Parallel Resistive Circuits Part 2
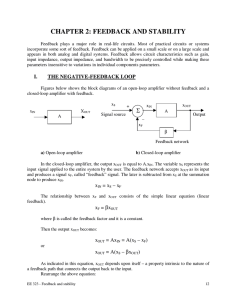
... Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law- the sum of all voltages in a closed loop equals zero Kirchhoff’s Current Law- the sum of the currents into a node is equal to the sum of the currents leaving the node Node- a branching point where current splits or combines Series Circuit- a circuit with only one pat ...
... Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law- the sum of all voltages in a closed loop equals zero Kirchhoff’s Current Law- the sum of the currents into a node is equal to the sum of the currents leaving the node Node- a branching point where current splits or combines Series Circuit- a circuit with only one pat ...
1. A 2.0-ohm resistor and a 4.0-ohm resistor
... 6. A 3-ohm resistor and a 6-ohm resistor are connected in parallel across a 9-volt battery. Which statement best compares the potential difference across each resistor? A) The potential difference across the 6-ohm resistor is the same as the potential difference across the 3-ohm resistor. B) The pot ...
... 6. A 3-ohm resistor and a 6-ohm resistor are connected in parallel across a 9-volt battery. Which statement best compares the potential difference across each resistor? A) The potential difference across the 6-ohm resistor is the same as the potential difference across the 3-ohm resistor. B) The pot ...
Fundamentals of Electronic Circuit Design
... When a voltage is applied across a conductor, a current will begin to flow. The ratio between voltage and current is known as resistance. For most metallic conductors, the relationship between voltage and current is linear. Stated mathematically, this property is known as Ohm’s law, where ...
... When a voltage is applied across a conductor, a current will begin to flow. The ratio between voltage and current is known as resistance. For most metallic conductors, the relationship between voltage and current is linear. Stated mathematically, this property is known as Ohm’s law, where ...
Experiment 5 - Portal UniMAP
... obtain full-scale deflection will be recorded, without changing the applied voltage (VFS), Add a shunt resistor (RS) in parallel with the galvanometer. Vary the load resistance to get the full-scale deflection in the galvanometer. The new load resistance, R2 will be recorded. In both circuits, the p ...
... obtain full-scale deflection will be recorded, without changing the applied voltage (VFS), Add a shunt resistor (RS) in parallel with the galvanometer. Vary the load resistance to get the full-scale deflection in the galvanometer. The new load resistance, R2 will be recorded. In both circuits, the p ...
Multiple-Load Circuits CHAPTER 5
... The diagrams of Fig. 5-8 show the open resistor. However, in a real physical circuit, R2 may look just like R1 and R3. There may be no physical evidence to indicate that it is open. A technician repairing the circuit would have to interpret the voltmeter readings to conclude that R2 is open. Shorts ...
... The diagrams of Fig. 5-8 show the open resistor. However, in a real physical circuit, R2 may look just like R1 and R3. There may be no physical evidence to indicate that it is open. A technician repairing the circuit would have to interpret the voltmeter readings to conclude that R2 is open. Shorts ...
2.5 Signal Sources Word Document | GCE AS/A
... From the graph we can see that the output voltage falls in a non-linear way and therefore this type of circuit produces an analogue voltage. However in this case the range of voltage change is not very good, since the output voltage only changes by 3.5V (8-4.5V) even though the temperature has chang ...
... From the graph we can see that the output voltage falls in a non-linear way and therefore this type of circuit produces an analogue voltage. However in this case the range of voltage change is not very good, since the output voltage only changes by 3.5V (8-4.5V) even though the temperature has chang ...
Q.1 how is electric current expressed? ans. electric current is
... electrons actually move from negative to positive terminal? ans. -electrons were not known at the time when the phenomenon of electricity was first observed. -so electric current was considered to be the flow of positive charges and the direction of flow of positive charges was taken to be the direc ...
... electrons actually move from negative to positive terminal? ans. -electrons were not known at the time when the phenomenon of electricity was first observed. -so electric current was considered to be the flow of positive charges and the direction of flow of positive charges was taken to be the direc ...
25_InstructorSolutionsWin
... IDENTIFY: First use Ohm’s law to find the resistance at 20.0°C; then calculate the resistivity from the resistance. Finally use the dependence of resistance on temperature to calculate the temperature coefficient of resistance. SET UP: Ohm’s law is R = V/I, R = L/A, R = R0[1 + (T – T0)], and the r ...
... IDENTIFY: First use Ohm’s law to find the resistance at 20.0°C; then calculate the resistivity from the resistance. Finally use the dependence of resistance on temperature to calculate the temperature coefficient of resistance. SET UP: Ohm’s law is R = V/I, R = L/A, R = R0[1 + (T – T0)], and the r ...
current, resistance, and electromotive force
... IDENTIFY: First use Ohm’s law to find the resistance at 20.0°C; then calculate the resistivity from the resistance. Finally use the dependence of resistance on temperature to calculate the temperature coefficient of resistance. SET UP: Ohm’s law is R = V/I, R = ρL/A, R = R0[1 + α(T – T0)], and the r ...
... IDENTIFY: First use Ohm’s law to find the resistance at 20.0°C; then calculate the resistivity from the resistance. Finally use the dependence of resistance on temperature to calculate the temperature coefficient of resistance. SET UP: Ohm’s law is R = V/I, R = ρL/A, R = R0[1 + α(T – T0)], and the r ...
LCR Parallel Circuits - Learn About Electronics
... However, it should be noted that this formula ignores the effect of R in slightly shifting the phase of IL. In fact the formula only gives an approximate value for ƒr. However, because the internal resistance of L is usually quite small, so is its effect in shifting the resonant frequency of the cir ...
... However, it should be noted that this formula ignores the effect of R in slightly shifting the phase of IL. In fact the formula only gives an approximate value for ƒr. However, because the internal resistance of L is usually quite small, so is its effect in shifting the resonant frequency of the cir ...
What is a Resistor - Ajlon Technologies
... The Rheostat is the simplest way of using a variable resistor. Two terminals are used: one connected to an end of the track, the other to the moveable wiper. Turning the spindle changes the resistance between the two terminals from zero up to the maximum resistance. Rheostats are often used to vary ...
... The Rheostat is the simplest way of using a variable resistor. Two terminals are used: one connected to an end of the track, the other to the moveable wiper. Turning the spindle changes the resistance between the two terminals from zero up to the maximum resistance. Rheostats are often used to vary ...
Electric Circuits - Key
... Examine Picture A and Picture B closely. How are they similar? How are they different? How would each compare to the circuits below? ...
... Examine Picture A and Picture B closely. How are they similar? How are they different? How would each compare to the circuits below? ...