Biological Perspective Studies
... • Studied a group of Buddhist monks who went on a 72 hour pilgrimage to a holy mountain in Japan. Monks did not consume food or water, they did not speak, and they were exposed to the cold, late autumn weather. After about 48 hours, they began to have hallucinations, often seeing ancient ancestors o ...
... • Studied a group of Buddhist monks who went on a 72 hour pilgrimage to a holy mountain in Japan. Monks did not consume food or water, they did not speak, and they were exposed to the cold, late autumn weather. After about 48 hours, they began to have hallucinations, often seeing ancient ancestors o ...
Fundamentals of Nuclear Medicine Brain Imaging
... • FDG enters cell via GLUT proteins competing with glucose for hexokinase process, undergoes phosphorylation and trapped intraceullarly ...
... • FDG enters cell via GLUT proteins competing with glucose for hexokinase process, undergoes phosphorylation and trapped intraceullarly ...
Neural Networks
... On their own, neurons are not particularly complex Much of the brain’s information-processing capacity is thought to stem from the number of and interrelationships between the neurons. As such is an emergent property of the neurons, since each of its own does not have the power of the whole The huma ...
... On their own, neurons are not particularly complex Much of the brain’s information-processing capacity is thought to stem from the number of and interrelationships between the neurons. As such is an emergent property of the neurons, since each of its own does not have the power of the whole The huma ...
Ciccarelli SG Chapter 2
... neurons send commands from the spinal cord to our muscles, such as a command to pull your finger back. Interneurons connect sensory and motor neurons and help to coordinate the signals. All three of these neurons act together in the spinal cord to form a reflex arc. The ability of the brain and spin ...
... neurons send commands from the spinal cord to our muscles, such as a command to pull your finger back. Interneurons connect sensory and motor neurons and help to coordinate the signals. All three of these neurons act together in the spinal cord to form a reflex arc. The ability of the brain and spin ...
Visual development.
... • Because kittens are born blind, early deprivation (under 3 weeks) would have no effect. • By 3 months connections to the brain have been made, and deprivation has no effect since the critical period has ended. • The critical period is at about 4 weeks so lack of stimulation from the kitten’s envir ...
... • Because kittens are born blind, early deprivation (under 3 weeks) would have no effect. • By 3 months connections to the brain have been made, and deprivation has no effect since the critical period has ended. • The critical period is at about 4 weeks so lack of stimulation from the kitten’s envir ...
Visual development.
... • Because kittens are born blind, early deprivation (under 3 weeks) would have no effect. • By 3 months connections to the brain have been made, and deprivation has no effect since the critical period has ended. • The critical period is at about 4 weeks so lack of stimulation from the kitten’s envir ...
... • Because kittens are born blind, early deprivation (under 3 weeks) would have no effect. • By 3 months connections to the brain have been made, and deprivation has no effect since the critical period has ended. • The critical period is at about 4 weeks so lack of stimulation from the kitten’s envir ...
7-1_SegmOrgSpinCord_BogdanyP
... body. The butterfly-shape part of the cord is the grey matter, which contains cell bodies of neurons. The outer part is the white matter, which contains myelinated axons. The amount of the white and grey matter is different in sections of the cord. Lower levels contain less ascending and descending ...
... body. The butterfly-shape part of the cord is the grey matter, which contains cell bodies of neurons. The outer part is the white matter, which contains myelinated axons. The amount of the white and grey matter is different in sections of the cord. Lower levels contain less ascending and descending ...
Chapter 4: The Central Nervous System
... The parietal lobes receive information about touch, pressure, temperature, muscle movement and position. These are known as somatosensory functions. The somatosensory cortex is located in the parietal lobe behind the PMC. The parietal love also contains association areas which integrate information ...
... The parietal lobes receive information about touch, pressure, temperature, muscle movement and position. These are known as somatosensory functions. The somatosensory cortex is located in the parietal lobe behind the PMC. The parietal love also contains association areas which integrate information ...
THE HUMAN MEMORY The human brain, one of the most complex
... Since time immemorial, humans have tried to understand what memory is, how it works and why it goes wrong. It is an important part of what makes us truly human, and yet it is one of the most elusive and misunderstood of human attributes. The popular image of memory is as a kind of tiny filing cabine ...
