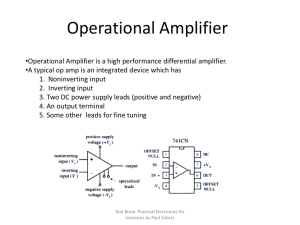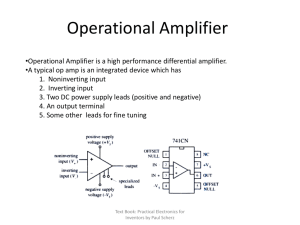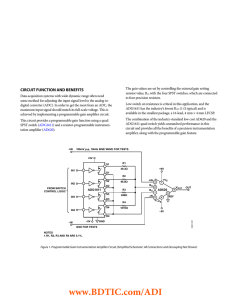
CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
... Excellent layout, grounding, and decoupling techniques must be used to achieve the desired performance from the circuits discussed (see Tutorial MT-031 and Tutorial MT-101). As a minimum, a 4-layer PCB should be used with one ground plane layer, one power plane layer, and two signal layers. ...
... Excellent layout, grounding, and decoupling techniques must be used to achieve the desired performance from the circuits discussed (see Tutorial MT-031 and Tutorial MT-101). As a minimum, a 4-layer PCB should be used with one ground plane layer, one power plane layer, and two signal layers. ...
Chapter 6: Parallel Circuits
... • When two equal sources are connected in parallel – Each source supplies half the required current ...
... • When two equal sources are connected in parallel – Each source supplies half the required current ...
Chapter 3
... Bridge circuits contain resistors that are connected in delta () and wye (Y) configurations. One way to analyze this circuit is to use a -Y or a Y- transformation. Y and connections of resistors are shown below: a ...
... Bridge circuits contain resistors that are connected in delta () and wye (Y) configurations. One way to analyze this circuit is to use a -Y or a Y- transformation. Y and connections of resistors are shown below: a ...
EXPERIMENT NO
... When the negative terminal of the battery is connected to the P-type and positive terminal of the battery is connected to the N-type of the PN junction, the bias applied is known as reverse bias. Under applied reverse bias, holes which form the majority carriers or the P-side moves towards the negat ...
... When the negative terminal of the battery is connected to the P-type and positive terminal of the battery is connected to the N-type of the PN junction, the bias applied is known as reverse bias. Under applied reverse bias, holes which form the majority carriers or the P-side moves towards the negat ...
Electricity and Measurement Experiments
... 1.6 V coulomb) was “shared” between the globes the charge passed through. The total energy transformed into thermal energy and light as charge travelled along a single path through the circuit was equal to the potential energy change of the charge. In Circuit F, for example, when a coulomb of charge ...
... 1.6 V coulomb) was “shared” between the globes the charge passed through. The total energy transformed into thermal energy and light as charge travelled along a single path through the circuit was equal to the potential energy change of the charge. In Circuit F, for example, when a coulomb of charge ...
10 GHz, Class-B, 0.5 V, 130 nm CMOS Cross
... with practical circuit is small. Figure 1 presents the proposed transformation of a crosscoupled oscillator with LC tank using differential inductor. Roman numerals on both schematics correspond to the same nodes in both circuits. Note that there are two loops present in the network. The main loop i ...
... with practical circuit is small. Figure 1 presents the proposed transformation of a crosscoupled oscillator with LC tank using differential inductor. Roman numerals on both schematics correspond to the same nodes in both circuits. Note that there are two loops present in the network. The main loop i ...
Experiment 2: Resistors in Series and Parallel
... 2.5 COMMENTS AND CONCLUSIONS Discuss the reasons for any differences in Table 2.1. Use Ohm’s Law to calculate the current flowing in the circuit It and hence calculate the voltage drop expected across each resistor (e.g. voltage drop across R1 is calculated as VR1 = ItR1, etc). Use the values as ind ...
... 2.5 COMMENTS AND CONCLUSIONS Discuss the reasons for any differences in Table 2.1. Use Ohm’s Law to calculate the current flowing in the circuit It and hence calculate the voltage drop expected across each resistor (e.g. voltage drop across R1 is calculated as VR1 = ItR1, etc). Use the values as ind ...
Basic Laws
... Properties of the bulb control how much current flows and how much power is dissipated (absorbed then emitted as light and heat). As with the circuit elements, we need to know the current through and voltage across the device are ralated. The relationship between the current and voltage can be linea ...
... Properties of the bulb control how much current flows and how much power is dissipated (absorbed then emitted as light and heat). As with the circuit elements, we need to know the current through and voltage across the device are ralated. The relationship between the current and voltage can be linea ...
chapter 2 - UniMAP Portal
... analysis) and to design electrical circuits with desired properties. The circuits are built with circuit elements. ...
... analysis) and to design electrical circuits with desired properties. The circuits are built with circuit elements. ...
Chapter 2
... Georg Simon Ohm (1787–1854), a German physicist, is credited with finding the relationship between current and voltage for a resistor. This relationship is known as Ohm’s law. That is, V r I ...
... Georg Simon Ohm (1787–1854), a German physicist, is credited with finding the relationship between current and voltage for a resistor. This relationship is known as Ohm’s law. That is, V r I ...
tisp61089 programmable overvoltage protectors dual
... tests are done at two levels. After first-level testing the equipment shall not be damaged and shall continue to operate correctly. Under second level testing the equipment shall not become a safety hazard. The equipment is permitted to fail as a result of second-level testing. When the equipment is ...
... tests are done at two levels. After first-level testing the equipment shall not be damaged and shall continue to operate correctly. Under second level testing the equipment shall not become a safety hazard. The equipment is permitted to fail as a result of second-level testing. When the equipment is ...
150QUIZ5ANSWERS Assignment Page
... 1. A parallel circuit contains two or more loads but only one path for current to flow from the source voltage through the loads and back to the source. Ans: False ...
... 1. A parallel circuit contains two or more loads but only one path for current to flow from the source voltage through the loads and back to the source. Ans: False ...