REPLACING THE HUMAN BRAIN: WILD IDEA PROMISES
... Of course, duplicating synapse firings in nanotube circuits does not mean that scientists are ready to replace the brain now. This organ is extremely complex. Unlike the static inner workings of computers, brains are constantly making new neurons and connections as they adapt to changing environment ...
... Of course, duplicating synapse firings in nanotube circuits does not mean that scientists are ready to replace the brain now. This organ is extremely complex. Unlike the static inner workings of computers, brains are constantly making new neurons and connections as they adapt to changing environment ...
Introduction
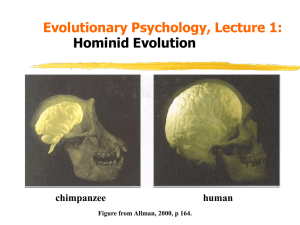
... to deal better with changing and unpredictable environments then why don't all species have large and complex brains? In fact animals with large brains are rare, probably due to the costs involved: A large brain is extremely energy demanding, and must compete with other body organs for resources. ...
... to deal better with changing and unpredictable environments then why don't all species have large and complex brains? In fact animals with large brains are rare, probably due to the costs involved: A large brain is extremely energy demanding, and must compete with other body organs for resources. ...
Word version - World Book Encyclopedia
... 7. The part of the brain that coordinates muscular movements with sensory information and helps maintain your body’s sense of balance is the: a. cerebrum b. cerebellum c. thalamus 8. The brain controls actions that you choose to do. Give two examples of voluntary actions. 1. _______________________ ...
... 7. The part of the brain that coordinates muscular movements with sensory information and helps maintain your body’s sense of balance is the: a. cerebrum b. cerebellum c. thalamus 8. The brain controls actions that you choose to do. Give two examples of voluntary actions. 1. _______________________ ...
The Nervous System Activity Sheet
... 7. The part of the brain that coordinates muscular movements with sensory information and helps maintain your body’s sense of balance is the: a. cerebrum b. cerebellum c. thalamus 8. The brain controls actions that you choose to do. Give two examples of voluntary actions. 1. _____ ...
... 7. The part of the brain that coordinates muscular movements with sensory information and helps maintain your body’s sense of balance is the: a. cerebrum b. cerebellum c. thalamus 8. The brain controls actions that you choose to do. Give two examples of voluntary actions. 1. _____ ...
Neural and Genetic Bases of Behavior
... Reorganization – Split Brain – a condition in which the two hemispheres of the brain are isolated by cutting the connecting fibers (mainly those of the corpus callosum) between them ...
... Reorganization – Split Brain – a condition in which the two hemispheres of the brain are isolated by cutting the connecting fibers (mainly those of the corpus callosum) between them ...
The Teenage Brain and Substance Abuse
... › Research continues to gain new insights into ways to optimize treatments to counteract addiction's powerful disruptive effects on brain and behavior What works best: prolonged abstinence, our brains can recover some of their former functioning, enabling people to regain control of their lives. How ...
... › Research continues to gain new insights into ways to optimize treatments to counteract addiction's powerful disruptive effects on brain and behavior What works best: prolonged abstinence, our brains can recover some of their former functioning, enabling people to regain control of their lives. How ...
Cross Section Head Model
... Skull—skeletal structure of the head that protects the brain and other organs Nasal bone—side-by-side bones in the middle and upper part of the face that vary in size, depending on the individual Nasal cavity—inside area of the nose lined with a mucus membrane that keeps the nose moist Tongue—muscul ...
... Skull—skeletal structure of the head that protects the brain and other organs Nasal bone—side-by-side bones in the middle and upper part of the face that vary in size, depending on the individual Nasal cavity—inside area of the nose lined with a mucus membrane that keeps the nose moist Tongue—muscul ...
Unit 3 Study Guide
... 1. controls voluntary muscle movements iii. Autonomic 1. controls responses to stress 2. sympathetic arouses 3. parasympathetic calms iv. Our pain reflexes help prevent us from harming ourselves 4. Brain a. Ways to Study it i. Accidents 1. studying the effects ii. Lesions 1. the removal or destructi ...
... 1. controls voluntary muscle movements iii. Autonomic 1. controls responses to stress 2. sympathetic arouses 3. parasympathetic calms iv. Our pain reflexes help prevent us from harming ourselves 4. Brain a. Ways to Study it i. Accidents 1. studying the effects ii. Lesions 1. the removal or destructi ...
Introduction to the Brain
... Largest part of brain Controls higher mental functions Divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres Surface layer of gray matter (neural cortex) ...
... Largest part of brain Controls higher mental functions Divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres Surface layer of gray matter (neural cortex) ...
Ch 3
... 5. According to the authors, what is the heart of the controversy regarding the concept of evolution, particular Darwin’s concept of evolution? 6. How are we different from either of our parents? 7. Distinguish between the terms “genotype” and “phenotype.” Why is the phenotype not completely determi ...
... 5. According to the authors, what is the heart of the controversy regarding the concept of evolution, particular Darwin’s concept of evolution? 6. How are we different from either of our parents? 7. Distinguish between the terms “genotype” and “phenotype.” Why is the phenotype not completely determi ...
The Brain Lesson
... • The third brain system is our neo-cortex brain and is our language-intelligence brain. (human brain) ...
... • The third brain system is our neo-cortex brain and is our language-intelligence brain. (human brain) ...
Brain PowerPoint
... ONE MORE TIME :) learning changes the brain learning occurs through trying out new things, not through getting the “right” answer - preventing mistakes is not healthy for a growing, adaptive brain repeated electrical stimulation, along with increased input of nutrients, fosters cell growth through ...
... ONE MORE TIME :) learning changes the brain learning occurs through trying out new things, not through getting the “right” answer - preventing mistakes is not healthy for a growing, adaptive brain repeated electrical stimulation, along with increased input of nutrients, fosters cell growth through ...
Sensory Disorders
... The normal functioning of the CNS can be affected by a number of disorders, the most common of which are headaches, tumors, vascular problems, infections, epilepsy, head trauma, demyelinating diseases, and ...
... The normal functioning of the CNS can be affected by a number of disorders, the most common of which are headaches, tumors, vascular problems, infections, epilepsy, head trauma, demyelinating diseases, and ...
File
... The human brain is divided into two hemispheres, the left and right, connected by a bundle of nerve fibers called the corpus callosum. The hemispheres are strongly, though not entirely, symmetrical. The left brain controls all the muscles on the right-hand side of the body; and the right brain contr ...
... The human brain is divided into two hemispheres, the left and right, connected by a bundle of nerve fibers called the corpus callosum. The hemispheres are strongly, though not entirely, symmetrical. The left brain controls all the muscles on the right-hand side of the body; and the right brain contr ...
______ 1
... _____________________ 3. The difference in electrical charge across a membrane _____________________ 4. Another name for a receiving neuron _____________________ 5. Another name for a transmitting neuron _____________________ 6. Is generated when a dendrite or cell body is stimulated _______________ ...
... _____________________ 3. The difference in electrical charge across a membrane _____________________ 4. Another name for a receiving neuron _____________________ 5. Another name for a transmitting neuron _____________________ 6. Is generated when a dendrite or cell body is stimulated _______________ ...