... Since time immemorial, humans have tried to understand what memory is, how it works and why it goes wrong. It is an important part of what makes us truly human, and yet it is one of the most elusive and misunderstood of human attributes. The popular image of memory is as a kind of tiny filing cabine ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM I
... system in the body. It is the center of all mental activity including: Thought, Learning, Behavior and Memory. Together with the endocrine system, the nervous system is responsible for regulating and maintaining homeostasis. ...
... system in the body. It is the center of all mental activity including: Thought, Learning, Behavior and Memory. Together with the endocrine system, the nervous system is responsible for regulating and maintaining homeostasis. ...
Illusions: A Moving Experience
... shown in a series of physiological experiments published in 2005 by Bevil R. Conway of Harvard Medical School and his colleagues. Thus, by monitoring the activity of motion-detecting neurons in animals and simultaneously exploring human motion perception using cunningly contrived displays such as a ...
... shown in a series of physiological experiments published in 2005 by Bevil R. Conway of Harvard Medical School and his colleagues. Thus, by monitoring the activity of motion-detecting neurons in animals and simultaneously exploring human motion perception using cunningly contrived displays such as a ...
Multisensory brain mechanisms of bodily self
... many-dimensional Self (and the Person) • Visual Recognition: Recognizing one's image in a mirror • Memory: Autobiographical memory • Language: first-person pronouns, self-narrative • Social: ability to adapt the perspective of the other to ...
... many-dimensional Self (and the Person) • Visual Recognition: Recognizing one's image in a mirror • Memory: Autobiographical memory • Language: first-person pronouns, self-narrative • Social: ability to adapt the perspective of the other to ...
1 KARMA, REBIRTH, AND MENTAL CAUSATION Christian Coseru
... of the new array of methodological tools at our disposal. Specifically, I explore the potential benefits of a neurophenomenological account of karma. Acknowledging the demand for naturalist explanations of human and social interaction, such an approach nevertheless recognizes the irreducible nature ...
... of the new array of methodological tools at our disposal. Specifically, I explore the potential benefits of a neurophenomenological account of karma. Acknowledging the demand for naturalist explanations of human and social interaction, such an approach nevertheless recognizes the irreducible nature ...
Why are Drug Addicts Compelled to Risk Their Lives for Something
... Meth raises this chemical abnormally. Crystal meth raises dopamine levels over 10 times more than regular pleasures of life. Meth creates an extreme rush of pleasure which plays a large role in the addiction to meth. ...
... Meth raises this chemical abnormally. Crystal meth raises dopamine levels over 10 times more than regular pleasures of life. Meth creates an extreme rush of pleasure which plays a large role in the addiction to meth. ...
Neurons and Neurotransmitters
... Neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs ...
... Neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs ...
Nervous System
... such as for smiling and swallowing. In addition, some cranial nerves contain somatic and autonomic motor fibers. The involuntary nervous system (autonomic nervous system) maintains homeostasis. As its name implies, this system works automatically and without voluntary input. Its parts include recept ...
... such as for smiling and swallowing. In addition, some cranial nerves contain somatic and autonomic motor fibers. The involuntary nervous system (autonomic nervous system) maintains homeostasis. As its name implies, this system works automatically and without voluntary input. Its parts include recept ...
N-Squad Episode Three: Mission Debrief
... Asian people flush and their rate of heartbeat increases after drinking alcohol, because they have faulty alcohol metabolizing proteins. Peers: Sometimes friends can influence alcohol use by urging somebody to drink alcohol. For example, they could insist that it would be “cool” to drink. Family: Wh ...
... Asian people flush and their rate of heartbeat increases after drinking alcohol, because they have faulty alcohol metabolizing proteins. Peers: Sometimes friends can influence alcohol use by urging somebody to drink alcohol. For example, they could insist that it would be “cool” to drink. Family: Wh ...
Chapter Two
... C. Receptor sites are places on a neuron where neurotransmitters can be received. 1. It is the interaction of neurotransmitter and receptor site that causes inhibition or excitation. 2. Once released form their receptor sites, neurotransmitter are either destroyed by enzymes, or taken back up into t ...
