Chapter Two
... What puts us at a major advantage over other animals which puts us at the top of the food chain? ...
... What puts us at a major advantage over other animals which puts us at the top of the food chain? ...
Information Theoretic Approach to the Study of Auditory Coding
... than MGB and AI neurons. Since AI neurons convey half the information that IC neurons do about stimulus identity we conclude that cortical neurons code the identity of the stimuli well without characterizing their ”physical” aspects. This observation hints that the cortex is sensitive to complex str ...
... than MGB and AI neurons. Since AI neurons convey half the information that IC neurons do about stimulus identity we conclude that cortical neurons code the identity of the stimuli well without characterizing their ”physical” aspects. This observation hints that the cortex is sensitive to complex str ...
subcortical white matter (centrum semiovale)
... - located posterior to the genu are corticobulbar tracts from the motor cortex to cranial nerve motor nuclei in brainstem and corticospinal tracts in spinal cord - located both anterior and posterior to corticobulbar and corticospinal tracts in internal capsule are corticopontinecerebellar tracts fr ...
... - located posterior to the genu are corticobulbar tracts from the motor cortex to cranial nerve motor nuclei in brainstem and corticospinal tracts in spinal cord - located both anterior and posterior to corticobulbar and corticospinal tracts in internal capsule are corticopontinecerebellar tracts fr ...
Flowers and weeds: cell-type specific pruning in the developing
... activity of excitatory neurons so they operate at regimes that are more energy efficient; but this advantage would come at the expense of limiting the percentage of inhibitory cells in the nucleus (20 to 25 %). As a consequence, they would require a larger retinal convergence to achieve an equivalen ...
... activity of excitatory neurons so they operate at regimes that are more energy efficient; but this advantage would come at the expense of limiting the percentage of inhibitory cells in the nucleus (20 to 25 %). As a consequence, they would require a larger retinal convergence to achieve an equivalen ...
PSYC465 - neuroanatomy
... The National Dysautonomia Research Foundation site; good overview of function and disorders like Shy-Drager Syndrome, Guillain Barre Syndrome, and more well-known disorders like diabetes and Parkinson's Disease. Neurons and Glia: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/introb.html From Dr. Eric Chudle ...
... The National Dysautonomia Research Foundation site; good overview of function and disorders like Shy-Drager Syndrome, Guillain Barre Syndrome, and more well-known disorders like diabetes and Parkinson's Disease. Neurons and Glia: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/introb.html From Dr. Eric Chudle ...
What and Where Pathways
... Figure 4.8 (a) Response of a complex cell recorded from the visual cortex of a cat. The stimulus bar is moved back and forth across the receptive field. The cell fires best when the bar is positioned with a specific orientation and is moved in a specific direction (*). (From Hubel and Wiesel, 1959. ...
... Figure 4.8 (a) Response of a complex cell recorded from the visual cortex of a cat. The stimulus bar is moved back and forth across the receptive field. The cell fires best when the bar is positioned with a specific orientation and is moved in a specific direction (*). (From Hubel and Wiesel, 1959. ...
consciousness as an afterthought
... Some structures supporting awareness states in the neocortex are the reticular formation, ventral pons, mesencephalic tegmentum, subthalamus, hypothalamus and internal capsule. H.W. Magoun in 1952 (12)defined “An ascending reticular activating system in the brain stem”, since abbreviated as RAS. The ...
... Some structures supporting awareness states in the neocortex are the reticular formation, ventral pons, mesencephalic tegmentum, subthalamus, hypothalamus and internal capsule. H.W. Magoun in 1952 (12)defined “An ascending reticular activating system in the brain stem”, since abbreviated as RAS. The ...
Visual System - UAB School of Optometry
... ganglion cells in the retina, connects to parvo cells in LGN, is most strongly associated with extrastriate visual areas in the inferior temporal lobe. Neurons respond well to color and fine detail, not so strongly to rapid motion or low contrast. Magnocellular System: originates with the parasol ga ...
... ganglion cells in the retina, connects to parvo cells in LGN, is most strongly associated with extrastriate visual areas in the inferior temporal lobe. Neurons respond well to color and fine detail, not so strongly to rapid motion or low contrast. Magnocellular System: originates with the parasol ga ...
