Trainee Content for Day 1, Segment 4C
... vulnerability: Sensitive periods for neural systems (and the functions they mediate) will be when that system is in the midst of organizing itself (the developmental ‘hot zone’). Since the brainstem must organize key systems by birth, the sensitive period for those brainstem-mediated functions is du ...
... vulnerability: Sensitive periods for neural systems (and the functions they mediate) will be when that system is in the midst of organizing itself (the developmental ‘hot zone’). Since the brainstem must organize key systems by birth, the sensitive period for those brainstem-mediated functions is du ...
Lab 9
... Functions of Basal Nuclei • Though somewhat elusive, the following are thought to be functions of basal nuclei – Influence muscular activity – Regulate attention and cognition – Regulate intensity of slow or stereotyped movements – Inhibit antagonistic and unnecessary movement ...
... Functions of Basal Nuclei • Though somewhat elusive, the following are thought to be functions of basal nuclei – Influence muscular activity – Regulate attention and cognition – Regulate intensity of slow or stereotyped movements – Inhibit antagonistic and unnecessary movement ...
Chapter 5. The Sensual and Perceptual Theories of Visual
... The viewer constructs the scene with short-lived eye fixations that the mind combines into a whole picture Researchers found that the content, size, and placement of photos on a newspaper page are more important than whether the image is printed in ...
... The viewer constructs the scene with short-lived eye fixations that the mind combines into a whole picture Researchers found that the content, size, and placement of photos on a newspaper page are more important than whether the image is printed in ...
Brain - Cloudfront.net
... (apple) presented in the right visual field can be named. Objects (pencil) in the left visual field cannot. ...
... (apple) presented in the right visual field can be named. Objects (pencil) in the left visual field cannot. ...
The Nervous System - Hastings High School
... 1) Superior colliculi – controls reflex movements having to do with visual stimulus (blinding light) 2) Inferior colliculi – controls reflex movements having to do with auditory stimulus (loud noise) 3) Cerebral peduncles –descending tracts from the eyes that go to the cortex and cerebellum II. Pons ...
... 1) Superior colliculi – controls reflex movements having to do with visual stimulus (blinding light) 2) Inferior colliculi – controls reflex movements having to do with auditory stimulus (loud noise) 3) Cerebral peduncles –descending tracts from the eyes that go to the cortex and cerebellum II. Pons ...
chapter32_part2
... • The spinal cord also has a role in some simple reflexes, automatic responses that occur without conscious thought or learning. Signals from sensory neurons enter the cord through the dorsal root of spinal nerves. Commands for responses go out along the ventral root of these nerves. ...
... • The spinal cord also has a role in some simple reflexes, automatic responses that occur without conscious thought or learning. Signals from sensory neurons enter the cord through the dorsal root of spinal nerves. Commands for responses go out along the ventral root of these nerves. ...
43.99 - XBrain
... fatigue, anxiety, and brain fog? Do you want your thoughts to be smoother and more productive? Do you want to supercharge your brain for better learning and faster thinking without the side effects of stimulants? That’s a big part of learning to be in the Bulletproof state of high performance. It’s ...
... fatigue, anxiety, and brain fog? Do you want your thoughts to be smoother and more productive? Do you want to supercharge your brain for better learning and faster thinking without the side effects of stimulants? That’s a big part of learning to be in the Bulletproof state of high performance. It’s ...
Central Nervous System (CNS)
... 1. Inhibition of muscle tone 2. Coordination of slow, sustained movements 3. Suppression of useless patterns of movements 1. Relay station for all synaptic input 2. Crude awareness of sensation 3. Some degree of consciousness 4. Role in motor control 1. Regulation of many homeostatic functions, such ...
... 1. Inhibition of muscle tone 2. Coordination of slow, sustained movements 3. Suppression of useless patterns of movements 1. Relay station for all synaptic input 2. Crude awareness of sensation 3. Some degree of consciousness 4. Role in motor control 1. Regulation of many homeostatic functions, such ...
the nervous system powerpoint
... Sensory inputs are still crossed Motor outputs are still crossed Hemispheres can’t exchange data ...
