Vestibular senses
... hormonal (master gland) responses. What is the role of the telencephalon in the forebrain? It consists of three main parts: 1. the cerebral cortex (neocortex), which is the youngest, most evolved part of the brain; it integrates sensory information, plans responses and controls the peripheral nervou ...
... hormonal (master gland) responses. What is the role of the telencephalon in the forebrain? It consists of three main parts: 1. the cerebral cortex (neocortex), which is the youngest, most evolved part of the brain; it integrates sensory information, plans responses and controls the peripheral nervou ...
Module 3 - Victor Valley College
... • relatively short neuron whose primary task is making connections between other neurons – Efferent neuron • carry information away from the spinal cord to produce responses in various muscles and organs throughout the body ...
... • relatively short neuron whose primary task is making connections between other neurons – Efferent neuron • carry information away from the spinal cord to produce responses in various muscles and organs throughout the body ...
Modeling the Evolution of Decision Rules in the Human Brain
... people or social structures) — and positive or negative affective states. This region creates such linkages via connections between neural activity patterns in the sensory cortex that reflect past sensory events, and other neural activity patterns in subcortical regions that reflect emotional states ...
... people or social structures) — and positive or negative affective states. This region creates such linkages via connections between neural activity patterns in the sensory cortex that reflect past sensory events, and other neural activity patterns in subcortical regions that reflect emotional states ...
Nervous System - Calgary Christian School
... Frontal Lobe: controls movement (walking and talking), sometimes linked to intellectual activities and personality Temporal Lobe: controls smelling and ...
... Frontal Lobe: controls movement (walking and talking), sometimes linked to intellectual activities and personality Temporal Lobe: controls smelling and ...
Ross Chezem
... Travis Hammenheimer will have to travel along the nerve in the finger which will lead to the median nerve. If he keeps going along the median nerve he will eventually reach the brachial plexus which is located in the shoulder area of the body. If Travis keeps traveling up the brachial plexus he will ...
... Travis Hammenheimer will have to travel along the nerve in the finger which will lead to the median nerve. If he keeps going along the median nerve he will eventually reach the brachial plexus which is located in the shoulder area of the body. If Travis keeps traveling up the brachial plexus he will ...
Jeopardy - Zion-Benton Township High School
... Brain & Addiction B: The limbic system is involved in emotions, learning and memory, and other functions necessary for survival. The reward circuit is part of the limbic system and is activated by pleasurable activities, such as hanging out with friends and by drugs of abuse. ...
... Brain & Addiction B: The limbic system is involved in emotions, learning and memory, and other functions necessary for survival. The reward circuit is part of the limbic system and is activated by pleasurable activities, such as hanging out with friends and by drugs of abuse. ...
Descending Spinal Tracts
... Receptors - also called hair cells encode location and movement relative to gravity ...
... Receptors - also called hair cells encode location and movement relative to gravity ...
Sacrificing America On The Altar Of Mediocrity
... Statistical data reflects the same increase in sedentary life for children in other activities as well. In most any area you want to compare, you would find the same. Far more time today is spent by children watching television and playing video games and far less time is spent outside running aroun ...
... Statistical data reflects the same increase in sedentary life for children in other activities as well. In most any area you want to compare, you would find the same. Far more time today is spent by children watching television and playing video games and far less time is spent outside running aroun ...
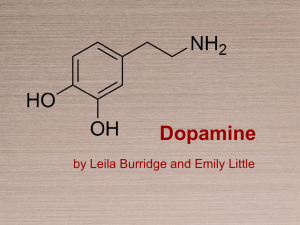
Dopamine 2013
... ● http://www.news-medical.net/health/What-is-Dopamine.aspx ● http://www.news-medical.net/health/Dopamine-Functions.aspx ● http://www.livestrong.com/article/195851-what-are-the-causes-of-lowdopamine-levels/ ...
... ● http://www.news-medical.net/health/What-is-Dopamine.aspx ● http://www.news-medical.net/health/Dopamine-Functions.aspx ● http://www.livestrong.com/article/195851-what-are-the-causes-of-lowdopamine-levels/ ...
Neuroplasticity
... Hippocampus • the subiculum • hippocampus = hippocampus proper = Ammon’s horn • dentate gyrus – a thin band of cortex that lies on the upper surface of the parahippocampal gyrus. – an input centre and receives signals that are relayed to it via the enthorhinal cortex and its cells project to cells ...
... Hippocampus • the subiculum • hippocampus = hippocampus proper = Ammon’s horn • dentate gyrus – a thin band of cortex that lies on the upper surface of the parahippocampal gyrus. – an input centre and receives signals that are relayed to it via the enthorhinal cortex and its cells project to cells ...
Part I - QIBA Wiki
... Figure 3. Potential method to link structural MRI features to amyloid PET biomarker signal levels (modified from fig. 5 of J et al. Lancet Neurol, vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 207–216, Feb. 2013). Hypothetical model of dynamic biomarkers of the A|zheimer's disease pathological cascade over time (years). Neu ...
... Figure 3. Potential method to link structural MRI features to amyloid PET biomarker signal levels (modified from fig. 5 of J et al. Lancet Neurol, vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 207–216, Feb. 2013). Hypothetical model of dynamic biomarkers of the A|zheimer's disease pathological cascade over time (years). Neu ...