Biopsychology, Neuroscience, Physiological Psychology
... The motor cortex, an arch-shaped region at the rear of the frontal lobes, controls voluntary muscle movements on the opposite side of the body. Body parts requiring the most precise control occupy the greatest amount of cortical space. In an effort to find the source of motor control, researchers ha ...
... The motor cortex, an arch-shaped region at the rear of the frontal lobes, controls voluntary muscle movements on the opposite side of the body. Body parts requiring the most precise control occupy the greatest amount of cortical space. In an effort to find the source of motor control, researchers ha ...
The Five Senses In the Brain
... unprovoked seizures. • Seizures are the changes in behavior caused by disordered abnormal electrical activity in the brain. ...
... unprovoked seizures. • Seizures are the changes in behavior caused by disordered abnormal electrical activity in the brain. ...
to undergo a fundamental change in its normal mode of
... and center-surround interaction The Local Field Potential reflects the activity of many neurons in the local region around the electrode. ...
... and center-surround interaction The Local Field Potential reflects the activity of many neurons in the local region around the electrode. ...
Neural processes underlying conscious perception
... and a decrease in the parahippocampal place area, and vice versa when conscious perception changed from ‘‘face’’ to ‘‘house’’. Thus, although the retinal input was unchanged, activity in stimulus specific areas correlated with the subjective alternation of conscious perception [57]. So far, we have d ...
... and a decrease in the parahippocampal place area, and vice versa when conscious perception changed from ‘‘face’’ to ‘‘house’’. Thus, although the retinal input was unchanged, activity in stimulus specific areas correlated with the subjective alternation of conscious perception [57]. So far, we have d ...
Introduction to Neuroscience: Systems Neuroscience – Concepts
... 9. Active sensing: Closing motor-sensory loops. (Ahissar) [2/1/2013] 10. The cerebellum in motor learning and cognition. (Cohen) [9/1/2012] 11. Remembering: Overview of memory systems. (Dudai) [16/1/2013] 12. Learning: The basal ganglia, amygdala and prefrontal cortex. (Paz) [23/1/2013] 13. Methodol ...
... 9. Active sensing: Closing motor-sensory loops. (Ahissar) [2/1/2013] 10. The cerebellum in motor learning and cognition. (Cohen) [9/1/2012] 11. Remembering: Overview of memory systems. (Dudai) [16/1/2013] 12. Learning: The basal ganglia, amygdala and prefrontal cortex. (Paz) [23/1/2013] 13. Methodol ...
Document
... This can result in behaviors such as giggling, head turning, or simulated vivid recall. Researchers can see which neurons or neural networks fire in conjunction with certain mental experiences, and even specific concepts. ...
... This can result in behaviors such as giggling, head turning, or simulated vivid recall. Researchers can see which neurons or neural networks fire in conjunction with certain mental experiences, and even specific concepts. ...
2
... This can result in behaviors such as giggling, head turning, or simulated vivid recall. Researchers can see which neurons or neural networks fire in conjunction with certain mental experiences, and even specific concepts. ...
... This can result in behaviors such as giggling, head turning, or simulated vivid recall. Researchers can see which neurons or neural networks fire in conjunction with certain mental experiences, and even specific concepts. ...
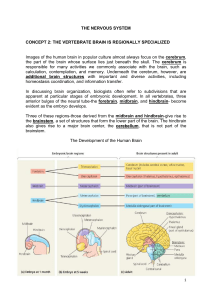
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN
... carrying sensory information to and motor instructions from higher brain regions pass through the brainstem. The medulla and pons also help coordinate large-scale body movements, such as running and climbing. In carrying instructions about these movements from cell bodies in the midbrain and forebra ...
... carrying sensory information to and motor instructions from higher brain regions pass through the brainstem. The medulla and pons also help coordinate large-scale body movements, such as running and climbing. In carrying instructions about these movements from cell bodies in the midbrain and forebra ...
Abstract View OPTICAL RECORDING OF THE TRITONIA SWIMMING CENTRAL PATTERN GENERATOR. ;
... including the dorsal swim interneurons (DSI), C2, and ventral swim interneurons (VSI). A number of other neurons were also identified in the cerebral ganglion that burst in phase with identified swimming interneurons. All bursting neurons were classified roughly as either DSI-like or VSI-like. In ge ...
