Di (n)-Butyl Phthalate Induced Neuronal Perturbations in Rat Brain
... showing alterations in the cytoarchitecture of CC and CB. Brain cortex was characterised by the severity of focal aggregates of inflammatory infiltration upon DBP exposure while F1 rats showed neuroglial cells with degenerative changes. While F2 and F3 rats had a focal aggregate of inflammatory infi ...
... showing alterations in the cytoarchitecture of CC and CB. Brain cortex was characterised by the severity of focal aggregates of inflammatory infiltration upon DBP exposure while F1 rats showed neuroglial cells with degenerative changes. While F2 and F3 rats had a focal aggregate of inflammatory infi ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... ANS structures in the PNS – ganglionic neurons, the adrenal medulla, and all autonomic ganglia – derive from the neural crest ...
... ANS structures in the PNS – ganglionic neurons, the adrenal medulla, and all autonomic ganglia – derive from the neural crest ...
Comparative molecular neuroanatomy of mammalian neocortex
... cortical inputs and layers 2/3 project to other cortical areas. Although this is a very simplified view with many exceptions, there appears to exist a canonical cortical circuit that can adapt to a range of information processing (Douglas and Martin 2004; Bannister 2005). The current evidence indica ...
... cortical inputs and layers 2/3 project to other cortical areas. Although this is a very simplified view with many exceptions, there appears to exist a canonical cortical circuit that can adapt to a range of information processing (Douglas and Martin 2004; Bannister 2005). The current evidence indica ...
Commentary: Saccadic eye movements
... There are also important inputs to the brainstem saccadic burst generator that arise from the cerebellum (see Scudder et al., 2002 for review). The superior colliculus and oculomotor areas in the frontal cortex project to the nucleus reticularis tegmenti pontis and other pontine nuclei. Neurons in t ...
... There are also important inputs to the brainstem saccadic burst generator that arise from the cerebellum (see Scudder et al., 2002 for review). The superior colliculus and oculomotor areas in the frontal cortex project to the nucleus reticularis tegmenti pontis and other pontine nuclei. Neurons in t ...
Physiological Psychology
... are sensory organs that give one a visual image of the surrounding area. The ears also are sensory organs. The central nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. The brain can store information, generate thoughts, create ambition, and determine reactions that the body performs in respo ...
... are sensory organs that give one a visual image of the surrounding area. The ears also are sensory organs. The central nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. The brain can store information, generate thoughts, create ambition, and determine reactions that the body performs in respo ...
The Nervous System
... • Satellite cells (amphicytes): surround and support neuron cell bodies in the PNS, helping to regulate the environment around neurons – These cells are similar in function to astrocytes of the CNS • Schwann cells (neurilemmocytes): form myelin sheaths (neurilemma) around all axons outside of the CN ...
... • Satellite cells (amphicytes): surround and support neuron cell bodies in the PNS, helping to regulate the environment around neurons – These cells are similar in function to astrocytes of the CNS • Schwann cells (neurilemmocytes): form myelin sheaths (neurilemma) around all axons outside of the CN ...
A part of the cholinergic fibers in mouse superior cervical ganglia
... GAD65-immunopositive baskets per one section (12 grmu m thick) were 48.6+/-9.8 (n=5). All GAD65-immunopositive boutons exhibited VAchT immunoreactivity (Fig. 1). GAD65-immunopositive boutons and nNOS-immunopositive fibers often encircled the same postganglionic neurons and were very close to each ot ...
... GAD65-immunopositive baskets per one section (12 grmu m thick) were 48.6+/-9.8 (n=5). All GAD65-immunopositive boutons exhibited VAchT immunoreactivity (Fig. 1). GAD65-immunopositive boutons and nNOS-immunopositive fibers often encircled the same postganglionic neurons and were very close to each ot ...
ling411-11-Columns - OWL-Space
... The cortex in each hemisphere • Appears to be a three-dimensional structure • But it is actually very thin and very broad The grooves – sulci – are there because the cortex is “crumpled” so it will fit inside the skull ...
... The cortex in each hemisphere • Appears to be a three-dimensional structure • But it is actually very thin and very broad The grooves – sulci – are there because the cortex is “crumpled” so it will fit inside the skull ...
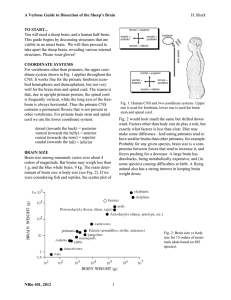
Neural and Voluntary Control of Breathing
... – anxiety triggered state in which breathing is so rapid that it expels CO2 from the body faster than it is produced – CO2 levels drop – pH rises causing the cerebral arteries to constrict reducing cerebral perfusion which may cause dizziness or fainting – can be brought under control by having the ...
