Worksheet 3: Series vs Parallel Circuits and Combo`s
... 1. A series circuit has 3 resistors of values 200 Ω, 300 Ω and 700 Ω all connected to a 6-Volt power supply. a. What is the total resistance of the circuit? b. What current flows from the battery? c. What is the current through, voltage across and power dissipated by the 300 Ω resistor? d. Which of ...
... 1. A series circuit has 3 resistors of values 200 Ω, 300 Ω and 700 Ω all connected to a 6-Volt power supply. a. What is the total resistance of the circuit? b. What current flows from the battery? c. What is the current through, voltage across and power dissipated by the 300 Ω resistor? d. Which of ...
Three Phase Circuits Ch 4 - Biosystems and Agricultural Engineering
... The loss energy shows up as voltage drop. All conductors have resistance = all conductors have voltage drop. What must be avoided is excessive voltage drop. ...
... The loss energy shows up as voltage drop. All conductors have resistance = all conductors have voltage drop. What must be avoided is excessive voltage drop. ...
Alternative assignment for furlough day – Analog Galvanometer
... 11. Why would we want to use an external resistor in conjunction with the galvanometer to measure current? Be specific. 12. Do we want this external resistor to have large or small resistance (to measure current)? How specifically does the ________ resistance external resistor help us get the range ...
... 11. Why would we want to use an external resistor in conjunction with the galvanometer to measure current? Be specific. 12. Do we want this external resistor to have large or small resistance (to measure current)? How specifically does the ________ resistance external resistor help us get the range ...
This course contains - College of Micronesia
... 4. Define magnetism and electromagnetism and their characteristics; describe how these characteristics are utilized in the operation of the relay, magnetic circuit breaker and meter. 5. Describe the function of the multimeter and its controls. Safely and accurately use a multimeter to measure the ci ...
... 4. Define magnetism and electromagnetism and their characteristics; describe how these characteristics are utilized in the operation of the relay, magnetic circuit breaker and meter. 5. Describe the function of the multimeter and its controls. Safely and accurately use a multimeter to measure the ci ...
Chapter #9 electric-current-circuits-chapter
... 2. If the current through a resister were 0.5 A; how much electric charge would flow through it in 2 min? 3. How long would it take for 300 C of electric charge to pass through an aluminum wire if the current through it is 0.6 A? ...
... 2. If the current through a resister were 0.5 A; how much electric charge would flow through it in 2 min? 3. How long would it take for 300 C of electric charge to pass through an aluminum wire if the current through it is 0.6 A? ...
Unit Three - geetaselectronics
... What can you do with Op amps? • You can make music louder when they are used in stereo equipment. • You can amplify the heartbeat by using them in medical cardiographs. • You can use them as comparators in heating systems. • You can use them for Math operations like summing, integration etc. ...
... What can you do with Op amps? • You can make music louder when they are used in stereo equipment. • You can amplify the heartbeat by using them in medical cardiographs. • You can use them as comparators in heating systems. • You can use them for Math operations like summing, integration etc. ...
RESiSTORS 101
... What is a Resistor? • The resistor is the most common and well-known of the passive electrical components. A resistor resists or limits the flow of electric current in a circuit. There are many uses for resistors: they are used to drop voltage, limit current, attenuate signals, act as heaters, act ...
... What is a Resistor? • The resistor is the most common and well-known of the passive electrical components. A resistor resists or limits the flow of electric current in a circuit. There are many uses for resistors: they are used to drop voltage, limit current, attenuate signals, act as heaters, act ...
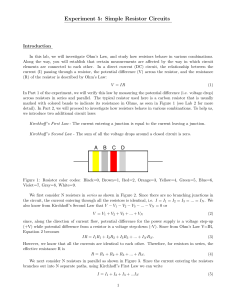
Experiment 5: Simple Resistor Circuits
... have one Voltmeter, so hook it up initially across R1 (your first resistor). Setting the power supply to 10 V, measure the current in the circuit, and the potential difference across R1 . Record this as V1 . Move the Voltmeter to measure the potential difference across R2 and record this as V2 . Re ...
... have one Voltmeter, so hook it up initially across R1 (your first resistor). Setting the power supply to 10 V, measure the current in the circuit, and the potential difference across R1 . Record this as V1 . Move the Voltmeter to measure the potential difference across R2 and record this as V2 . Re ...
Document
... 26.5.IDENTIFY: The equivalent resistance will vary for the different connections because the series-parallel combinations vary, and hence the current will vary. SET UP: First calculate the equivalent resistance using the series-parallel formulas, then use Ohm’s law (V = RI) to find the current. EXEC ...
... 26.5.IDENTIFY: The equivalent resistance will vary for the different connections because the series-parallel combinations vary, and hence the current will vary. SET UP: First calculate the equivalent resistance using the series-parallel formulas, then use Ohm’s law (V = RI) to find the current. EXEC ...
Summary of lesson
... Answer: y = mx + b (b = 0) I = Vt x 1/Rt or I = V/R This is a rearrangement of Ohm's Law Q24. What do you notice about the values of the two resistances in series? Answer: Ra + Rb = Rab or total resistance; resistances add in series Q25. What do you notice about the voltages across the two resistors ...
... Answer: y = mx + b (b = 0) I = Vt x 1/Rt or I = V/R This is a rearrangement of Ohm's Law Q24. What do you notice about the values of the two resistances in series? Answer: Ra + Rb = Rab or total resistance; resistances add in series Q25. What do you notice about the voltages across the two resistors ...
Experiment 5: Simple Resistor Circuits
... Along the way, you will establish that certain measurements are affected by the way in which circuit elements are connected to each other. In a direct current (DC) circuit, the relationship between the current (I) passing through a resistor, the potential difference (V) across the resistor, and the ...
... Along the way, you will establish that certain measurements are affected by the way in which circuit elements are connected to each other. In a direct current (DC) circuit, the relationship between the current (I) passing through a resistor, the potential difference (V) across the resistor, and the ...
Word
... In a parallel circuit, charge flows from one point to another along alternative paths. Circuit rules: 1. The potential difference across components in parallel is the same for each component. 2. The current through a parallel combination is equal to the sum of the currents through the individual com ...
... In a parallel circuit, charge flows from one point to another along alternative paths. Circuit rules: 1. The potential difference across components in parallel is the same for each component. 2. The current through a parallel combination is equal to the sum of the currents through the individual com ...