... including the dorsal swim interneurons (DSI), C2, and ventral swim interneurons (VSI). A number of other neurons were also identified in the cerebral ganglion that burst in phase with identified swimming interneurons. All bursting neurons were classified roughly as either DSI-like or VSI-like. In ge ...
PSC - University of Pittsburgh
... replacing redundant storage by on-the-fly computing. The second aim is to provide a convenient framework for efficient on-the-fly computation on multidimensional datasets within high performance parallel computing environments using both CPU and GPGPU processing. We are also interested in the image ...
... replacing redundant storage by on-the-fly computing. The second aim is to provide a convenient framework for efficient on-the-fly computation on multidimensional datasets within high performance parallel computing environments using both CPU and GPGPU processing. We are also interested in the image ...
The Brain - Polk School District
... • White matter—made of long myelinated axons connecting different parts of gray matter to each other. – Diencephalon (between brainstem and cerebellum) – Relays sensory information from the rest of the body to the cerebral cortex (allows NS to communicate) , ANS functions, expression of emotions, re ...
... • White matter—made of long myelinated axons connecting different parts of gray matter to each other. – Diencephalon (between brainstem and cerebellum) – Relays sensory information from the rest of the body to the cerebral cortex (allows NS to communicate) , ANS functions, expression of emotions, re ...
BIOL 2402 Lecture Outline Chapter 5
... each full cycle lasts about 90 minutes, and in each successive cycle the amount of paradoxical/REM sleep increases paradoxical sleep involves low muscle tone, increased cortical activity, and dreaming switching between slow wave/NREM and paradoxical/REM is controlled by paradoxical/REM “sleep-on” ne ...
... each full cycle lasts about 90 minutes, and in each successive cycle the amount of paradoxical/REM sleep increases paradoxical sleep involves low muscle tone, increased cortical activity, and dreaming switching between slow wave/NREM and paradoxical/REM is controlled by paradoxical/REM “sleep-on” ne ...
Neurophysiological foundations of sleep, arousal, awareness and
... The state of arousal of the cerebral cortex is affected by two main neuroanatomical areas: the ascending reticular system, which is in the pons, and the cognitive system, located in the cerebral cortex and subcortical nuclei. These two regions communicate via the diencephalon, where ascending signal ...
... The state of arousal of the cerebral cortex is affected by two main neuroanatomical areas: the ascending reticular system, which is in the pons, and the cognitive system, located in the cerebral cortex and subcortical nuclei. These two regions communicate via the diencephalon, where ascending signal ...
Nervous Systems
... Reduced fear response Lack of homeostatic control Loss of long-term memory formation ...
... Reduced fear response Lack of homeostatic control Loss of long-term memory formation ...
Outline for cognitive neuroscience Chapter 1 Introduction to Method
... The complex cognitive task require the integrative activity of many component operations. Patient with specific brain lesion may lost the ability of one particular operation. Study dysfunctional behavior can help identify the component operations that underlie normal cognitive performance. Kee ...
... The complex cognitive task require the integrative activity of many component operations. Patient with specific brain lesion may lost the ability of one particular operation. Study dysfunctional behavior can help identify the component operations that underlie normal cognitive performance. Kee ...
Older Brain Structures
... Brain’s sensory switchboard Located on top of the brainstem Functions: Directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex Transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla ...
... Brain’s sensory switchboard Located on top of the brainstem Functions: Directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex Transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla ...
Neuron is the basic working unit of the nervous system, specialized
... clot, or pressure on a blood vessel (as by a tumor). Without oxygen, neurons in the affected area die and the part of the body controlled by those cells cannot function. A stroke can result in loss of consciousness and death. SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM ‐ A branch of the autonomic nervous system ...
... clot, or pressure on a blood vessel (as by a tumor). Without oxygen, neurons in the affected area die and the part of the body controlled by those cells cannot function. A stroke can result in loss of consciousness and death. SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM ‐ A branch of the autonomic nervous system ...
Neural correlates of consciousness

The neural correlates of consciousness (NCC) constitute the minimal set of neuronal events and mechanisms sufficient for a specific conscious percept. Neuroscientists use empirical approaches to discover neural correlates of subjective phenomena. The set should be minimal because, under the assumption that the brain is sufficient to give rise to any given conscious experience, the question is which of its components is necessary to produce it.