... C. Receptor sites are places on a neuron where neurotransmitters can be received. 1. It is the interaction of neurotransmitter and receptor site that causes inhibition or excitation. 2. Once released form their receptor sites, neurotransmitter are either destroyed by enzymes, or taken back up into t ...
Born in Jan 2004 & weighing just 10 oz (284 gms)
... Pregnancy&Lactation (Cod liver Oil) may improve child’s IQ’ -Helland et al Paed Jan2003 Breast-fed Babies have a Higher IQ ( 8 points ) -Lancet 1994 ...
... Pregnancy&Lactation (Cod liver Oil) may improve child’s IQ’ -Helland et al Paed Jan2003 Breast-fed Babies have a Higher IQ ( 8 points ) -Lancet 1994 ...
TEACHERS`NOTES AND REFERENCES
... messages take the form of electric signals, they are known as impulses. Neurons can be classified into three types according to the directions in which these impulses move. Sensory neurons carry impulses from the sense organs to the brain and the spinal cord. Motor neurons carry impulses from the br ...
... messages take the form of electric signals, they are known as impulses. Neurons can be classified into three types according to the directions in which these impulses move. Sensory neurons carry impulses from the sense organs to the brain and the spinal cord. Motor neurons carry impulses from the br ...
CNS - FIU
... 3 layers of the meninges (dura, arachnoid and pia mater). First, identify the 12 cranial nerves by gently peeling the dura and/or arachnoid matter from the ventral surface of the brain (if it has not already been removed). Note that the hypophyseal gland is still attached with its adherent dura mate ...
... 3 layers of the meninges (dura, arachnoid and pia mater). First, identify the 12 cranial nerves by gently peeling the dura and/or arachnoid matter from the ventral surface of the brain (if it has not already been removed). Note that the hypophyseal gland is still attached with its adherent dura mate ...
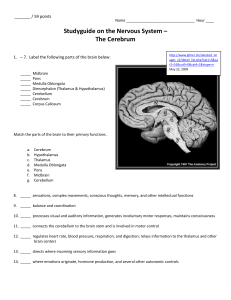
Major Parts of the Brain:
... 36. _____ Receives visual signals 37. _____ Interprets what you are seeing 38. _____ Receives messages about taste 39. _____ Receives signals about scent 40. _____ Controls direct voluntary movements 41. _____ Coordinates movements that have already been learned in the past. 42. _____ Relays feeling ...
... 36. _____ Receives visual signals 37. _____ Interprets what you are seeing 38. _____ Receives messages about taste 39. _____ Receives signals about scent 40. _____ Controls direct voluntary movements 41. _____ Coordinates movements that have already been learned in the past. 42. _____ Relays feeling ...
Neurons and Networks. An Introduction to Behavioral Neuroscience, Second Edition Brochure
... and concepts that have stood the test of time; abundant high-quality illustrations; exceptionally clear explanations of technical terms. Completely revised and enlarged with six new chapters, the second edition of Neurons and Networks is an introduction not just to neurobiology, but to all of behavi ...
... and concepts that have stood the test of time; abundant high-quality illustrations; exceptionally clear explanations of technical terms. Completely revised and enlarged with six new chapters, the second edition of Neurons and Networks is an introduction not just to neurobiology, but to all of behavi ...
Brain and mind - Scheme of work and lesson plan
... B6.2.17. Recall that the cerebral cortex is the part of our brain most concerned with intelligence, memory, language and consciousness. B6.2.18. Understand that scientists can map the regions of the brain to particular functions (including studies of patients with brain damage, studies in which diff ...
... B6.2.17. Recall that the cerebral cortex is the part of our brain most concerned with intelligence, memory, language and consciousness. B6.2.18. Understand that scientists can map the regions of the brain to particular functions (including studies of patients with brain damage, studies in which diff ...
references - Academic Science,International Journal of Computer
... The basic scheme of the proposed EEG-based wireless brain wave system is shown in Figure 1. The hardware of this system consists mainly of two major parts: a wireless physiological signal acquisition module and an embedded signal processing module. So, in our proposed project work we are analyzing t ...
... The basic scheme of the proposed EEG-based wireless brain wave system is shown in Figure 1. The hardware of this system consists mainly of two major parts: a wireless physiological signal acquisition module and an embedded signal processing module. So, in our proposed project work we are analyzing t ...