Ch. 35.3
... • Controls voluntary activities of the body • Intelligence, learning, and judgment Broken ...
... • Controls voluntary activities of the body • Intelligence, learning, and judgment Broken ...
Slide ()
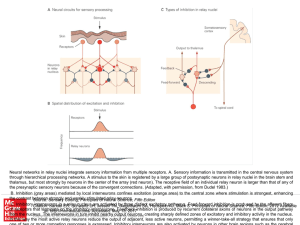
... Neural networks in relay nuclei integrate sensory information from multiple receptors. A. Sensory information is transmitted in the central nervous system through hierarchical processing networks. A stimulus to the skin is registered by a large group of postsynaptic neurons in relay nuclei in the br ...
... Neural networks in relay nuclei integrate sensory information from multiple receptors. A. Sensory information is transmitted in the central nervous system through hierarchical processing networks. A stimulus to the skin is registered by a large group of postsynaptic neurons in relay nuclei in the br ...
Masking, conscious access, and the blind spot of introspection
... For many years, introspection and consciousness were rejected from scientific psychology. In my talk, I will show that introspection is often a valid source of information that, combined with neuroimaging methods, can provide a window into the architecture underlying conscious processing. A first se ...
... For many years, introspection and consciousness were rejected from scientific psychology. In my talk, I will show that introspection is often a valid source of information that, combined with neuroimaging methods, can provide a window into the architecture underlying conscious processing. A first se ...
ANPS 019 Beneyto-Santonja 10-24
... Produces hormone Melatonin Regulates sleep/wake “cycle” Circadian (daily) rhythms Cerebellum Second largest part of brain Coordinates body movements 2 Hemispheres (just like the cerebrum) Covered with cerebellar cortex (just like the cerebrum) Brainstem: Controls the daily functions that ...
... Produces hormone Melatonin Regulates sleep/wake “cycle” Circadian (daily) rhythms Cerebellum Second largest part of brain Coordinates body movements 2 Hemispheres (just like the cerebrum) Covered with cerebellar cortex (just like the cerebrum) Brainstem: Controls the daily functions that ...
Decoding visual consciousness from human
... Despite many years of research on the neural correlates of consciousness (NCCs), it is still unclear how the detailed contents of consciousness are represented in the human brain. It is often assumed that specific contents of consciousness are encoded in dedicated core NCCs – one for each different ...
... Despite many years of research on the neural correlates of consciousness (NCCs), it is still unclear how the detailed contents of consciousness are represented in the human brain. It is often assumed that specific contents of consciousness are encoded in dedicated core NCCs – one for each different ...
Introduction to Neural Networks
... should be able to produce similar responses and behaviours in artificial systems. ...
... should be able to produce similar responses and behaviours in artificial systems. ...
Development
... • Growth cones respond to chemicals. • Attraction and repulsion (e.g. slit and netrin, and their receptors). • Myelination of axons by oligodendoglia. ...
... • Growth cones respond to chemicals. • Attraction and repulsion (e.g. slit and netrin, and their receptors). • Myelination of axons by oligodendoglia. ...
Introduction
... Visual pathways to the brain. (a) Input from the right half of the visual field strikes the left side of each retina and is transmitted to the left hemisphere (shown in red). Input from the left half of the visual field strikes the right side of each retina and is transmitted to the right hemisphere ...
... Visual pathways to the brain. (a) Input from the right half of the visual field strikes the left side of each retina and is transmitted to the left hemisphere (shown in red). Input from the left half of the visual field strikes the right side of each retina and is transmitted to the right hemisphere ...
Focusing on connections and signaling mechanisms to
... as well as qualitatively which changes are due to rewiring and which due to changes in the efficacy of existing synapses. In the study of learning, it seems possible that different experiences that give rise to different patterns of activity may analagously engage distinct mechanisms to regulate the ...
... as well as qualitatively which changes are due to rewiring and which due to changes in the efficacy of existing synapses. In the study of learning, it seems possible that different experiences that give rise to different patterns of activity may analagously engage distinct mechanisms to regulate the ...
Bayesian Curve Fitting and Neuron Firing Patterns
... ABSTRACT One of the most important techniques in learning about the functioning of the brain has involved examining neuronal activity in laboratory animals under varying experimental conditions. Neural information is represented and communicated through series of action potentials, or spike trains, ...
... ABSTRACT One of the most important techniques in learning about the functioning of the brain has involved examining neuronal activity in laboratory animals under varying experimental conditions. Neural information is represented and communicated through series of action potentials, or spike trains, ...
PSYCH 2 StudyGuide
... 3- What is selective attention and what is it used for? Selective attention is the focusing of conscious awareness on a particular stimulus. Intentional blindness is failing to see visible objects when our attention is directed elsewhere. 4- What is circadian rhythm: Circadian rhythm is the biologic ...
... 3- What is selective attention and what is it used for? Selective attention is the focusing of conscious awareness on a particular stimulus. Intentional blindness is failing to see visible objects when our attention is directed elsewhere. 4- What is circadian rhythm: Circadian rhythm is the biologic ...
The Great Brain Drain Review
... from a black widow spider is an agonist. Acetylcholine must also be involved in memory because decreased amounts of it in the brain are associated with the disease, Alzheimers. Neurotransmitters can be excitatory or inhibitory. GABA is an example of an inhibitory neurotransmitter. The neural impulse ...
... from a black widow spider is an agonist. Acetylcholine must also be involved in memory because decreased amounts of it in the brain are associated with the disease, Alzheimers. Neurotransmitters can be excitatory or inhibitory. GABA is an example of an inhibitory neurotransmitter. The neural impulse ...
