Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
... This talk will provide an overview of this state-of-the-art brain imaging technique. MEG is a non-invasive technique to study cognitive functions and their disorders in both adults and children. MEG can measure the faint magnetic fields generated by large numbers of neurons in the cortex, providing ...
... This talk will provide an overview of this state-of-the-art brain imaging technique. MEG is a non-invasive technique to study cognitive functions and their disorders in both adults and children. MEG can measure the faint magnetic fields generated by large numbers of neurons in the cortex, providing ...
Human Physiology
... Causes temporary euphoria or disorientation More damaging to the lungs than cigarettes Quadruples chances of heart attacks Long term effects on the brain-Memory loss, inability to concentrate, difficulty with problem solving, uncoordinated movements, problems with sensory and time perception ...
... Causes temporary euphoria or disorientation More damaging to the lungs than cigarettes Quadruples chances of heart attacks Long term effects on the brain-Memory loss, inability to concentrate, difficulty with problem solving, uncoordinated movements, problems with sensory and time perception ...
The Nervous System
... Parkinson’s Disease – degeneration of nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine; leads to uncoordinated muscular movement Multiple Sclerosis – auto-immune disease; destruction of nerve cell insulation Alzheimer’s – mental deterioration usually associated with age Epilepsy – sudden episo ...
... Parkinson’s Disease – degeneration of nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine; leads to uncoordinated muscular movement Multiple Sclerosis – auto-immune disease; destruction of nerve cell insulation Alzheimer’s – mental deterioration usually associated with age Epilepsy – sudden episo ...
University of Split Danica Škara, PhD e
... individual development. Long-term memory is either achieved by changes on the synapses (more strength connections) or by changes of functional units (new cell assemblies). A connection can become stronger when the same path is used often, the other way round a connection that is rarely used will wea ...
... individual development. Long-term memory is either achieved by changes on the synapses (more strength connections) or by changes of functional units (new cell assemblies). A connection can become stronger when the same path is used often, the other way round a connection that is rarely used will wea ...
6-Janata_Natarajan - School of Electronic Engineering and
... • Activation consistently appears in the vicinity of the B-major label • However, activation is biased toward different key regions, and the biasing depends on the harmonic structure of the input stimuli • The 2.0 s time-scale activation patterns indicate the stable key. This analysis can be extende ...
... • Activation consistently appears in the vicinity of the B-major label • However, activation is biased toward different key regions, and the biasing depends on the harmonic structure of the input stimuli • The 2.0 s time-scale activation patterns indicate the stable key. This analysis can be extende ...
Cognitive Science News
... Stanford University Palo Alto, California The annual meeting of the Cognitive Science Society brings together researchers from many fields-including artificial intelligence, education, linguistics, philosophy, and psychology-who hold a common goal: understanding the nature of the mind. The Society’s ...
... Stanford University Palo Alto, California The annual meeting of the Cognitive Science Society brings together researchers from many fields-including artificial intelligence, education, linguistics, philosophy, and psychology-who hold a common goal: understanding the nature of the mind. The Society’s ...
Cognitive Architecture www.AssignmentPoint.com A cognitive
... In 1983 John R. Anderson published the seminal work in this area, entitled The Architecture of Cognition. One can distinguish between the theory of cognition and the implementation of the theory. The theory of cognition outlined the structure of the various parts of the mind and made commitments to ...
... In 1983 John R. Anderson published the seminal work in this area, entitled The Architecture of Cognition. One can distinguish between the theory of cognition and the implementation of the theory. The theory of cognition outlined the structure of the various parts of the mind and made commitments to ...
The Blank Slate
... Evolutionary Psychology researches the adaptive design or purpose of the mind as it was engineered in ancestral environments. It examines the way natural selection simulated engineering processes to examine the ways in which how well something works played a causal role in the way it originated (52) ...
... Evolutionary Psychology researches the adaptive design or purpose of the mind as it was engineered in ancestral environments. It examines the way natural selection simulated engineering processes to examine the ways in which how well something works played a causal role in the way it originated (52) ...
Scientific priorities for the BRAIN Initiative
... that we therefore need to invest heavily in technology that would enable us to record from many more neurons than we can currently. Electrical probes must be made smaller and more durable, and we need to develop less invasive devices that allow longer recording with higher spatial and temporal resol ...
... that we therefore need to invest heavily in technology that would enable us to record from many more neurons than we can currently. Electrical probes must be made smaller and more durable, and we need to develop less invasive devices that allow longer recording with higher spatial and temporal resol ...
The Nervous System
... It consists of the brain and spinal cord. Cerebrospinal fluid bathes the brain and spinal cord and acts as a shock absorber to protect the central nervous system! It allows for exchange of nutrients and waste products between blood and nervous tissue. ...
... It consists of the brain and spinal cord. Cerebrospinal fluid bathes the brain and spinal cord and acts as a shock absorber to protect the central nervous system! It allows for exchange of nutrients and waste products between blood and nervous tissue. ...
The Review
... 5. What are the lobes of the brain? What is each lobe responsible for? 6. What is the somatosensory cortex and primary motor cortex? 7. Who is Phineas Gage, what happen to him, what were the effects? 8. What parts make up the hindbrain? What is the function of each part? 9. What makes up the midbrai ...