The impact of brain science on education
... cerebrum. The cerebrum is divided into two halves (right and left hemispheres) by a deep fissure. Each hemisphere has its own specialties but they work together through a thick bundle of nerves, called the corpus callosum, at the base of the fissure. Each hemisphere controls functions that for reaso ...
... cerebrum. The cerebrum is divided into two halves (right and left hemispheres) by a deep fissure. Each hemisphere has its own specialties but they work together through a thick bundle of nerves, called the corpus callosum, at the base of the fissure. Each hemisphere controls functions that for reaso ...
International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science
... Here, instead of a central nervous system, there are decentralized nerve nets where sensory neurons communicate with motor neurons by electric signals. This communication can be seen as a logic circuit where some action is done if signals from a certain group of input sensory neurons are present. Th ...
... Here, instead of a central nervous system, there are decentralized nerve nets where sensory neurons communicate with motor neurons by electric signals. This communication can be seen as a logic circuit where some action is done if signals from a certain group of input sensory neurons are present. Th ...
Slide 1
... • Three paired fiber tracts connect the cerebellum to the brain stem – Superior peduncles connect the cerebellum to the midbrain – Middle peduncles connect the pons to the cerebellum – Inferior peduncles connect the medulla to the cerebellum ...
... • Three paired fiber tracts connect the cerebellum to the brain stem – Superior peduncles connect the cerebellum to the midbrain – Middle peduncles connect the pons to the cerebellum – Inferior peduncles connect the medulla to the cerebellum ...
Cortex
... (a) In one version of their task the monkey was presented with a color cue and was required to retain it for up to 20 seconds prior to the choice. They identified cells that fired differentially to specific colors of the sample and choice. (b) Some of these cells maintained high levels of activity d ...
... (a) In one version of their task the monkey was presented with a color cue and was required to retain it for up to 20 seconds prior to the choice. They identified cells that fired differentially to specific colors of the sample and choice. (b) Some of these cells maintained high levels of activity d ...
Ch. 7 - Nervous System
... • The dendrite of the next neuron has receptors that are stimulated by the neurotransmitter • An action potential (impulse) is started ...
... • The dendrite of the next neuron has receptors that are stimulated by the neurotransmitter • An action potential (impulse) is started ...
BRAINS OF NORWAY
... In the lab, they adapted the standard experimental technique for studying place cells: implanting electrodes directly into a rat’s hippocampus and recording from them as the animal runs freely in a large box (see ‘A sense of place’). The electrodes — which are sensitive enough to pick up activity fr ...
... In the lab, they adapted the standard experimental technique for studying place cells: implanting electrodes directly into a rat’s hippocampus and recording from them as the animal runs freely in a large box (see ‘A sense of place’). The electrodes — which are sensitive enough to pick up activity fr ...
Human brain
The human brain is the main organ of the human nervous system. It is located in the head, protected by the skull. It has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but with a more developed cerebral cortex. Large animals such as whales and elephants have larger brains in absolute terms, but when measured using a measure of relative brain size, which compensates for body size, the quotient for the human brain is almost twice as large as that of a bottlenose dolphin, and three times as large as that of a chimpanzee. Much of the size of the human brain comes from the cerebral cortex, especially the frontal lobes, which are associated with executive functions such as self-control, planning, reasoning, and abstract thought. The area of the cerebral cortex devoted to vision, the visual cortex, is also greatly enlarged in humans compared to other animals.The human cerebral cortex is a thick layer of neural tissue that covers most of the brain. This layer is folded in a way that increases the amount of surface that can fit into the volume available. The pattern of folds is similar across individuals, although there are many small variations. The cortex is divided into four lobes – the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe. (Some classification systems also include a limbic lobe and treat the insular cortex as a lobe.) Within each lobe are numerous cortical areas, each associated with a particular function, including vision, motor control, and language. The left and right sides of the cortex are broadly similar in shape, and most cortical areas are replicated on both sides. Some areas, though, show strong lateralization, particularly areas that are involved in language. In most people, the left hemisphere is dominant for language, with the right hemisphere playing only a minor role. There are other functions, such as visual-spatial ability, for which the right hemisphere is usually dominant.Despite being protected by the thick bones of the skull, suspended in cerebrospinal fluid, and isolated from the bloodstream by the blood–brain barrier, the human brain is susceptible to damage and disease. The most common forms of physical damage are closed head injuries such as a blow to the head, a stroke, or poisoning by a variety of chemicals which can act as neurotoxins, such as ethanol alcohol. Infection of the brain, though serious, is rare because of the biological barriers which protect it. The human brain is also susceptible to degenerative disorders, such as Parkinson's disease, and Alzheimer's disease, (mostly as the result of aging) and multiple sclerosis. A number of psychiatric conditions, such as schizophrenia and clinical depression, are thought to be associated with brain dysfunctions, although the nature of these is not well understood. The brain can also be the site of brain tumors and these can be benign or malignant.There are some techniques for studying the brain that are used in other animals that are just not suitable for use in humans and vice versa. It is easier to obtain individual brain cells taken from other animals, for study. It is also possible to use invasive techniques in other animals such as inserting electrodes into the brain or disabling certains parts of the brain in order to examine the effects on behaviour – techniques that are not possible to be used in humans. However, only humans can respond to complex verbal instructions or be of use in the study of important brain functions such as language and other complex cognitive tasks, but studies from humans and from other animals, can be of mutual help. Medical imaging technologies such as functional neuroimaging and EEG recordings are important techniques in studying the brain. The complete functional understanding of the human brain is an ongoing challenge for neuroscience.