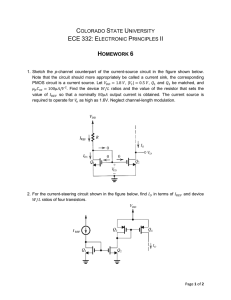
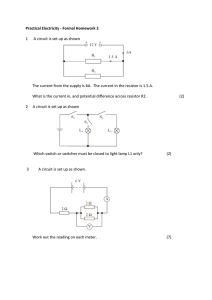
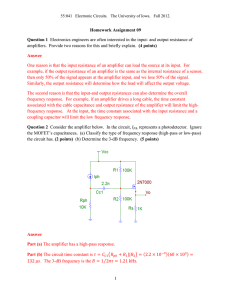
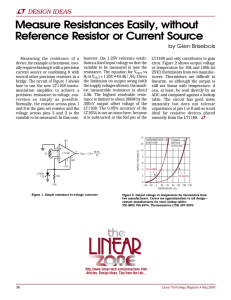
Ohm`s Law Lab
... 1. Connect the source of current, the switch (opened), an ammeter, and a low ohm resistor in series. Place the voltmeter in parallel across the resistance. 2. Use the voltmeter to set the voltage source to 3 volts through the resistor. You will have to change this each time. 3. NOTE Leave the switch ...
... 1. Connect the source of current, the switch (opened), an ammeter, and a low ohm resistor in series. Place the voltmeter in parallel across the resistance. 2. Use the voltmeter to set the voltage source to 3 volts through the resistor. You will have to change this each time. 3. NOTE Leave the switch ...
AP_Physics_C_-_ohmslaw_Lab_II
... Date_____________________PER____ AP Physics C – Ohm’s Law Purpose: To calculate the resistance of 2 resistors, and see if, when connected in series, they act as a single resistor equal to the sum of the two. Materials: Power supply, DMM ( Digital Multimeter), ANALOG ammeter, alligator clip wires, Pa ...
... Date_____________________PER____ AP Physics C – Ohm’s Law Purpose: To calculate the resistance of 2 resistors, and see if, when connected in series, they act as a single resistor equal to the sum of the two. Materials: Power supply, DMM ( Digital Multimeter), ANALOG ammeter, alligator clip wires, Pa ...
Exercise 3.4.1
... Lets consider a solar cell as an ideal pn-junction, for simplicities sake even without the current contributions from the space charge region, but with a built in series resistance Rser and a shunt resistance Rshunt We have the following equivalent circuit diagram (also defining what is meant by a s ...
... Lets consider a solar cell as an ideal pn-junction, for simplicities sake even without the current contributions from the space charge region, but with a built in series resistance Rser and a shunt resistance Rshunt We have the following equivalent circuit diagram (also defining what is meant by a s ...
Physics - cloudfront.net
... • Current is how much water flows through a river (in our case how much electricity flows through the wire) ...
... • Current is how much water flows through a river (in our case how much electricity flows through the wire) ...
Topics for Exam #1
... Conductors, Insulators, and Semiconductors Charge Coulomb Charge/Time = Current DC Current --- Constant, do not change with time Voltage – Joule/Coulomb Resistance and Conductance Resistivity Determine resistance of a piece of material Resistors Standard Values Tolerance Color Coding ...
... Conductors, Insulators, and Semiconductors Charge Coulomb Charge/Time = Current DC Current --- Constant, do not change with time Voltage – Joule/Coulomb Resistance and Conductance Resistivity Determine resistance of a piece of material Resistors Standard Values Tolerance Color Coding ...
Unit 5: Electricity
... negative terminal of the next battery and so on. • Increases the amount of voltage. • Typical electrical cell is 1.5 V • Example: If you connect 3 cells, the voltage becomes 4.5 V. • The electrons get three boosts of energy instead of one. ...
... negative terminal of the next battery and so on. • Increases the amount of voltage. • Typical electrical cell is 1.5 V • Example: If you connect 3 cells, the voltage becomes 4.5 V. • The electrons get three boosts of energy instead of one. ...
Experiment Name Student Name:Sajedah AlMarzouq ID# 20700199
... Overall, both parts of this lab demonstrated the relationship outlined by Ohm’s Law and fostered a higher comprehension of the mechanisms driving circuit behavior. The direct relationships between voltage, current, and resistance allow measurement of the voltage and current without resistance being ...
... Overall, both parts of this lab demonstrated the relationship outlined by Ohm’s Law and fostered a higher comprehension of the mechanisms driving circuit behavior. The direct relationships between voltage, current, and resistance allow measurement of the voltage and current without resistance being ...
Name ______ period ____
... 30. A resistor has a resistance of 2.3 . How much current is in the resistor if there is a potential difference of 11.5 V across the resistor? 31. Electric field lines point towards a _________________ charge, away from a _________________ charge and never _____________________ each other. 32. When ...
... 30. A resistor has a resistance of 2.3 . How much current is in the resistor if there is a potential difference of 11.5 V across the resistor? 31. Electric field lines point towards a _________________ charge, away from a _________________ charge and never _____________________ each other. 32. When ...
PHY2054_02-08
... of the 10 Ω and 5 Ω resistors. (b) Calculate the combined equivalent resistance of the 10 Ω, 5 Ω, and 4 Ω resistors. (c) Calculate the equivalent resistance found in part b and the parallel 3 Ω resistor. (d) Combine the equivalent resistance from part c and the 2 Ω resistor. (e) Calculate the total ...
... of the 10 Ω and 5 Ω resistors. (b) Calculate the combined equivalent resistance of the 10 Ω, 5 Ω, and 4 Ω resistors. (c) Calculate the equivalent resistance found in part b and the parallel 3 Ω resistor. (d) Combine the equivalent resistance from part c and the 2 Ω resistor. (e) Calculate the total ...
This quiz will cover ONLY Section 2
... Electric Current: flow of electrons through a material Voltage: causes current to flow through an electric circuit Voltage source: creates a potential difference in electric circuit Ohm: units of resistance Voltmeter: measures voltage Ammeter: measures amps (or current) Concepts to know: ...
... Electric Current: flow of electrons through a material Voltage: causes current to flow through an electric circuit Voltage source: creates a potential difference in electric circuit Ohm: units of resistance Voltmeter: measures voltage Ammeter: measures amps (or current) Concepts to know: ...
Ohms - HCC Learning Web
... 1) Convert the unit of OHM into its combination of the fundamental SI units. ...
... 1) Convert the unit of OHM into its combination of the fundamental SI units. ...