Unit 2: Biological Psychology
... What are neural networks and where are they found? What is the peripheral nervous system, and what does it do? What is the central nervous system, and what structures is it comprised of? What are the two components of the peripheral nervous system? What does the somatic nervous system do? What is th ...
... What are neural networks and where are they found? What is the peripheral nervous system, and what does it do? What is the central nervous system, and what structures is it comprised of? What are the two components of the peripheral nervous system? What does the somatic nervous system do? What is th ...
Teleconference on Iridology
... depending on the severity of the condition. This signs results from chemical imbalances in the body due to an excessive intake of salt or bicarbonate of soda, drugs such as sodium salicylate, calcium out of solution and high cholesterol or triglycerides in the blood. It may be associated with harden ...
... depending on the severity of the condition. This signs results from chemical imbalances in the body due to an excessive intake of salt or bicarbonate of soda, drugs such as sodium salicylate, calcium out of solution and high cholesterol or triglycerides in the blood. It may be associated with harden ...
PDF
... through distinct sensory domains or submodular pathways. For example, if a central node in a small neural circuit (e.g., C. elegans) needs to cover all possible connectivity wiring patterns to represent eight distinct types of inputs or information, a total of 255 principal projection neurons would ...
... through distinct sensory domains or submodular pathways. For example, if a central node in a small neural circuit (e.g., C. elegans) needs to cover all possible connectivity wiring patterns to represent eight distinct types of inputs or information, a total of 255 principal projection neurons would ...
The Brain of the Planarian as the Ancestor of the Human Brain
... Neurons whose axons cross the midline in the planarian brain are of special interest. A phylogenetic hypothesis to explain crossed cerebral control in vertebrates was proposed by us, exemplified by the amphioxus, a primitive protochordate (pre-vertebrate) as a model of cerebral organization.6 The de ...
... Neurons whose axons cross the midline in the planarian brain are of special interest. A phylogenetic hypothesis to explain crossed cerebral control in vertebrates was proposed by us, exemplified by the amphioxus, a primitive protochordate (pre-vertebrate) as a model of cerebral organization.6 The de ...
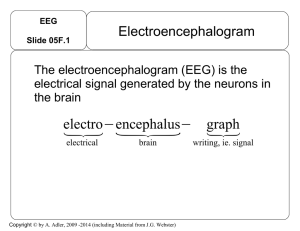
ELECTROENCEPHALOGRAM_(EEG).
... only frequency group found in every part of the brain. • When the brain needs to simultaneously process information from different areas, its hypothesized that the 40Hz activity consolidates the required areas for simultaneous processing. • A good memory is associated with well-regulated and efficie ...
... only frequency group found in every part of the brain. • When the brain needs to simultaneously process information from different areas, its hypothesized that the 40Hz activity consolidates the required areas for simultaneous processing. • A good memory is associated with well-regulated and efficie ...
Understanding the Gut Brain
... Supports development of neurons in gut & gut wall So premature &/or none breast fed – high risk for diarrhea & necrotizing enterocolitis Seems to have memory – not breast fed (trauma to gut wall) & being fed solid foods too soon leads to infection & gut diseases later in life ...
... Supports development of neurons in gut & gut wall So premature &/or none breast fed – high risk for diarrhea & necrotizing enterocolitis Seems to have memory – not breast fed (trauma to gut wall) & being fed solid foods too soon leads to infection & gut diseases later in life ...
The Brain and Cranial Nerves
... • 14-8 Identify the main components of the limbic system, and specify the locations and functions of each. • 14-9 Identify the major anatomical subdivisions and functions of the cerebrum, and discuss the origin and significance of the major types of brain waves seen in an electroencephalogram. • 14- ...
... • 14-8 Identify the main components of the limbic system, and specify the locations and functions of each. • 14-9 Identify the major anatomical subdivisions and functions of the cerebrum, and discuss the origin and significance of the major types of brain waves seen in an electroencephalogram. • 14- ...
Find out how much carbohydrate you should be consuming
... another third should be fruit and vegetables. This means that about half of your calorie intake should come from starchy foods, fruit and vegetables. So, if you get 2,000 calories a day, about 1,000 of these should be from carbohydrates, which is approximately 250g of carbohydrate a day. You should ...
