Chapter 3 Class Notes / Biological Foundations
... The synapse or synaptic cleft is the tiny gap found between the axon (terminal buttons) of one neuron and the dendrites of another. When a neural message is received at the dendrites, it is processed through the cell body, transmitted along the axon to the terminal buttons found at the end of each a ...
... The synapse or synaptic cleft is the tiny gap found between the axon (terminal buttons) of one neuron and the dendrites of another. When a neural message is received at the dendrites, it is processed through the cell body, transmitted along the axon to the terminal buttons found at the end of each a ...
Visual Brain
... • Fovea accounts for .01% of retina • Signals from fovea account for 8% to 10% of the visual cortex • This provides extra processing for highacuity tasks. ...
... • Fovea accounts for .01% of retina • Signals from fovea account for 8% to 10% of the visual cortex • This provides extra processing for highacuity tasks. ...
Chapter 2
... Broca’s Area – interferes w/ speech production (frontal lobe damage) can understand language words not properly formed speech is slow and slurred some aware of deficits Wernicke’s Area – loss of ability to understand language (parietal/temporal) can speak clearly most of the time words p ...
... Broca’s Area – interferes w/ speech production (frontal lobe damage) can understand language words not properly formed speech is slow and slurred some aware of deficits Wernicke’s Area – loss of ability to understand language (parietal/temporal) can speak clearly most of the time words p ...
Chapter 7 part two
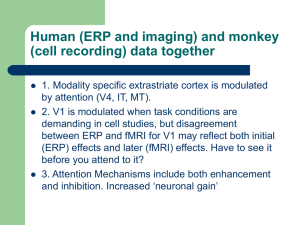
... More about biased competition One theory that brings together all of the reviewed attention effects (top-down biases, gain modulation, enhancement and suppression) is Desimone and Duncan’s ‘biased competition’model of attention. The theory rests on three assumptions. First, given the limits on ou ...
... More about biased competition One theory that brings together all of the reviewed attention effects (top-down biases, gain modulation, enhancement and suppression) is Desimone and Duncan’s ‘biased competition’model of attention. The theory rests on three assumptions. First, given the limits on ou ...
Stereological estimates of neuronal loss in the primary motor cortex
... progressive MS (pwPMS) (Trapp & Nave. Annu Rev Neurosci 2008; Kolasinski, et al. Brain 2012). Impaired motor function is one of the most important components of disability pwPMS accrue over time. Using unbiased sampling techniques applied to whole central nervous systems of pwPMS we investigate whet ...
... progressive MS (pwPMS) (Trapp & Nave. Annu Rev Neurosci 2008; Kolasinski, et al. Brain 2012). Impaired motor function is one of the most important components of disability pwPMS accrue over time. Using unbiased sampling techniques applied to whole central nervous systems of pwPMS we investigate whet ...
Psychology
... abstraction, this is a meta-object. The 0-brane is actually a Riemann-sphere and its surface. • Denctor (| >) or thinking vector with which we could formally express the above idea and also create the basic concepts of mathematics: Tr|><| = < | >= 0 = {{}} = ...
... abstraction, this is a meta-object. The 0-brane is actually a Riemann-sphere and its surface. • Denctor (| >) or thinking vector with which we could formally express the above idea and also create the basic concepts of mathematics: Tr|><| = < | >= 0 = {{}} = ...
Halle Berry as a Computational Brain Abstraction
... The sparse collection or singular grandmother cells must respond to complex objects by connection to neurons at a lower level of abstraction, since sensory input to the visual system is in the form c ...
... The sparse collection or singular grandmother cells must respond to complex objects by connection to neurons at a lower level of abstraction, since sensory input to the visual system is in the form c ...
corticospinal tract
... – ventral portion – pontine nucleus – info about movement and sensation from cc to cerebellum – dorsal portion – respiration, taste, sleep ...
... – ventral portion – pontine nucleus – info about movement and sensation from cc to cerebellum – dorsal portion – respiration, taste, sleep ...
Volunteerism
... two….brought empirical methods of physiology to the question of philosophy Important to Wundt is the concept of “will”…..we decide what to attend to and not…..Different than associationist’s passive ‘mental chemistry’, but he still called Apperception (equivalent to Attention), but voluntary behavio ...
... two….brought empirical methods of physiology to the question of philosophy Important to Wundt is the concept of “will”…..we decide what to attend to and not…..Different than associationist’s passive ‘mental chemistry’, but he still called Apperception (equivalent to Attention), but voluntary behavio ...
Copy Notes
... motor cortex: an area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements sensory cortex: an area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations association areas: areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor o ...
... motor cortex: an area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements sensory cortex: an area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations association areas: areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor o ...
Sleep Brain Labelling
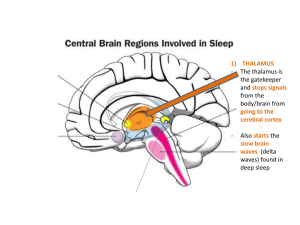
... 1) THALAMUS - The thalamus is the gatekeeper and stops signals from the body/brain from going to the cerebral cortex ...
