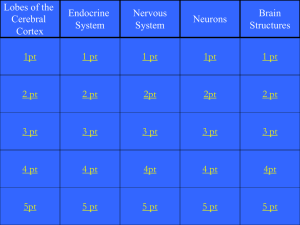
2. Nervous system anatomy
... • Neurons grow into adult form with dendrites, axons & terminal buttons • Neurons that do not connect with other neurons die ...
... • Neurons grow into adult form with dendrites, axons & terminal buttons • Neurons that do not connect with other neurons die ...
05/01 --- The Human Brain Project
... The Human Brain Project will impact many different areas of society. Brain simulation will provide new insights into the basic causes of neurological diseases such as autism, depression, Parkinson's, and Alzheimer's. It will give us new ways of testing drugs and understanding the way they work. It w ...
... The Human Brain Project will impact many different areas of society. Brain simulation will provide new insights into the basic causes of neurological diseases such as autism, depression, Parkinson's, and Alzheimer's. It will give us new ways of testing drugs and understanding the way they work. It w ...
PAC Newsletter - March 2015
... the world” since their brains can adapt to any language in the world. Then at about 11 months of age and onwards babies hear the same sounds as their parents. Introducing a foreign language to a child 5 years and under assists them to create the “foreign pathways’ so they will have the ability to sp ...
... the world” since their brains can adapt to any language in the world. Then at about 11 months of age and onwards babies hear the same sounds as their parents. Introducing a foreign language to a child 5 years and under assists them to create the “foreign pathways’ so they will have the ability to sp ...
Biological Impact
... The cerebral cortex • For convenience sake, each hemisphere of the brain is often subdivided into four different lobes—or four different geographic regions.. • The cerebral cortex provides many functions for the body—some of these functions have been “localized” (i.e., the particular part of the co ...
... The cerebral cortex • For convenience sake, each hemisphere of the brain is often subdivided into four different lobes—or four different geographic regions.. • The cerebral cortex provides many functions for the body—some of these functions have been “localized” (i.e., the particular part of the co ...
Cerebral Cortex
... Located at front of parietal lobes Registers and processes body touch and movement sensations (Input) ...
... Located at front of parietal lobes Registers and processes body touch and movement sensations (Input) ...
Class 1 notes
... (hippocampus and limbic connections). Clinically the main tests for temporal lobe functions are those of memory, mostly declarative. Antioxidants help keep this healthy as do omega 3 fatty acids, exercise moving oxygen and increasing profusion, brain plasticity exercises, acupuncture which increase ...
... (hippocampus and limbic connections). Clinically the main tests for temporal lobe functions are those of memory, mostly declarative. Antioxidants help keep this healthy as do omega 3 fatty acids, exercise moving oxygen and increasing profusion, brain plasticity exercises, acupuncture which increase ...
LS Chapter 18: Control and Coordination The Nervous System
... o The _______________Gland, located in the _______________, signals the body to _______________ o _______________Glands in the abdomen release _______________to help respond to stress o The _______________secretes _______________to control blood sugar o In females, _______________release ___________ ...
... o The _______________Gland, located in the _______________, signals the body to _______________ o _______________Glands in the abdomen release _______________to help respond to stress o The _______________secretes _______________to control blood sugar o In females, _______________release ___________ ...
Development of the Brain
... Development of the Brain • At birth, the human brain weighs approximately 350 grams. • By the first year. the brain weighs approximately 1000 grams. • The adult brain weighs 1200-1400 grams. ...
... Development of the Brain • At birth, the human brain weighs approximately 350 grams. • By the first year. the brain weighs approximately 1000 grams. • The adult brain weighs 1200-1400 grams. ...
Introduction
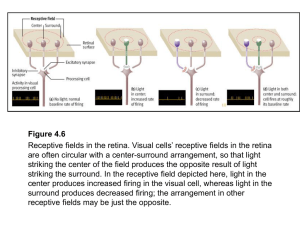
... (a) Input from the right half of the visual field strikes the left side of each retina and is transmitted to the left hemisphere (shown in red). Input from the left half of the visual field strikes the right side of each retina and is transmitted to the right hemisphere (shown in green). The nerve f ...
... (a) Input from the right half of the visual field strikes the left side of each retina and is transmitted to the left hemisphere (shown in red). Input from the left half of the visual field strikes the right side of each retina and is transmitted to the right hemisphere (shown in green). The nerve f ...
