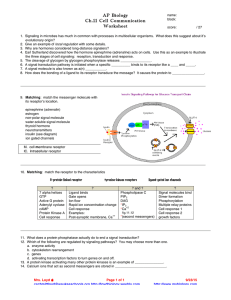
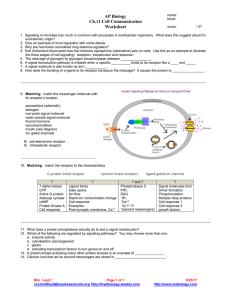
Prediction of Regulatory Elements for Non
... Determination of regulatory networks from available data is one of the major challenges in bioinformatics research. A regulatory network of an organism is represented by a set of genes and their regulatory relationships, which indicate how a gene or a group of genes affect (inhibit or activate) prod ...
... Determination of regulatory networks from available data is one of the major challenges in bioinformatics research. A regulatory network of an organism is represented by a set of genes and their regulatory relationships, which indicate how a gene or a group of genes affect (inhibit or activate) prod ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... Foreign genes have been introduced into plant cells. Foreign genes transferred to cotton, corn, and potato strains have made these plants resistant to pests. Transgenic Animals Techniques have been developed to insert genes into the eggs of animals. Gene pharming is the use of transgenic farm animal ...
... Foreign genes have been introduced into plant cells. Foreign genes transferred to cotton, corn, and potato strains have made these plants resistant to pests. Transgenic Animals Techniques have been developed to insert genes into the eggs of animals. Gene pharming is the use of transgenic farm animal ...
Assembling the nuclear receptor genesets
... Nuclear receptors are well-established mediators in metabolic processes. One aim of the study was to determine whether subsets of nuclear receptors might be transcriptionally altered in insulin resistant or diabetic phenotypes. Three nuclear receptor genesets were assembled based on the nuclear rece ...
... Nuclear receptors are well-established mediators in metabolic processes. One aim of the study was to determine whether subsets of nuclear receptors might be transcriptionally altered in insulin resistant or diabetic phenotypes. Three nuclear receptor genesets were assembled based on the nuclear rece ...
91159 Demonstrate understanding of gene expression
... Biological ideas and processes relating to the determination of phenotype via metabolic pathways are selected from: biochemical reactions are catalysed by specific enzymes and every enzyme is coded for by a specific gene(s) biochemical reactions do not occur in isolation but form part of a chain ...
... Biological ideas and processes relating to the determination of phenotype via metabolic pathways are selected from: biochemical reactions are catalysed by specific enzymes and every enzyme is coded for by a specific gene(s) biochemical reactions do not occur in isolation but form part of a chain ...
Differential Gene Expression
... In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development and is responsible for differences in cell types RNA molecules play many roles in regulating gene expression in eukaryotes ...
... In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development and is responsible for differences in cell types RNA molecules play many roles in regulating gene expression in eukaryotes ...
Chapter 18
... In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development and is responsible for differences in cell types RNA molecules play many roles in regulating gene expression in eukaryotes ...
... In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development and is responsible for differences in cell types RNA molecules play many roles in regulating gene expression in eukaryotes ...
4.2 Sources of DNA
... Increases occur when enhancer molecules interact with the RNA polymerase or with other enhancer DNA regions where molecules attach to the DNA and increase gene transcription ...
... Increases occur when enhancer molecules interact with the RNA polymerase or with other enhancer DNA regions where molecules attach to the DNA and increase gene transcription ...
Joseph Jez, PhD
... EXROP students can fit into any of the three major projects in the lab, all of which use a combination of biochemical and structural biology approaches. Specific projects can be tailored to fit the background and expertise of a student but typically include molecular cloning, protein expression and ...
... EXROP students can fit into any of the three major projects in the lab, all of which use a combination of biochemical and structural biology approaches. Specific projects can be tailored to fit the background and expertise of a student but typically include molecular cloning, protein expression and ...