... 1) THALAMUS - The thalamus is the gatekeeper and stops signals from the body/brain from going to the cerebral cortex ...
Nervous System
... • Constantly interacts with the central nervous system via 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves • Nerves are the bundles axons and dendrites of many neurons • Each spinal nerve has a dorsal root and a ...
... • Constantly interacts with the central nervous system via 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves • Nerves are the bundles axons and dendrites of many neurons • Each spinal nerve has a dorsal root and a ...
fahime_sheikhzadeh
... Why should one use computational models to address questions in neuroscience? • Dealing with complexity • Checking conceptual models and revealing assumptions • Comparing and discovering hypotheses • Suggesting fruitful areas for new experiments ...
... Why should one use computational models to address questions in neuroscience? • Dealing with complexity • Checking conceptual models and revealing assumptions • Comparing and discovering hypotheses • Suggesting fruitful areas for new experiments ...
The gustatory pathway - West Virginia University
... parvocellular division of the ventral posterior medial nucleus of the thalamus From the thalamus, neurons project to the insular cortex, the posterior limb of the internal capsule, and the operculum (primary gustatory areas) ...
... parvocellular division of the ventral posterior medial nucleus of the thalamus From the thalamus, neurons project to the insular cortex, the posterior limb of the internal capsule, and the operculum (primary gustatory areas) ...
study notes quiz 1
... (c) smooth muscle tone (cardiovasular) Metencephalon: 1) Pons: “bridge” (a) part of reticular formation responsible for sleep and arousal (b) relay nuclei between cortex and cerebellum 2) Cerebellum: “little brain” (a) responsible for coordinated movements (b) receives all sensory input except olfac ...
... (c) smooth muscle tone (cardiovasular) Metencephalon: 1) Pons: “bridge” (a) part of reticular formation responsible for sleep and arousal (b) relay nuclei between cortex and cerebellum 2) Cerebellum: “little brain” (a) responsible for coordinated movements (b) receives all sensory input except olfac ...
Properties of Neuronal circuits
... –6o order –Innervated by simple cells –Straight bars or borders at specific angles –Do not have topographically fixed RF •Correct stimulus anywhere on retina –Bars of specific orientation –On one side/off other –Border moving in only one direction ...
... –6o order –Innervated by simple cells –Straight bars or borders at specific angles –Do not have topographically fixed RF •Correct stimulus anywhere on retina –Bars of specific orientation –On one side/off other –Border moving in only one direction ...
Autobiography for 2016 Kavli Prize in Neuroscience Carla J. Shatz
... circuits of almost crystalline- like perfection. Every day as a student I watched the beauty of visual system organization unfold before my eyes. I thought, “all research must be like this”! Of course, that was not true, but from David and Torsten I learned the joy of research, the importance of art ...
... circuits of almost crystalline- like perfection. Every day as a student I watched the beauty of visual system organization unfold before my eyes. I thought, “all research must be like this”! Of course, that was not true, but from David and Torsten I learned the joy of research, the importance of art ...
Vision - Ms. Fahey
... 18-2. Discuss the different levels of processing that occur as information travels from the retina to the brain’s cortex. We process information at progressively more abstract levels. The information from the retina’s 130 million rods and cones travels to our bipolar cells, then to our million or so ...
... 18-2. Discuss the different levels of processing that occur as information travels from the retina to the brain’s cortex. We process information at progressively more abstract levels. The information from the retina’s 130 million rods and cones travels to our bipolar cells, then to our million or so ...
General Psychology - K-Dub
... People with intact brains also show left-right hemispheric differences in mental abilities. A number of brain scan studies show normal individuals engage their right brain when completing a perceptual task and their left brain when carrying out a linguistic task. ...
... People with intact brains also show left-right hemispheric differences in mental abilities. A number of brain scan studies show normal individuals engage their right brain when completing a perceptual task and their left brain when carrying out a linguistic task. ...
Unit 3B: The Brain Messing with the Brain Scientists can electrically
... Mind’s subsystems localized in particular brain regions yet brain acts as whole unit Brain divides mental functions (speaking, perceiving, thinking, remembering) into sub-functions o Ex: breaks vision into color, depth, movement, form Continuous stream of experience is actually subdivided info ...
... Mind’s subsystems localized in particular brain regions yet brain acts as whole unit Brain divides mental functions (speaking, perceiving, thinking, remembering) into sub-functions o Ex: breaks vision into color, depth, movement, form Continuous stream of experience is actually subdivided info ...
Neural correlates of consciousness

The neural correlates of consciousness (NCC) constitute the minimal set of neuronal events and mechanisms sufficient for a specific conscious percept. Neuroscientists use empirical approaches to discover neural correlates of subjective phenomena. The set should be minimal because, under the assumption that the brain is sufficient to give rise to any given conscious experience, the question is which of its components is necessary to produce it.