Neuroscience and Behavior
... A group of forebrain structures including the hypothalamus, amygdala and hippocampus which are involved in motivation, emotion, learning and memory. Hippocampus A structure for creating new memories and integrating them into a network of knowledge so that they can be stored indefinitely in other par ...
... A group of forebrain structures including the hypothalamus, amygdala and hippocampus which are involved in motivation, emotion, learning and memory. Hippocampus A structure for creating new memories and integrating them into a network of knowledge so that they can be stored indefinitely in other par ...
Biological Psychology Modules 3 & 4
... Cerebral Cortex • Sensory Cortex – receives information from our senses – Visual cortex • visual info – Auditory cortex • auditory info – Somatosensory cortex • info from skin • Association cortex – involved in complex cognitive tasks associating words with images • Broca’s area (aphasia) • Wernick ...
... Cerebral Cortex • Sensory Cortex – receives information from our senses – Visual cortex • visual info – Auditory cortex • auditory info – Somatosensory cortex • info from skin • Association cortex – involved in complex cognitive tasks associating words with images • Broca’s area (aphasia) • Wernick ...
Introduction to Psychology
... The Cerebral Cortex Cerebral Cortex the intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres the body’s ultimate control and information ...
... The Cerebral Cortex Cerebral Cortex the intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres the body’s ultimate control and information ...
Chapter 2 PPT Neuroscience and Behavior
... The Cerebral Cortex Cerebral Cortex the intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres the body’s ultimate control and information ...
... The Cerebral Cortex Cerebral Cortex the intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres the body’s ultimate control and information ...
Human brain
The human brain is the main organ of the human nervous system. It is located in the head, protected by the skull. It has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but with a more developed cerebral cortex. Large animals such as whales and elephants have larger brains in absolute terms, but when measured using a measure of relative brain size, which compensates for body size, the quotient for the human brain is almost twice as large as that of a bottlenose dolphin, and three times as large as that of a chimpanzee. Much of the size of the human brain comes from the cerebral cortex, especially the frontal lobes, which are associated with executive functions such as self-control, planning, reasoning, and abstract thought. The area of the cerebral cortex devoted to vision, the visual cortex, is also greatly enlarged in humans compared to other animals.The human cerebral cortex is a thick layer of neural tissue that covers most of the brain. This layer is folded in a way that increases the amount of surface that can fit into the volume available. The pattern of folds is similar across individuals, although there are many small variations. The cortex is divided into four lobes – the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe. (Some classification systems also include a limbic lobe and treat the insular cortex as a lobe.) Within each lobe are numerous cortical areas, each associated with a particular function, including vision, motor control, and language. The left and right sides of the cortex are broadly similar in shape, and most cortical areas are replicated on both sides. Some areas, though, show strong lateralization, particularly areas that are involved in language. In most people, the left hemisphere is dominant for language, with the right hemisphere playing only a minor role. There are other functions, such as visual-spatial ability, for which the right hemisphere is usually dominant.Despite being protected by the thick bones of the skull, suspended in cerebrospinal fluid, and isolated from the bloodstream by the blood–brain barrier, the human brain is susceptible to damage and disease. The most common forms of physical damage are closed head injuries such as a blow to the head, a stroke, or poisoning by a variety of chemicals which can act as neurotoxins, such as ethanol alcohol. Infection of the brain, though serious, is rare because of the biological barriers which protect it. The human brain is also susceptible to degenerative disorders, such as Parkinson's disease, and Alzheimer's disease, (mostly as the result of aging) and multiple sclerosis. A number of psychiatric conditions, such as schizophrenia and clinical depression, are thought to be associated with brain dysfunctions, although the nature of these is not well understood. The brain can also be the site of brain tumors and these can be benign or malignant.There are some techniques for studying the brain that are used in other animals that are just not suitable for use in humans and vice versa. It is easier to obtain individual brain cells taken from other animals, for study. It is also possible to use invasive techniques in other animals such as inserting electrodes into the brain or disabling certains parts of the brain in order to examine the effects on behaviour – techniques that are not possible to be used in humans. However, only humans can respond to complex verbal instructions or be of use in the study of important brain functions such as language and other complex cognitive tasks, but studies from humans and from other animals, can be of mutual help. Medical imaging technologies such as functional neuroimaging and EEG recordings are important techniques in studying the brain. The complete functional understanding of the human brain is an ongoing challenge for neuroscience.