The Brain: How does it work?
... (the only musical element that did) Pitch activated an area on the left back of the brain - the precuneus. Melody activated both sides of the brain. Composite listening - Left and Right Hemisphere - Auditory Cortex Understanding lyrics - Wernicke's Area ...
... (the only musical element that did) Pitch activated an area on the left back of the brain - the precuneus. Melody activated both sides of the brain. Composite listening - Left and Right Hemisphere - Auditory Cortex Understanding lyrics - Wernicke's Area ...
Article on Rewiring the Brain
... the left prefrontal cortex than in the right correlates with a higher baseline level of contentment. The relative left/right activity came to be seen as a marker for the happiness set point, since people tend to return to this level no matter whether they win the lottery or lose their spouse. If men ...
... the left prefrontal cortex than in the right correlates with a higher baseline level of contentment. The relative left/right activity came to be seen as a marker for the happiness set point, since people tend to return to this level no matter whether they win the lottery or lose their spouse. If men ...
Sensory Cortex
... • The scientist who won a Nobel Prize for his work with split brain patients is • A. Walter Cannon • B. Paul Broca • C. Roger Sperry • D. James Olds • E. Cheech Marin ...
... • The scientist who won a Nobel Prize for his work with split brain patients is • A. Walter Cannon • B. Paul Broca • C. Roger Sperry • D. James Olds • E. Cheech Marin ...
Introduction to Brain Structure - Center for Behavioral Neuroscience
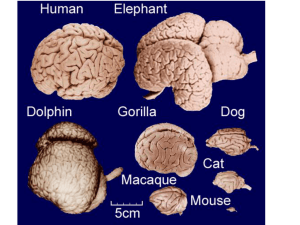
... intelligence. Furthermore, if two species of animals had the same brain weight, it would be likely that the species with the lower body weight would be more intelligent. One way to increase brain weight while maintaining the same brain size is to pack the neurons in more densely. One of the ways th ...
... intelligence. Furthermore, if two species of animals had the same brain weight, it would be likely that the species with the lower body weight would be more intelligent. One way to increase brain weight while maintaining the same brain size is to pack the neurons in more densely. One of the ways th ...
The Nervous System
... oxygen-after this cells begin to die You will go unconscious after just 10 seconds of no blood getting to the brain After 40-110 seconds of no blood to the brain the ...
... oxygen-after this cells begin to die You will go unconscious after just 10 seconds of no blood getting to the brain After 40-110 seconds of no blood to the brain the ...
Brain Notes - Cloudfront.net
... different neurons, which provide information throughout the nervous system. Within a single neuron, information travels through electrical signals, but when information is transmitted from one neuron to the next neuron, the transmission is considered ‘chemical’. For two neurons to communicate neurot ...
... different neurons, which provide information throughout the nervous system. Within a single neuron, information travels through electrical signals, but when information is transmitted from one neuron to the next neuron, the transmission is considered ‘chemical’. For two neurons to communicate neurot ...
PSYC 100 Chapter 2
... Severed neurons do not regenerate, but some neural tissue can reorganize in response to damage. In the case of blind or hearing impaired individuals, the unused brain areas are available for other uses. For example, when a blind person reads Braille, the brain area dedicated to that finger expands a ...
... Severed neurons do not regenerate, but some neural tissue can reorganize in response to damage. In the case of blind or hearing impaired individuals, the unused brain areas are available for other uses. For example, when a blind person reads Braille, the brain area dedicated to that finger expands a ...
The Binding Problem
... identify the members of a representation as belonging together and to distinguish them from other representations that may be present at the same time. What internal dynamic structure of a cell assembly would distinguish it from all other neuronal activity present simultaneously in the cortical netw ...
... identify the members of a representation as belonging together and to distinguish them from other representations that may be present at the same time. What internal dynamic structure of a cell assembly would distinguish it from all other neuronal activity present simultaneously in the cortical netw ...
Brain Development - Pottstown School District
... world and forms attachments to parents, family members and other caregivers. In the first decade of life, a child’s brain forms trillions of connections or synapses. Axons hook up with dendrites, and chemicals called neurotransmitters facilitate the passage of impulses across the resulting synapses. ...