AP Biology 12
... First, cells can adjust the activity of enzymes already present. ○ This may happen by feedback inhibition, in which the activity of the first enzyme in a pathway is inhibited by the pathway’s end product. ○ Feedback inhibition, typical of anabolic (biosynthetic) pathways, allows a cell to adapt to ...
... First, cells can adjust the activity of enzymes already present. ○ This may happen by feedback inhibition, in which the activity of the first enzyme in a pathway is inhibited by the pathway’s end product. ○ Feedback inhibition, typical of anabolic (biosynthetic) pathways, allows a cell to adapt to ...
The P53-Mdm2 Network: From Oscillations To Apoptosis
... Abstract. The p53 tumour suppressor gene, often characterized as the “guardian of the genome” plays a central role in protecting cells from malignant transformation. It is the most frequently mutated of genes in human cancer. The gene constitutes a highly connected node in a network of signaling pat ...
... Abstract. The p53 tumour suppressor gene, often characterized as the “guardian of the genome” plays a central role in protecting cells from malignant transformation. It is the most frequently mutated of genes in human cancer. The gene constitutes a highly connected node in a network of signaling pat ...
CELL AND DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY SUBTRACK
... chemistry and enzymology of replication, transcription, translation, cell transformation, regulation of gene expression. Prerequisite: 099:120. 002:104 Introduction to Developmental Biology 3 s.h. Fundamental mechanisms of differentiation, organogenesis, morphogenesis and pattern formation; mechanis ...
... chemistry and enzymology of replication, transcription, translation, cell transformation, regulation of gene expression. Prerequisite: 099:120. 002:104 Introduction to Developmental Biology 3 s.h. Fundamental mechanisms of differentiation, organogenesis, morphogenesis and pattern formation; mechanis ...
Uncovering the regulatory networks of gastrulation: A systems
... gastrulation stages of mammalian development, relatively little is known about the regulatory network that controls these critical stages of development. Indeed, the known signaling events and master regulators (MRs) - genes that serve as central control points of the regulatory network for gastrula ...
... gastrulation stages of mammalian development, relatively little is known about the regulatory network that controls these critical stages of development. Indeed, the known signaling events and master regulators (MRs) - genes that serve as central control points of the regulatory network for gastrula ...
Homeostasis and Transport Vocabulary Worksheet 1 Answers
... material and then is extruded through an opening in the cell membrane. ...
... material and then is extruded through an opening in the cell membrane. ...
1) Definition of the gene
... HOUSEKEEPING GENES These are genes that are active at all times, in all cells in the body. There are about 2,000 housekeeping genes. Examples: Na/K-ATPase – enzyme that pumps Na out, and K out, to maintain normal ion distribution inside the cell Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH): converts pyruvate to ace ...
... HOUSEKEEPING GENES These are genes that are active at all times, in all cells in the body. There are about 2,000 housekeeping genes. Examples: Na/K-ATPase – enzyme that pumps Na out, and K out, to maintain normal ion distribution inside the cell Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH): converts pyruvate to ace ...
Judgement Statement – 2012
... Dominant C allele required to convert colourless precursor into pigmented intermediate. Dominant P allele required to convert pigment into purple. If P allele is not present / mutant / recessive, red only will be expressed. If c / recessive allele is present / C allele is absent, no colour will be e ...
... Dominant C allele required to convert colourless precursor into pigmented intermediate. Dominant P allele required to convert pigment into purple. If P allele is not present / mutant / recessive, red only will be expressed. If c / recessive allele is present / C allele is absent, no colour will be e ...
Schedule
... Only C allele will allow colour expression. Then only P allele will convert / make to purple / pigment. In this case for all purple seeds to be produced by a white-seeded and red-seeded plant, there must have been two dominant alleles present for each of C and P genes. This is an example of a gene i ...
... Only C allele will allow colour expression. Then only P allele will convert / make to purple / pigment. In this case for all purple seeds to be produced by a white-seeded and red-seeded plant, there must have been two dominant alleles present for each of C and P genes. This is an example of a gene i ...