... 5. What are the lobes of the brain? What is each lobe responsible for? 6. What is the somatosensory cortex and primary motor cortex? 7. Who is Phineas Gage, what happen to him, what were the effects? 8. What parts make up the hindbrain? What is the function of each part? 9. What makes up the midbrai ...
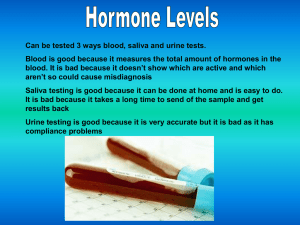
Hormone Levels and EEG (Ashanti)
... scalp. The electrical pulses are know as EEG and show an electrical signal caused by the neurones in the brain EEG is useful because the time resolution is very high. As other methods for researching brain activity have time resolution between seconds and minutes, the EEG has a resolution down to su ...
... scalp. The electrical pulses are know as EEG and show an electrical signal caused by the neurones in the brain EEG is useful because the time resolution is very high. As other methods for researching brain activity have time resolution between seconds and minutes, the EEG has a resolution down to su ...
Slide 1
... The Nervous System • The control center for the entire body. • Made up of brain, spinal cord, and neurons. ...
... The Nervous System • The control center for the entire body. • Made up of brain, spinal cord, and neurons. ...
Madison Pejsa Pd.4
... continuous with the spinal cord and comprises the medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain, and parts of the hypothalamus, functioning in the control of the reflexes and such essential internal mechanisms as respiration and heartbeat. Cerebellum- A large portion of the brain, serving to coordinate voluntar ...
... continuous with the spinal cord and comprises the medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain, and parts of the hypothalamus, functioning in the control of the reflexes and such essential internal mechanisms as respiration and heartbeat. Cerebellum- A large portion of the brain, serving to coordinate voluntar ...
Health - Nervous System Review
... to muscle cells 4. Eyes, ears, tongue, nose, and skin are examples of ___ organs. 5. Part of the brain that controls actions of muscles and maintains balance 6. Gap between two neurons 7. Nervous system that consists of a network of nerves branching out from the central nervous system 9. Automatic r ...
... to muscle cells 4. Eyes, ears, tongue, nose, and skin are examples of ___ organs. 5. Part of the brain that controls actions of muscles and maintains balance 6. Gap between two neurons 7. Nervous system that consists of a network of nerves branching out from the central nervous system 9. Automatic r ...
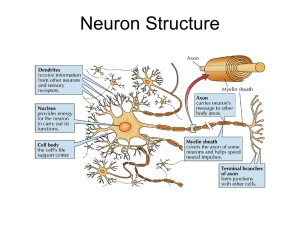
Neuroscience
... Neurons contain cytoplasm, mitochondria and other organelles. Neurons carry out basic cellular processes such as protein synthesis and energy production. ...
... Neurons contain cytoplasm, mitochondria and other organelles. Neurons carry out basic cellular processes such as protein synthesis and energy production. ...
Brain Plasticity
... In one of them, a surgeon in his 50s suffers a stroke. His left arm is paralyzed. During his rehabilitation, his good arm and hand are immobilized, and he is set to cleaning tables. The task is at first impossible. Then slowly the bad arm remembers how to move. He learns to write again, to play tenn ...
... In one of them, a surgeon in his 50s suffers a stroke. His left arm is paralyzed. During his rehabilitation, his good arm and hand are immobilized, and he is set to cleaning tables. The task is at first impossible. Then slowly the bad arm remembers how to move. He learns to write again, to play tenn ...
Unit 3ABC Reading and Study Guide
... How does the endocrine system- the boy’s slower information system- transmit its messages? How do neuroscientists study the brain’s connections to behavior and mind? What are the functions of important lower-level brain structures? What functions are served by the various cerebral cortex regions? Wh ...
... How does the endocrine system- the boy’s slower information system- transmit its messages? How do neuroscientists study the brain’s connections to behavior and mind? What are the functions of important lower-level brain structures? What functions are served by the various cerebral cortex regions? Wh ...
Chapter 2
... • Cortex refers to the outer covering of the brain – Consists of left and right hemispheres – Cortex is divided into lobes • Frontal: Self-awareness, planning, voluntary movement, emotional control, speech, working memory • Parietal: Body sensations • Occipital: Vision • Temporal: Hearing, language ...
... • Cortex refers to the outer covering of the brain – Consists of left and right hemispheres – Cortex is divided into lobes • Frontal: Self-awareness, planning, voluntary movement, emotional control, speech, working memory • Parietal: Body sensations • Occipital: Vision • Temporal: Hearing, language ...
Slide 1
... Studying the Brain • Imaging techniques allow the living brain to be studied for its activity during behavior – CT scans (computed tomography) used to detect brain structure abnormalities in people w/ mental illness meningitis ...
... Studying the Brain • Imaging techniques allow the living brain to be studied for its activity during behavior – CT scans (computed tomography) used to detect brain structure abnormalities in people w/ mental illness meningitis ...