... Sensory inputs are still crossed Motor outputs are still crossed Hemispheres can’t exchange data ...
Presentation 14 - Foundations of Human Social
... MRI images, the method is not efficient in region were there is high complexity or fibre ...
... MRI images, the method is not efficient in region were there is high complexity or fibre ...
3 layers
... – memory = the process by which information that is acquired through learning is stored and retrieved – role for long-term potentiation (LTP) – enhances transmission at the hippocampus after a period of high-frequency stimulation – role for glutamate = binds NMDA glutamate receptors on post-synaptic ...
... – memory = the process by which information that is acquired through learning is stored and retrieved – role for long-term potentiation (LTP) – enhances transmission at the hippocampus after a period of high-frequency stimulation – role for glutamate = binds NMDA glutamate receptors on post-synaptic ...
The First Open International Symposium
... Then, how is the spatial gradient detected in klinotaxis? Because worms sense chemicals at one point at the anterior end of the body, comparison between two sensors is unlikely. By stimulating the sensory neuron by using chanelrhodopsin in synchrony with head swing, it was suggested that spatial gra ...
... Then, how is the spatial gradient detected in klinotaxis? Because worms sense chemicals at one point at the anterior end of the body, comparison between two sensors is unlikely. By stimulating the sensory neuron by using chanelrhodopsin in synchrony with head swing, it was suggested that spatial gra ...
Slide 1
... • Wernicke’s aphasia - condition resulting from damage to Wernicke’s area (usually in left temporal lobe), causing the affected person to be unable to understand or produce meaningful language. • Spatial neglect - condition produced by damage to the association areas of the right hemisphere resultin ...
... • Wernicke’s aphasia - condition resulting from damage to Wernicke’s area (usually in left temporal lobe), causing the affected person to be unable to understand or produce meaningful language. • Spatial neglect - condition produced by damage to the association areas of the right hemisphere resultin ...
Document
... – A region in the left temporal lobe that is important to language, particularly the semantic content in speech – Wernicke’s aphasia: serious disruptions in comprehension • Speak fairly grammatical sentences that are almost devoid of meaning ...
... – A region in the left temporal lobe that is important to language, particularly the semantic content in speech – Wernicke’s aphasia: serious disruptions in comprehension • Speak fairly grammatical sentences that are almost devoid of meaning ...
Neuroanatomy 18 [4-20
... Injection of sodium amytal is used to sedate one half of the brain, after which language skills are tested in order to determine the dominant hemisphere In patients with a nonfunctional medial temporal lobe, injection of the good side causes severe memory difficulties i. Since common carotid is ...
... Injection of sodium amytal is used to sedate one half of the brain, after which language skills are tested in order to determine the dominant hemisphere In patients with a nonfunctional medial temporal lobe, injection of the good side causes severe memory difficulties i. Since common carotid is ...
Exploring Our Senses
... level of fatigue This theory assumes there is no absolute threshold Seeks to explain why the same person’s reactions vary as circumstances change. ...
... level of fatigue This theory assumes there is no absolute threshold Seeks to explain why the same person’s reactions vary as circumstances change. ...
Chap 2 Outline
... The nervous system is an extensive network of cells that carry information to and from all parts of the body. Structure of the Neuron: the Nervous System’s Building Network o The brain is made up of two types of cells, neurons and glial cells. o Neurons have dendrites, which receive input, a soma or ...
... The nervous system is an extensive network of cells that carry information to and from all parts of the body. Structure of the Neuron: the Nervous System’s Building Network o The brain is made up of two types of cells, neurons and glial cells. o Neurons have dendrites, which receive input, a soma or ...