... another third should be fruit and vegetables. This means that about half of your calorie intake should come from starchy foods, fruit and vegetables. So, if you get 2,000 calories a day, about 1,000 of these should be from carbohydrates, which is approximately 250g of carbohydrate a day. You should ...
accepted manuscript - Radboud Repository
... The eight Macaque brain maps in Caret already cover many regions defined in CoCoMac. We have registered one additional brain map to the F99 surface, the Regional Map (RM). This is a map with a special status in CoCoMac. It does not originate from one of the publications that make up CoCoMac, but it ...
... The eight Macaque brain maps in Caret already cover many regions defined in CoCoMac. We have registered one additional brain map to the F99 surface, the Regional Map (RM). This is a map with a special status in CoCoMac. It does not originate from one of the publications that make up CoCoMac, but it ...
The endocrine system
... HORMONES: Literally means: “to activate” they move through the bloodstream, they have specific structure or shape for each specific hormone. b. GLANDS: Produce hormones *** EVERYTHING works TOGETHER with the brain *** All glands and chemicals that are produced that are taken together are called the ...
... HORMONES: Literally means: “to activate” they move through the bloodstream, they have specific structure or shape for each specific hormone. b. GLANDS: Produce hormones *** EVERYTHING works TOGETHER with the brain *** All glands and chemicals that are produced that are taken together are called the ...
The changing impact of genes and environment on brain
... mean value between them. The degree to which the heterozygote departs from this is the degree of dominance (d). ...
... mean value between them. The degree to which the heterozygote departs from this is the degree of dominance (d). ...
the brain - Medical Research Council
... side of your body and the right part controls the left side. There is some evidence for each side managing different tasks – for instance, language is mainly processed in the left side of the brain in most people. And whether you are left- or right-handed seems to be down to a division of labour bet ...
... side of your body and the right part controls the left side. There is some evidence for each side managing different tasks – for instance, language is mainly processed in the left side of the brain in most people. And whether you are left- or right-handed seems to be down to a division of labour bet ...
Ch - Humble ISD
... L - language; dominate the control of hand movements like _________; & logic (math) ...
... L - language; dominate the control of hand movements like _________; & logic (math) ...
Food for Thought: Essential Fatty Acid Protects
... in Williams syndrome shows that neural development is a highly constrained process; the impact of genetic alterations can be quite specific in the brain, as they are in the heart (note that Williams syndrome is also characterized by numerous physical features such as supravalvular aortic stenosis; M ...
... in Williams syndrome shows that neural development is a highly constrained process; the impact of genetic alterations can be quite specific in the brain, as they are in the heart (note that Williams syndrome is also characterized by numerous physical features such as supravalvular aortic stenosis; M ...
sugars in growing up milk and its effects on children`s
... References: 1. Monro JA, et al. Baselines representing blood glucose clearance improve in vitro prediction of the glycemic impact of customarily consumed food quantities. Br J Nutr 2010;103(2):295-305. 2. de Onis M, et al. Global prevalence and trends of overweight and obesity among preschool childr ...
... References: 1. Monro JA, et al. Baselines representing blood glucose clearance improve in vitro prediction of the glycemic impact of customarily consumed food quantities. Br J Nutr 2010;103(2):295-305. 2. de Onis M, et al. Global prevalence and trends of overweight and obesity among preschool childr ...
Your Nervous System - Springfield Public Schools
... such as a flame? Most likely you have noticed that your hand automatically jerks away. This type of automatic response to your environment is called a reflex. A reflex action is shown in Figure 12. In some reflex actions, the actions of the skeletal muscles are controlled by the spinal cord only—not ...
... such as a flame? Most likely you have noticed that your hand automatically jerks away. This type of automatic response to your environment is called a reflex. A reflex action is shown in Figure 12. In some reflex actions, the actions of the skeletal muscles are controlled by the spinal cord only—not ...
Chapter 14 Lecture Outline
... allow pathogens to enter brain tissue – Circumventricular organs (CVOs)—places in the third and fourth ventricles where the barrier is absent • Blood has direct access to the brain • Enables the brain to monitor and respond to fluctuations in blood glucose, pH, osmolarity, and other variables • CVOs ...
