write the range setting and measured resistance on Part A of the worksheet. 2. Replace the 100Ω resistor with the 10kΩ resistor. Adjust the meter for maximum accuracy, and write the range setting and measured resistance on Part A of the ...
... Adjust the meter for maximum accuracy, and write the range setting and measured resistance on Part A of the worksheet. 2. Replace the 100Ω resistor with the 10kΩ resistor. Adjust the meter for maximum accuracy, and write the range setting and measured resistance on Part A of the ...
Solutions to Period 12 Exercises E.1 You have four identical pieces
... Each wire is 10 feet long and has a resistance of 1.0 ohms. If you connect the four wires in series, what is their combined resistance? a) 0.25 ohms b) 1 ohm c) ...
... Each wire is 10 feet long and has a resistance of 1.0 ohms. If you connect the four wires in series, what is their combined resistance? a) 0.25 ohms b) 1 ohm c) ...
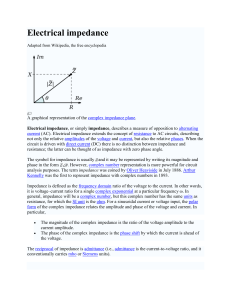
Electrical impedance
... current (AC). Electrical impedance extends the concept of resistance to AC circuits, describing not only the relative amplitudes of the voltage and current, but also the relative phases. When the circuit is driven with direct current (DC) there is no distinction between impedance and resistance; the ...
... current (AC). Electrical impedance extends the concept of resistance to AC circuits, describing not only the relative amplitudes of the voltage and current, but also the relative phases. When the circuit is driven with direct current (DC) there is no distinction between impedance and resistance; the ...
doc - University of Iowa Physics
... reported in the units (cm3/C). InAs has a relatively small band gap so the carrier density should be roughly the intrinsic carrier density. These carriers are produced by the thermal excitation of the electrons from the valence band into the conduction band. You can estimate this as the density of v ...
... reported in the units (cm3/C). InAs has a relatively small band gap so the carrier density should be roughly the intrinsic carrier density. These carriers are produced by the thermal excitation of the electrons from the valence band into the conduction band. You can estimate this as the density of v ...
Voltage, Current and Resistance
... One can have closed circuits, through which current flows, or open circuits in which there are no currents. Sometimes, usually by accident, wires may touch, causing a short circuit. Most of the current flows through the short, while very little will flow through the load. This may burn out a piece o ...
... One can have closed circuits, through which current flows, or open circuits in which there are no currents. Sometimes, usually by accident, wires may touch, causing a short circuit. Most of the current flows through the short, while very little will flow through the load. This may burn out a piece o ...
LT1311 - Quad 12MHz, 145ns Settling Precision Current-to
... to 20mV/µA; the change with temperature is typically – 70ppm/°C. The gain matching of the four amplifiers is ten times better. The input offset voltage and bias current are trimmed as well. The trimming also minimizes the resulting output offset drift. For more detailed circuit information, please s ...
... to 20mV/µA; the change with temperature is typically – 70ppm/°C. The gain matching of the four amplifiers is ten times better. The input offset voltage and bias current are trimmed as well. The trimming also minimizes the resulting output offset drift. For more detailed circuit information, please s ...
Test probe
A test probe (test lead, test prod, or scope probe) is a physical device used to connect electronic test equipment to a device under test (DUT). They range from very simple, robust devices to complex probes that are sophisticated, expensive, and fragile.