... world and forms attachments to parents, family members and other caregivers. In the first decade of life, a child’s brain forms trillions of connections or synapses. Axons hook up with dendrites, and chemicals called neurotransmitters facilitate the passage of impulses across the resulting synapses. ...
D. Brain
... can often talk and are smart, but can be mistaken for mentally retarded due to the need for helmets (since the cannot control their body movements) and their look. ...
... can often talk and are smart, but can be mistaken for mentally retarded due to the need for helmets (since the cannot control their body movements) and their look. ...
PSYC465 - neuroanatomy
... Mind and body are in constant communication (neuroscientists call this the brain-body loop), but the loop can get out-of-sync-- even broken. This hour: stories of people whose brains and bodies have lost each other. We begin with a century-old mystery: why do many amputees still feel their missing l ...
... Mind and body are in constant communication (neuroscientists call this the brain-body loop), but the loop can get out-of-sync-- even broken. This hour: stories of people whose brains and bodies have lost each other. We begin with a century-old mystery: why do many amputees still feel their missing l ...
Exploring Our Senses
... brain (in the visual cortex) that respond to specific features of the stimulus, such as shape, angle, movement. Hubel and Weisel. Colin Blakemore does terrible things to kittens. For science! 3:10-5:10, ...
... brain (in the visual cortex) that respond to specific features of the stimulus, such as shape, angle, movement. Hubel and Weisel. Colin Blakemore does terrible things to kittens. For science! 3:10-5:10, ...
Heroin - WordPress.com
... According to the Specification you need to be able to : Describe, with reference to heroin and nicotine 1. Mode of action 2. Effects 3. Tolerance 4. Physical / psychological dependencies 5. withdrawal ...
... According to the Specification you need to be able to : Describe, with reference to heroin and nicotine 1. Mode of action 2. Effects 3. Tolerance 4. Physical / psychological dependencies 5. withdrawal ...
the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
... that satisfies the conditions of life isn't anything like life on earth now, but might represent life as it began or could exist elsewhere in the universe. these genes would launch the new form of life down the Darwinian evolutionary path researchers are trying to design a completely novel form of l ...
... that satisfies the conditions of life isn't anything like life on earth now, but might represent life as it began or could exist elsewhere in the universe. these genes would launch the new form of life down the Darwinian evolutionary path researchers are trying to design a completely novel form of l ...
Dynamic Decision Making in Complex Task Environments
... • Fundamental tenets of the research: – Decision making occurs through a real-time dynamic process that depends upon neural activity distributed across a wide range of participating brain areas, each shaping the decision making process in its own way. – An effort to understand decision making as an ...
... • Fundamental tenets of the research: – Decision making occurs through a real-time dynamic process that depends upon neural activity distributed across a wide range of participating brain areas, each shaping the decision making process in its own way. – An effort to understand decision making as an ...
The basics of brain communication
... system. They operate through electrical impulses, communicate with other neurons through chemical signals, and form neural networks. (page 76). Neuron Structure (see Figure 3.5 on page 79) ...
... system. They operate through electrical impulses, communicate with other neurons through chemical signals, and form neural networks. (page 76). Neuron Structure (see Figure 3.5 on page 79) ...
Science of Addiction WebquestKEY
... Click the “Back” button and return to the page titled “The New Science of Addiction: Genetics and the Brain”. Follow the link, “Drugs alter the Brain’s Reward Pathway”. 7. Which part of the brain do drugs cause dramatic changes in? synapses in the brain 8. Explain why drug users develop a “tolerance ...
... Click the “Back” button and return to the page titled “The New Science of Addiction: Genetics and the Brain”. Follow the link, “Drugs alter the Brain’s Reward Pathway”. 7. Which part of the brain do drugs cause dramatic changes in? synapses in the brain 8. Explain why drug users develop a “tolerance ...
Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations
... – Consists of the brain and the spinal cord (brain will be discussed later) – The spinal cord is a column of nerves about as thick as a thumb that extends from the brain down the back – Spinal cord is responsible for: Transmitting messages between the brain and the muscles and glands in the body The ...