... allow pathogens to enter brain tissue – Circumventricular organs (CVOs)—places in the third and fourth ventricles where the barrier is absent • Blood has direct access to the brain • Enables the brain to monitor and respond to fluctuations in blood glucose, pH, osmolarity, and other variables • CVOs ...
ch14_lecture - Napa Valley College
... allow pathogens to enter brain tissue – Circumventricular organs (CVOs)—places in the third and fourth ventricles where the barrier is absent • Blood has direct access to the brain • Enables the brain to monitor and respond to fluctuations in blood glucose, pH, osmolarity, and other variables • CVOs ...
... allow pathogens to enter brain tissue – Circumventricular organs (CVOs)—places in the third and fourth ventricles where the barrier is absent • Blood has direct access to the brain • Enables the brain to monitor and respond to fluctuations in blood glucose, pH, osmolarity, and other variables • CVOs ...
Sedentary Lifestyles and High-fat, High
... lifestyles,” said Worldwatch Institute Chairman Lester R. Brown. “For many of those who are overweight, achieving a healthy body weight depends on both reducing caloric intake and burning more calories through exercise. … [E]xercise may be a genetic imperative.”9 The number of obese and overweight p ...
... lifestyles,” said Worldwatch Institute Chairman Lester R. Brown. “For many of those who are overweight, achieving a healthy body weight depends on both reducing caloric intake and burning more calories through exercise. … [E]xercise may be a genetic imperative.”9 The number of obese and overweight p ...
Motivation - Blackwell Publishing
... Leptin administration decreases food intake in wild type (lean) mice (who have one copy being dominant (in which OBOB or OBob genes, so that they produce leptin) but also in obob mice. This case the phenotype, or body characfinding shows that obob mice do have receptors sensitive to leptin, but they ...
... Leptin administration decreases food intake in wild type (lean) mice (who have one copy being dominant (in which OBOB or OBob genes, so that they produce leptin) but also in obob mice. This case the phenotype, or body characfinding shows that obob mice do have receptors sensitive to leptin, but they ...
49-Nervous System - Northwest ISD Moodle
... lacks clusters of neurons that perform specialized functions. In more complex animals, the axons of multiple nerve cells are often bundled together, forming nerves. These fibrous structures channel and organize information flow along specific routes through the nervous system. For example, sea stars ...
... lacks clusters of neurons that perform specialized functions. In more complex animals, the axons of multiple nerve cells are often bundled together, forming nerves. These fibrous structures channel and organize information flow along specific routes through the nervous system. For example, sea stars ...
Nervous System - AP Psychology: 2(A)
... • Reuptake - process by which neurotransmitters are taken back into the synaptic vesicles. (Many anti-depressant drugs work by blocking this process.) • Enzyme - a complex protein that is manufactured by cells. • One type specifically breaks up acetylcholine because muscle activity needs to happen r ...
... • Reuptake - process by which neurotransmitters are taken back into the synaptic vesicles. (Many anti-depressant drugs work by blocking this process.) • Enzyme - a complex protein that is manufactured by cells. • One type specifically breaks up acetylcholine because muscle activity needs to happen r ...
REVIEWS - Ping Pong
... energy flux within adipocytes20,21. As a result, during periods of negative energy balance, levels of leptin fall considerably faster than the rate at which adipose tissue is consumed. Leptin receptors are found in numerous peripheral tissues, as well as in several regions of the brain, with the hig ...
... energy flux within adipocytes20,21. As a result, during periods of negative energy balance, levels of leptin fall considerably faster than the rate at which adipose tissue is consumed. Leptin receptors are found in numerous peripheral tissues, as well as in several regions of the brain, with the hig ...
Nervous Systems
... The cerebral cortex controls voluntary movement and cognitive functions Changes in synaptic connections underlie memory and learning Many nervous system disorders can be explained in molecular terms ...
... The cerebral cortex controls voluntary movement and cognitive functions Changes in synaptic connections underlie memory and learning Many nervous system disorders can be explained in molecular terms ...
EEG - OCIBME
... Why are EEG signals on the surface of the scalp so small? Why are the brain neuronal signals obtained with needle electrodes so much larger? How accurately is it possible to know the thoughts in the brain from the EEG signals? The ECG is described as a vector field? Why not the EEG? What is the freq ...
... Why are EEG signals on the surface of the scalp so small? Why are the brain neuronal signals obtained with needle electrodes so much larger? How accurately is it possible to know the thoughts in the brain from the EEG signals? The ECG is described as a vector field? Why not the EEG? What is the freq ...