Chapter 13 Viruses
... Either have DNA or RNA Surrounded by a protein coat (capsid). Envelope – proteins, carbohydrates, lipids. Obligate intracellular parasites ...
... Either have DNA or RNA Surrounded by a protein coat (capsid). Envelope – proteins, carbohydrates, lipids. Obligate intracellular parasites ...
Viruses - Madeira City Schools
... 2. Plant viruses only attack plants and animal viruses only attack animals. 3. May only attack one species (polio and measles…humans only) 4. Why? host cells have receptor proteins on their membranes that give off signals. Viruses only identify certain ones. ...
... 2. Plant viruses only attack plants and animal viruses only attack animals. 3. May only attack one species (polio and measles…humans only) 4. Why? host cells have receptor proteins on their membranes that give off signals. Viruses only identify certain ones. ...
Viruses
... - It stunts the growth of tobacco plants & gives the leaves a mottled, or mosaic, coloration - Disease was contagious; he concluded it was tiny bacteria, unable to be seen w/ a light mic. - But, could only reproduce w/in host cell. - Alcohol did not inactivate the disease, which is generally lethal ...
... - It stunts the growth of tobacco plants & gives the leaves a mottled, or mosaic, coloration - Disease was contagious; he concluded it was tiny bacteria, unable to be seen w/ a light mic. - But, could only reproduce w/in host cell. - Alcohol did not inactivate the disease, which is generally lethal ...
Virus Presentation
... These men start with what appears to be flu-like symptoms, and when brought to the Hospital they very rapidly develop the most vicious type of pneumonia that has ever been seen. Two hours after admission they have the mahogany spots over the cheek bones, and a few hours later you can begin to see th ...
... These men start with what appears to be flu-like symptoms, and when brought to the Hospital they very rapidly develop the most vicious type of pneumonia that has ever been seen. Two hours after admission they have the mahogany spots over the cheek bones, and a few hours later you can begin to see th ...
03-131 Genes, Diseases and Drugs Lecture 1 August 23, 2015
... 1. Fundamental building blocks and polymers: sugars, amino acids, nucleic acids 2. Properties of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic cells (similarities/differences) 3. Structural properties of viruses (helical, polyhedral, enveloped, complex) 4. HIV virus structure/enzymes 5. HIV virus life-cycle 6. Other f ...
... 1. Fundamental building blocks and polymers: sugars, amino acids, nucleic acids 2. Properties of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic cells (similarities/differences) 3. Structural properties of viruses (helical, polyhedral, enveloped, complex) 4. HIV virus structure/enzymes 5. HIV virus life-cycle 6. Other f ...
Chapter 13 Notes
... Host range –the __________________ of host cells that virus can ________________ Most viruses are limited to ____________________ type of _________________ species Host range determined by: o Virus’ requirements for _____________________________ – can the virus latch on? o Availability of ____ ...
... Host range –the __________________ of host cells that virus can ________________ Most viruses are limited to ____________________ type of _________________ species Host range determined by: o Virus’ requirements for _____________________________ – can the virus latch on? o Availability of ____ ...
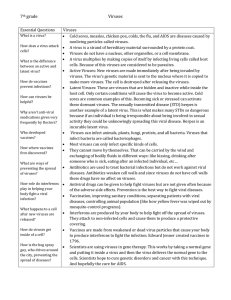
Human Viruses
... occurring pandemic threats and agents of bioterrorism. Additionally, the device provides a strategy to augment the benefit of approved antiviral drug regimens. ...
... occurring pandemic threats and agents of bioterrorism. Additionally, the device provides a strategy to augment the benefit of approved antiviral drug regimens. ...
Virus
... 3.a.1 – DNA, and in some cases RNA, is the primary source of heritable information (19.2). 3.c.3 – Viral replication results in genetic variation, and viral infection can introduce genetic variation into the hosts (19.1 & 19.2). ...
... 3.a.1 – DNA, and in some cases RNA, is the primary source of heritable information (19.2). 3.c.3 – Viral replication results in genetic variation, and viral infection can introduce genetic variation into the hosts (19.1 & 19.2). ...