Editorial: Modulating Prokaryotic Lifestyle by DNA
... interest from the healthcare point of view. As it is well-known the antibiotic-resistance strains of pathogenic bacteria are a major world problem, so that there is an urgent need of innovative approaches to tackle it. Human and animal infectious diseases impose staggering costs worldwide in terms o ...
... interest from the healthcare point of view. As it is well-known the antibiotic-resistance strains of pathogenic bacteria are a major world problem, so that there is an urgent need of innovative approaches to tackle it. Human and animal infectious diseases impose staggering costs worldwide in terms o ...
Microarray Data Analysis Normalization
... GSEA: Detects blocks of functionally related genes 1316_at with significant coordinate 1320_at ...
... GSEA: Detects blocks of functionally related genes 1316_at with significant coordinate 1320_at ...
Regulation
... Adaptive – Ability to initiate Transcription –Control by signal Proteins Environmental Signals facilitate Transcription Positive Regulation Environmental Signals interfere with Transcription Negative Regulation ...
... Adaptive – Ability to initiate Transcription –Control by signal Proteins Environmental Signals facilitate Transcription Positive Regulation Environmental Signals interfere with Transcription Negative Regulation ...
Gene regulatory network

A gene regulatory network or genetic regulatory network (GRN) is a collection of regulators thatinteract with each other and with other substances in the cell to govern the gene expression levels of mRNA and proteins.The regulator can be DNA, RNA, protein and their complex. The interaction can be direct or indirect (through their transcribed RNA or translated protein).In general, each mRNA molecule goes on to make a specific protein (or set of proteins). In some cases this protein will be structural, and will accumulate at the cell membrane or within the cell to give it particular structural properties. In other cases the protein will be an enzyme, i.e., a micro-machine that catalyses a certain reaction, such as the breakdown of a food source or toxin. Some proteins though serve only to activate other genes, and these are the transcription factors that are the main players in regulatory networks or cascades. By binding to the promoter region at the start of other genes they turn them on, initiating the production of another protein, and so on. Some transcription factors are inhibitory.In single-celled organisms, regulatory networks respond to the external environment, optimising the cell at a given time for survival in this environment. Thus a yeast cell, finding itself in a sugar solution, will turn on genes to make enzymes that process the sugar to alcohol. This process, which we associate with wine-making, is how the yeast cell makes its living, gaining energy to multiply, which under normal circumstances would enhance its survival prospects.In multicellular animals the same principle has been put in the service of gene cascades that control body-shape. Each time a cell divides, two cells result which, although they contain the same genome in full, can differ in which genes are turned on and making proteins. Sometimes a 'self-sustaining feedback loop' ensures that a cell maintains its identity and passes it on. Less understood is the mechanism of epigenetics by which chromatin modification may provide cellular memory by blocking or allowing transcription. A major feature of multicellular animals is the use of morphogen gradients, which in effect provide a positioning system that tells a cell where in the body it is, and hence what sort of cell to become. A gene that is turned on in one cell may make a product that leaves the cell and diffuses through adjacent cells, entering them and turning on genes only when it is present above a certain threshold level. These cells are thus induced into a new fate, and may even generate other morphogens that signal back to the original cell. Over longer distances morphogens may use the active process of signal transduction. Such signalling controls embryogenesis, the building of a body plan from scratch through a series of sequential steps. They also control and maintain adult bodies through feedback processes, and the loss of such feedback because of a mutation can be responsible for the cell proliferation that is seen in cancer. In parallel with this process of building structure, the gene cascade turns on genes that make structural proteins that give each cell the physical properties it needs.It has been suggested that, because biological molecular interactions are intrinsically stochastic, gene networks are the result of cellular processes and not their cause (i.e. cellular Darwinism). However, recent experimental evidence has favored the attractor view of cell fates.