Nervous System Guided Notes
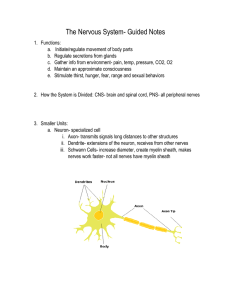
... a. Neuron- specialized cell i. Axon- transmits signals long distances to other structures ii. Dendrite- extensions of the neuron, receives from other nerves iii. Schwann Cells- increase diameter, create myelin sheath, makes nerves work faster- not all nerves have myelin sheath ...
... a. Neuron- specialized cell i. Axon- transmits signals long distances to other structures ii. Dendrite- extensions of the neuron, receives from other nerves iii. Schwann Cells- increase diameter, create myelin sheath, makes nerves work faster- not all nerves have myelin sheath ...
The Brain and The Nervous System
... • Her autonomic NS controls involuntary actions of internal organs. At the start of the race her sympathetic NS would be activated, resulting in an increase in Renees’ adrenaline, heart rate, respiration and sweating. After the race her parasympathetic NS would slow her heart rate and respiration ra ...
... • Her autonomic NS controls involuntary actions of internal organs. At the start of the race her sympathetic NS would be activated, resulting in an increase in Renees’ adrenaline, heart rate, respiration and sweating. After the race her parasympathetic NS would slow her heart rate and respiration ra ...
Evernote Questions
... A) occipital lobe; temporal lobe; parietal lobe; frontal lobe B) temporal lobe; frontal lobe; parietal lobe; occipital lobe C) frontal lobe; occipital lobe; temporal lobe; parietal lobe D) frontal lobe; parietal lobe; occipital lobe; temporal lobe ...
... A) occipital lobe; temporal lobe; parietal lobe; frontal lobe B) temporal lobe; frontal lobe; parietal lobe; occipital lobe C) frontal lobe; occipital lobe; temporal lobe; parietal lobe D) frontal lobe; parietal lobe; occipital lobe; temporal lobe ...
the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
... an area of the left frontal lobe that directs the muscle movements involved in speech Wernicke’s Area an area of the left temporal lobe involved in language comprehension and expression ...
... an area of the left frontal lobe that directs the muscle movements involved in speech Wernicke’s Area an area of the left temporal lobe involved in language comprehension and expression ...
Chapter 6
... Channels sensory information pain, taste, temperature, audition, vision Integrates sensorimotor information From Basal Ganglia, Cerebellum, and Cortex Regulates function of association cortex and cortically mediated speech, language, and cognitive functions. ...
... Channels sensory information pain, taste, temperature, audition, vision Integrates sensorimotor information From Basal Ganglia, Cerebellum, and Cortex Regulates function of association cortex and cortically mediated speech, language, and cognitive functions. ...
Chapter 12: The Central Nervous System
... Mammillary bodies - part of hypothalamus (odors can trigger memory) Parts of thalamus and hypothalamus Pathway from limbic system project into hypothalamus and exert widespread effect on body via autonomic nervous system and endocrine system (most limbic output is relayed through hypothalamus) Since ...
... Mammillary bodies - part of hypothalamus (odors can trigger memory) Parts of thalamus and hypothalamus Pathway from limbic system project into hypothalamus and exert widespread effect on body via autonomic nervous system and endocrine system (most limbic output is relayed through hypothalamus) Since ...
Organization of NS and the neuron File
... fever, vomiting, intense headache, stiff neck and possible rash. Left untreated can cause death. Meningitis is diagnosed by sampling the cerebrospinal fluid. The Brain (made up of 3 regions) ...
... fever, vomiting, intense headache, stiff neck and possible rash. Left untreated can cause death. Meningitis is diagnosed by sampling the cerebrospinal fluid. The Brain (made up of 3 regions) ...
Classes #9-11: Differentiation of the brain vesicles
... class sessions 9-11. The first 46 questions are for review, and can be answered from earlier lectures. Many of these questions are answered in the readings as well. 1. The forebrain probably expanded in evolution initially because of the importance of _________________________________. 2. Give an ex ...
... class sessions 9-11. The first 46 questions are for review, and can be answered from earlier lectures. Many of these questions are answered in the readings as well. 1. The forebrain probably expanded in evolution initially because of the importance of _________________________________. 2. Give an ex ...
Parts of the Peripheral Nervous System
... Darwin included behavior among the heritable traits that could evolve, ex. Noticed mammalian species show same reactions when frightened. To Darwin, similarities of this response pattern indicated that these different species evolved from a common ancestor, which possessed the same behavioral trait. ...
... Darwin included behavior among the heritable traits that could evolve, ex. Noticed mammalian species show same reactions when frightened. To Darwin, similarities of this response pattern indicated that these different species evolved from a common ancestor, which possessed the same behavioral trait. ...