Reading the neural code in behaving animals, ~1000 neurons at a ,me
... neurons and glia contribute to animal behavior and brain disease. Addressing this challenge has been difficult partly due to lack of appropriate brain imaging technology for visualizing cellular proper3es in aw ...
... neurons and glia contribute to animal behavior and brain disease. Addressing this challenge has been difficult partly due to lack of appropriate brain imaging technology for visualizing cellular proper3es in aw ...
LSU Seminar Neuroscience Center of Excellence
... effects on visual function, including loss of visual responsiveness to the deprived eye, reduced visual acuity, and loss of tuning to many stimulus characteristics. These changes occur faster than remodeling of thalamocortical axons, but the intracortical plasticity mechanisms that underlie them are ...
... effects on visual function, including loss of visual responsiveness to the deprived eye, reduced visual acuity, and loss of tuning to many stimulus characteristics. These changes occur faster than remodeling of thalamocortical axons, but the intracortical plasticity mechanisms that underlie them are ...
Chapter 14 - FacultyWeb
... Wernike’s area in the parietal lobe General interpretive area of the temporal lobe Primary visual cortex in the occipital lobe Broca’s area in the frontal lobe ...
... Wernike’s area in the parietal lobe General interpretive area of the temporal lobe Primary visual cortex in the occipital lobe Broca’s area in the frontal lobe ...
Assignment 2 - Gordon State College
... to keep them within allowable ranges (also called homeostasis). To do this, it produces both hormones and neurotransmitters and influencing the endocrine system through the __________________ gland. 35. The two hemispheres of the brain’s cerebral cortex and connected by a large band of axon fibers c ...
... to keep them within allowable ranges (also called homeostasis). To do this, it produces both hormones and neurotransmitters and influencing the endocrine system through the __________________ gland. 35. The two hemispheres of the brain’s cerebral cortex and connected by a large band of axon fibers c ...
Lecture 7A
... ball flanged at them and could sense when objects moved closer and farther. They even experienced waterfall illusion. • Similarly, Daniel Kish (see TED) who uses clicks to navigate the space shows strong activity in visual cortex while listening to reflected auditory clicks ...
... ball flanged at them and could sense when objects moved closer and farther. They even experienced waterfall illusion. • Similarly, Daniel Kish (see TED) who uses clicks to navigate the space shows strong activity in visual cortex while listening to reflected auditory clicks ...
File
... The thalamus is the main input center for sensory information, all senses are sorted in the thalamus and sent to the appropriate cerebral centers The hypothalamus contains the body’s thermostat and the central biological clock; it also controls the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus also regulates hu ...
... The thalamus is the main input center for sensory information, all senses are sorted in the thalamus and sent to the appropriate cerebral centers The hypothalamus contains the body’s thermostat and the central biological clock; it also controls the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus also regulates hu ...
Studying the Living Human Brain
... with our senses or muscle movements are called association areas. ...
... with our senses or muscle movements are called association areas. ...
Brain Anatomy PPT
... cortex: amygdala, hippocampus, and olfactory bulb These structures attach emotional “feelings” to survival-related functions Structures of the limbic system form in early development and provide a foundation for emotional memory, associating emotions with particular events or experiences ...
... cortex: amygdala, hippocampus, and olfactory bulb These structures attach emotional “feelings” to survival-related functions Structures of the limbic system form in early development and provide a foundation for emotional memory, associating emotions with particular events or experiences ...
Brain Structure - Updated 14
... Goal: gain a hands-on idea of how electrical information is passed along an axon for neural transmission to occur. ...
... Goal: gain a hands-on idea of how electrical information is passed along an axon for neural transmission to occur. ...
Nervous
... The limbic system, a ring of cortical and noncortical centers around the brainstem, mediates primary emotions and attaches emotional “feelings” to survival–related functions. The association of primary emotions with different situations during human development requires parts of the neocortex, espec ...
... The limbic system, a ring of cortical and noncortical centers around the brainstem, mediates primary emotions and attaches emotional “feelings” to survival–related functions. The association of primary emotions with different situations during human development requires parts of the neocortex, espec ...
Using Breakthroughs in Visual Neuroscience to
... human medical applications. Studies using an array of electrodes implanted in the brain show that monkeys can use their visual system to control an artificial limb remotely, by mental control alone.1 If this ability holds true in humans, it could dramatically improve sensory substitution treatments ...
... human medical applications. Studies using an array of electrodes implanted in the brain show that monkeys can use their visual system to control an artificial limb remotely, by mental control alone.1 If this ability holds true in humans, it could dramatically improve sensory substitution treatments ...
From Vision to Movement
... brain. Does this difference occur between different areas of the brain? Between different neurons? Within the same neurons at different times? Approaching the brain from a global view, one starts with the impression that vision is encoded in occipital cortex, movement in frontal cortex, and parietal ...
... brain. Does this difference occur between different areas of the brain? Between different neurons? Within the same neurons at different times? Approaching the brain from a global view, one starts with the impression that vision is encoded in occipital cortex, movement in frontal cortex, and parietal ...
Neural correlates of consciousness

The neural correlates of consciousness (NCC) constitute the minimal set of neuronal events and mechanisms sufficient for a specific conscious percept. Neuroscientists use empirical approaches to discover neural correlates of subjective phenomena. The set should be minimal because, under the assumption that the brain is sufficient to give rise to any given conscious experience, the question is which of its components is necessary to produce it.