... – anxiety triggered state in which breathing is so rapid that it expels CO2 from the body faster than it is produced – CO2 levels drop – pH rises causing the cerebral arteries to constrict reducing cerebral perfusion which may cause dizziness or fainting – can be brought under control by having the ...
Chapter 12 PowerPoint - Hillsborough Community College
... hemispheres • Third ventricle in the diencephalon • Fourth ventricle in the hindbrain, dorsal to the pons, develops from the lumen of the neural ...
... hemispheres • Third ventricle in the diencephalon • Fourth ventricle in the hindbrain, dorsal to the pons, develops from the lumen of the neural ...
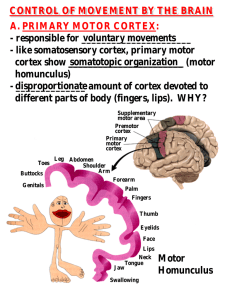
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR
... -caudate and putamen neurons then send their axons to ____________________; internal globus pallidus - in turn, GP axons contact the ________________, thalamus (VA/VL) which feedback onto cortex to modulate movement force. ...
... -caudate and putamen neurons then send their axons to ____________________; internal globus pallidus - in turn, GP axons contact the ________________, thalamus (VA/VL) which feedback onto cortex to modulate movement force. ...
A Verbose Guide to Dissection of the Sheep`s Brain H
... a good-sized optic nerve. In species that rely more on other sensory modalities, the optic nerve is punier (see alligator). In the Ganges River dolphin, "this nerve is as thin as a thread" (Pilleri & Gihr, 1970), as vision is of little use in its turgid environment. The 5th cranial nerve, the trigem ...
... a good-sized optic nerve. In species that rely more on other sensory modalities, the optic nerve is punier (see alligator). In the Ganges River dolphin, "this nerve is as thin as a thread" (Pilleri & Gihr, 1970), as vision is of little use in its turgid environment. The 5th cranial nerve, the trigem ...
The Isotropic Fractionator: A Fast, Reliable Method to Determine
... al., 2014). These include studies of the entire human brain (Azevedo et al., 2009), of the distribution of neurons across functional areas of the mouse cerebral cortex (Herculano-Houzel et al., 2013), across the human cerebral cortex (Ribeiro et al., 2013), and of the changes in the cellular composi ...
... al., 2014). These include studies of the entire human brain (Azevedo et al., 2009), of the distribution of neurons across functional areas of the mouse cerebral cortex (Herculano-Houzel et al., 2013), across the human cerebral cortex (Ribeiro et al., 2013), and of the changes in the cellular composi ...
cerebral cortex, sensations and movements
... composition, the cerebral cortex (with a thickness between 2mm and 4mm), which is composed of gray Cerebrum (which comprise about 80% of the matter (composed of local networks of neurons with brain) is consisted of right hemisphere and left dendrites and short unmyelinated axons), being located hemi ...
... composition, the cerebral cortex (with a thickness between 2mm and 4mm), which is composed of gray Cerebrum (which comprise about 80% of the matter (composed of local networks of neurons with brain) is consisted of right hemisphere and left dendrites and short unmyelinated axons), being located hemi ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... (In contrast to the large diameter and rapidly conducting α -motor neurons, preganglionic axons are small-diameter, myelinated, relatively slowly conducting B fibers.) (The axons of the postganglionic neurons are mostly unmyelinated C fibers and terminate on the visceral effectors.) • Neurotransmitt ...
... (In contrast to the large diameter and rapidly conducting α -motor neurons, preganglionic axons are small-diameter, myelinated, relatively slowly conducting B fibers.) (The axons of the postganglionic neurons are mostly unmyelinated C fibers and terminate on the visceral effectors.) • Neurotransmitt ...
Consolidation of motor memory
... the CS elicits precisely timed eyelid closure that precedes the US [7]. This defensive conditioned response (CR) can persist for long periods in the absence of exposure to the CS, but can be extinguished by relatively few trials of the CS without the US [8,9]. Extinction does not erase the motor mem ...
... the CS elicits precisely timed eyelid closure that precedes the US [7]. This defensive conditioned response (CR) can persist for long periods in the absence of exposure to the CS, but can be extinguished by relatively few trials of the CS without the US [8,9]. Extinction does not erase the motor mem ...