... – Consists of the brain and the spinal cord (brain will be discussed later) – The spinal cord is a column of nerves about as thick as a thumb that extends from the brain down the back – Spinal cord is responsible for: Transmitting messages between the brain and the muscles and glands in the body The ...
The Special Senses and Functional Aspects of the Nervous System
... Thought- What is a thought and how is it produced? A thought is a conscious understanding in the brain of image or language or words. It is the result of billions of exchanges of neurotransmitters across billions of synapses and the conductions of millions of impulses through millions of neurons. Th ...
... Thought- What is a thought and how is it produced? A thought is a conscious understanding in the brain of image or language or words. It is the result of billions of exchanges of neurotransmitters across billions of synapses and the conductions of millions of impulses through millions of neurons. Th ...
Biological_Bases
... Complex cable of nerves that connects brain to rest of the body Carries motor impulses from the brain to internal organs and muscles Carries sensory information from extremities and internal organs to the brain 400,000 people a year in US either partial or complete paralysis. ...
... Complex cable of nerves that connects brain to rest of the body Carries motor impulses from the brain to internal organs and muscles Carries sensory information from extremities and internal organs to the brain 400,000 people a year in US either partial or complete paralysis. ...
CMM/BIO4350
... Closure of neural tube have around 125,000 cells. At birth, the human brain contains around 100 billion neurons We can infer from this information that new neurons are being generated at the rate of about 250,000 per minute during the nine months of gestation. (Cowan, 1979) ...
... Closure of neural tube have around 125,000 cells. At birth, the human brain contains around 100 billion neurons We can infer from this information that new neurons are being generated at the rate of about 250,000 per minute during the nine months of gestation. (Cowan, 1979) ...
The basic unit of computation - Zador Lab
... In a digital computer, the basic nonlinearity is of course the transistor. In the brain, however, the answer is not as clear. Among brain modelers, the conventional view, first enunciated by McCulloch and Pitts1, is that the single neuron represents the basic unit. In these models, a neuron is usual ...
... In a digital computer, the basic nonlinearity is of course the transistor. In the brain, however, the answer is not as clear. Among brain modelers, the conventional view, first enunciated by McCulloch and Pitts1, is that the single neuron represents the basic unit. In these models, a neuron is usual ...
Nervous System
... b. evaluation of new experiences from past events c,. removal erases all memory d. activation can elicit rage and passivity MEMORY DEFINED: ...
... b. evaluation of new experiences from past events c,. removal erases all memory d. activation can elicit rage and passivity MEMORY DEFINED: ...
Central Nervous System
... equated with Wernicke’s area . • Only found in one hemisphere but not the other; most often the left hemisphere • Receives information from all sensory association areas…This area integrates sensory information ( especially, visual and auditory ) into a comprehensive understanding, then sends the ...
... equated with Wernicke’s area . • Only found in one hemisphere but not the other; most often the left hemisphere • Receives information from all sensory association areas…This area integrates sensory information ( especially, visual and auditory ) into a comprehensive understanding, then sends the ...
The Brain
... A. The sympathetic nervous system increases physiological arousal, while the parasympathetic nervous system returns the body to a calmer and relaxed state. B. The sympathetic nervous system is a subdivision of the somatic nervous system, while the parasympathetic nervous system is a subdivision of t ...
... A. The sympathetic nervous system increases physiological arousal, while the parasympathetic nervous system returns the body to a calmer and relaxed state. B. The sympathetic nervous system is a subdivision of the somatic nervous system, while the parasympathetic nervous system is a subdivision of t ...
Neuroesthetics

Neuroesthetics (or neuroaesthetics) is a relatively recent sub-discipline of empirical aesthetics. Empirical aesthetics takes a scientific approach to the study of aesthetic perceptions of art and music. Neuroesthetics received its formal definition in 2002 as the scientific study of the neural bases for the contemplation and creation of a work of art. Neuroesthetics uses neuroscience to explain and understand the aesthetic experiences at the neurological level. The topic attracts scholars from many disciplines including neuroscientists, art historians, artists, and psychologists.