Neurology Update Movement Disorders
... • Unknown functions but plays a role in regulation cell differentiation, synaptic plasticity, management of presynaptic vesicular pool, and dopaminergic regulation • Present in Substantia Nigra Cells naturally ...
... • Unknown functions but plays a role in regulation cell differentiation, synaptic plasticity, management of presynaptic vesicular pool, and dopaminergic regulation • Present in Substantia Nigra Cells naturally ...
Slide 1 - MisterSyracuse.com
... 16. Many tasks in the body are taken care of by the unconscious part of the brain, so that the brain’s owner doesn’t have to think about them. These tasks are performed by the A. Cerebrum B. Malpighian tubule C. Cortex D. Cerebellum _________ 17. Name three tasks that might be performed by the stru ...
... 16. Many tasks in the body are taken care of by the unconscious part of the brain, so that the brain’s owner doesn’t have to think about them. These tasks are performed by the A. Cerebrum B. Malpighian tubule C. Cortex D. Cerebellum _________ 17. Name three tasks that might be performed by the stru ...
Brain Development - Child Care Consultants, Inc.
... house. Heredity may determine the basic number of “neurons” (brain nerve cells) children are born with, and their initial arrangement, but this is just a framework. A child’s environment has enormous impact on how these cells get connected or “wired” to each other. Many parents and caregivers have u ...
... house. Heredity may determine the basic number of “neurons” (brain nerve cells) children are born with, and their initial arrangement, but this is just a framework. A child’s environment has enormous impact on how these cells get connected or “wired” to each other. Many parents and caregivers have u ...
16. Anatomy of Brainstem
... Limbic lobe of the cerebrum consists of 3 gyri that curve along the corpus callosum and medial surface of the temporal lobe. Limbic system the center of emotion – anger, fear, sexual arousal, pleasure, and sadness. ...
... Limbic lobe of the cerebrum consists of 3 gyri that curve along the corpus callosum and medial surface of the temporal lobe. Limbic system the center of emotion – anger, fear, sexual arousal, pleasure, and sadness. ...
3NervCase
... damage to what area of the patient's cortex? a. auditory cortex b. somatosensory association area c. motor association area d. primary motor cortex e. primary somatosensory cortex 8. The difficulties that the patient has with language indicate which area of the cerebrum was damaged by the stroke? A. ...
... damage to what area of the patient's cortex? a. auditory cortex b. somatosensory association area c. motor association area d. primary motor cortex e. primary somatosensory cortex 8. The difficulties that the patient has with language indicate which area of the cerebrum was damaged by the stroke? A. ...
The Central Nervous System LBHS Version
... The brain contains structurally and functionally de ned regions. ...
... The brain contains structurally and functionally de ned regions. ...
PoNS Fact Sheet - Helius Medical Technologies
... The Portable Neuromodulation Stimulator (PoNS™) device is an investigational noninvasive medical device being studied for the treatment of neurological symptoms caused by disease or trauma. PoNS™ Therapy combines the use of the device with physical therapy and is currently being studied in a pivotal ...
... The Portable Neuromodulation Stimulator (PoNS™) device is an investigational noninvasive medical device being studied for the treatment of neurological symptoms caused by disease or trauma. PoNS™ Therapy combines the use of the device with physical therapy and is currently being studied in a pivotal ...
http://www - Progetto Autismo FVG
... record small voltage changes called event-related potentials, or ERPs, that indicate brain activity. It's a strange scene, but the babies and their hairnets are part of a research project funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Autism Speaks Foundation. The goal is to identify children a ...
... record small voltage changes called event-related potentials, or ERPs, that indicate brain activity. It's a strange scene, but the babies and their hairnets are part of a research project funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Autism Speaks Foundation. The goal is to identify children a ...
a PowerPoint Presentation of Module 24
... of words such as the first time riding a bike, or facts about types of bicycles. Retrieval and use of explicit memories, which is in part a working memory or executive function, is directed by the frontal lobes. Encoding and storage of explicit memories is facilitated by the hippocampus. Events ...
... of words such as the first time riding a bike, or facts about types of bicycles. Retrieval and use of explicit memories, which is in part a working memory or executive function, is directed by the frontal lobes. Encoding and storage of explicit memories is facilitated by the hippocampus. Events ...
Name
... 1. What is homeostasis? Give examples. 2. What are the functions of the nervous system? 3. What is the structure of a neuron and what kinds of neurons are found in the body? 4. How do nerve impulses travel from one neuron to another? 5. What are the structure and functions of the central nervous sys ...
... 1. What is homeostasis? Give examples. 2. What are the functions of the nervous system? 3. What is the structure of a neuron and what kinds of neurons are found in the body? 4. How do nerve impulses travel from one neuron to another? 5. What are the structure and functions of the central nervous sys ...
SPHS 4050, Neurological bases, PP 01
... essentially structural mirror images of each other • This principle is used in medical diagnosis ...
... essentially structural mirror images of each other • This principle is used in medical diagnosis ...