Energy - Brain Mind Forum
... mitochondria (see note 1 below). Dementia There is another possibility regarding the onset of various forms of dementia. We all experience a loss of recall from time to time. We have the sensation we know an answer but cannot quite access it. It seems probable that the neural access algorithms succe ...
... mitochondria (see note 1 below). Dementia There is another possibility regarding the onset of various forms of dementia. We all experience a loss of recall from time to time. We have the sensation we know an answer but cannot quite access it. It seems probable that the neural access algorithms succe ...
Unit 3 Neuroscience and Behavior CHAPTER PREVIEW Our
... called the threshold. The neuron’s reaction is an all-or-none response. The impulse, called the action potential, is a brief electrical charge that travels down the axon rather like manhole covers flipping open. During the resting potential, the fluid interior of the axon carries mostly negatively c ...
... called the threshold. The neuron’s reaction is an all-or-none response. The impulse, called the action potential, is a brief electrical charge that travels down the axon rather like manhole covers flipping open. During the resting potential, the fluid interior of the axon carries mostly negatively c ...
doc nervous system notes
... thought, usually on the left hemisphere only. Receives info from all sensory areas and integrates into a single thought or understanding. Visceral Association Area: Conscious perception of sensations of organs eg. Full bladder, upset stomach. Hemisphere Lateralization: Physically both hemispheres ar ...
... thought, usually on the left hemisphere only. Receives info from all sensory areas and integrates into a single thought or understanding. Visceral Association Area: Conscious perception of sensations of organs eg. Full bladder, upset stomach. Hemisphere Lateralization: Physically both hemispheres ar ...
The Anatomy of Language Sydney Lamb Rice University, Houston
... Therefore, the linguistic system operates by means of connections A person’s linguistic system is largely represented in his/her cerebral cortex The cerebral cortex is a neural network A linguistic system is therefore represented as a neural network Therefore, any component of the system do ...
... Therefore, the linguistic system operates by means of connections A person’s linguistic system is largely represented in his/her cerebral cortex The cerebral cortex is a neural network A linguistic system is therefore represented as a neural network Therefore, any component of the system do ...
22-4 EUBANK
... awareness. Ergo, the cerebellum rightfully should be called the “Little Brain.” Without it, ideation will occur without action! (Figure 5) ...
... awareness. Ergo, the cerebellum rightfully should be called the “Little Brain.” Without it, ideation will occur without action! (Figure 5) ...
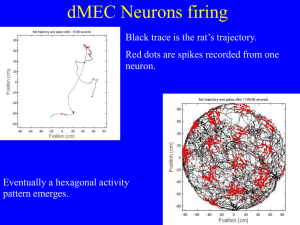
How grid cells neurons encode rat position
... Somehow increase the temporal resolution of fMRI? • Difficult to do • Ultimately not useful: the blood oxygen level changes slowly in response to activity The bold signal changes over the course of several seconds ...
... Somehow increase the temporal resolution of fMRI? • Difficult to do • Ultimately not useful: the blood oxygen level changes slowly in response to activity The bold signal changes over the course of several seconds ...
A general mechanism for perceptual decision
... direction-of-motion task, in which the monkey must decide whether a noisy field of dots is moving upward or downward, a decision can be formed by computing the difference in responses between lower-level neurons that are sensitive to upward motion and those sensitive to downward motion1–4. Similarly ...
... direction-of-motion task, in which the monkey must decide whether a noisy field of dots is moving upward or downward, a decision can be formed by computing the difference in responses between lower-level neurons that are sensitive to upward motion and those sensitive to downward motion1–4. Similarly ...
Neural correlates of consciousness

The neural correlates of consciousness (NCC) constitute the minimal set of neuronal events and mechanisms sufficient for a specific conscious percept. Neuroscientists use empirical approaches to discover neural correlates of subjective phenomena. The set should be minimal because, under the assumption that the brain is sufficient to give rise to any given conscious experience, the question is which of its components is necessary to produce it.