Cortical Neurons and Circuits: A Tutorial
... hemispheres. It is the ‘gray matter’ of the brain lying atop the cerebral ‘white matter’ composed of myelinated axons that interconnect different regions of the brain. All the higher-level psychophysical functions sensory perception, object- and event-representation, planning, and decision making ar ...
... hemispheres. It is the ‘gray matter’ of the brain lying atop the cerebral ‘white matter’ composed of myelinated axons that interconnect different regions of the brain. All the higher-level psychophysical functions sensory perception, object- and event-representation, planning, and decision making ar ...
Neurotransmitter Effects
... – Increases the metabolic rate of body cells – Raises _ – Mobilizes _ – Stimulates the reticular activating system (RAS) of the brain, increasing mental alertness ...
... – Increases the metabolic rate of body cells – Raises _ – Mobilizes _ – Stimulates the reticular activating system (RAS) of the brain, increasing mental alertness ...
Cortical Neurons and Circuits: A Tutorial
... hemispheres. It is the ‘gray matter’ of the brain lying atop the cerebral ‘white matter’ composed of myelinated axons that interconnect different regions of the brain. All the higher-level psychophysical functions sensory perception, object- and event-representation, planning, and decision making ar ...
... hemispheres. It is the ‘gray matter’ of the brain lying atop the cerebral ‘white matter’ composed of myelinated axons that interconnect different regions of the brain. All the higher-level psychophysical functions sensory perception, object- and event-representation, planning, and decision making ar ...
Lecture 12b - Spinal Cord
... • The larger the receptive field, the more difficult it is to localize a stimulus ...
... • The larger the receptive field, the more difficult it is to localize a stimulus ...
Lecture 12b - Spinal Cord
... • The larger the receptive field, the more difficult it is to localize a stimulus ...
... • The larger the receptive field, the more difficult it is to localize a stimulus ...
Loss of autophagy in the central nervous system causes
... several ubiquitin dots of small to large size, only a small number of cerebellar Purkinje cells stained for ubiquitin, and the immunoreactive dots were of small size (Fig. 3d). Electron microscopy showed that Atg7 flox/flox; nestin-Cre hypothalamic neurons had circular or elliptical large structures ...
... several ubiquitin dots of small to large size, only a small number of cerebellar Purkinje cells stained for ubiquitin, and the immunoreactive dots were of small size (Fig. 3d). Electron microscopy showed that Atg7 flox/flox; nestin-Cre hypothalamic neurons had circular or elliptical large structures ...
Specification of Cerebral Cortical Areas
... remarkable product of brain evolution, not only because it makes up two-thirds of the neuronal mass and contains about three-quarters of all our synapses, but also because it is the structure that most distinctively sets us apart from other species. One of the most prominent features of the cerebral ...
... remarkable product of brain evolution, not only because it makes up two-thirds of the neuronal mass and contains about three-quarters of all our synapses, but also because it is the structure that most distinctively sets us apart from other species. One of the most prominent features of the cerebral ...
Muscle Contraction
... perform the movement. These programs are broken down into subprograms that determine the movements of individual joints. The programs and subprograms are transmitted through descending pathways to the lowest control level. b. Structures: sensorimotor cortex, cerebellum, parts of basal nuclei, some b ...
... perform the movement. These programs are broken down into subprograms that determine the movements of individual joints. The programs and subprograms are transmitted through descending pathways to the lowest control level. b. Structures: sensorimotor cortex, cerebellum, parts of basal nuclei, some b ...
Chapter 15: Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic
... Two types of axons carry painful sensations: Type A and Type C fibers. 1. Myelinated Type A fibers carry sensations of fast pain, or prickling pain, such as that caused by an injection or deep cut. These sensations reach the CNS very quickly and often trigger somatic reflexes. They are also relayed ...
... Two types of axons carry painful sensations: Type A and Type C fibers. 1. Myelinated Type A fibers carry sensations of fast pain, or prickling pain, such as that caused by an injection or deep cut. These sensations reach the CNS very quickly and often trigger somatic reflexes. They are also relayed ...
Anatomy of the cerebellum

The anatomy of the cerebellum can be viewed at three levels. At the level of large-scale anatomy, the cerebellum consists of a tightly folded and crumpled layer of cortex, with white matter underneath, several deep nuclei embedded in the white matter, and a fluid-filled ventricle in the middle. At the intermediate level, the cerebellum and its auxiliary structures can be decomposed into several hundred or thousand independently functioning modules or ""microzones"". At the microscopic level, each module consists of the same small set of neuronal elements, laid out with a highly stereotyped geometry.