7th grade Viruses Essential Questions Viruses What is a virus? How
... incurable latent virus. Who developed Viruses can infect animals, plants, fungi, protists, and all bacteria. Viruses that vaccines? infect bacteria are called bacteriophages. Most viruses can only infect specific kinds of cells. How where vaccines They cannot move by themselves. That can be ca ...
... incurable latent virus. Who developed Viruses can infect animals, plants, fungi, protists, and all bacteria. Viruses that vaccines? infect bacteria are called bacteriophages. Most viruses can only infect specific kinds of cells. How where vaccines They cannot move by themselves. That can be ca ...
disease - TeacherWeb
... matches up with the shape of a molecule in the plasma membrane of the host cell (like interlocking puzzle pieces- this is how virus recognizes its host cell) 4. Some larger viruses have an envelope that surrounds the capsid ...
... matches up with the shape of a molecule in the plasma membrane of the host cell (like interlocking puzzle pieces- this is how virus recognizes its host cell) 4. Some larger viruses have an envelope that surrounds the capsid ...
Chapter 6 – Viral Replication Describe the viral replication cycle and
... Be prepared to match specific viruses and their corresponding receptor(s). What are some of the different ways in which receptor molecules can be used to mediate viral entry and viral spread? How are viruses able to use incorrect receptors and what role, if any, do these “false” receptors play in vi ...
... Be prepared to match specific viruses and their corresponding receptor(s). What are some of the different ways in which receptor molecules can be used to mediate viral entry and viral spread? How are viruses able to use incorrect receptors and what role, if any, do these “false” receptors play in vi ...
What are Viruses?
... response and creating immunity, but not causing illness. • Worldwide use of vaccines has resulted in a dramatic decline in morbidity (illness) and mortality (death) associated with viral infections such as polio, measles, mumps and rubella; smallpox have been eradicated; polio is expected to be erad ...
... response and creating immunity, but not causing illness. • Worldwide use of vaccines has resulted in a dramatic decline in morbidity (illness) and mortality (death) associated with viral infections such as polio, measles, mumps and rubella; smallpox have been eradicated; polio is expected to be erad ...
Return of the giant zombie virus
... very small,” Claverie told Science News. Then, last summer, his group identified a second family of giant viruses. Nowthey've pinpointed yet another whole new family. Giant viruses, as it turns out, come in many varieties. And that’s basically been adding to the confusion of what to expect from viru ...
... very small,” Claverie told Science News. Then, last summer, his group identified a second family of giant viruses. Nowthey've pinpointed yet another whole new family. Giant viruses, as it turns out, come in many varieties. And that’s basically been adding to the confusion of what to expect from viru ...
Part_1-_Viruses
... instructions (DNA or RNA) into the host (ENTRY). 3. injected genetic material ‘hi-jacks’ the cell’s machinery and recruits the host’s enzymes. 4. enzymes make parts for the new virus particles (REPLICATION). 5. new particles assemble the parts into new viruses (ASSEMBLY). ...
... instructions (DNA or RNA) into the host (ENTRY). 3. injected genetic material ‘hi-jacks’ the cell’s machinery and recruits the host’s enzymes. 4. enzymes make parts for the new virus particles (REPLICATION). 5. new particles assemble the parts into new viruses (ASSEMBLY). ...
viruses - Lisle CUSD 202
... vaccinating, diseases that are under control would eventually come back to cause epidemics. This has happened in several countries. 3. Help rid the world of diseases that have been crippling and killing children for centuries. Immunization allowed us to eradicate smallpox. Today polio is nearly gone ...
... vaccinating, diseases that are under control would eventually come back to cause epidemics. This has happened in several countries. 3. Help rid the world of diseases that have been crippling and killing children for centuries. Immunization allowed us to eradicate smallpox. Today polio is nearly gone ...
(1) Replication of negative ssRNA viruses
... Two types of spikes project from the s urface: One is composed of H protein and the second of N protein. [Note: This is in contrast to the paramyxoviruses, in which H and N activities reside in the same spike protein.] Both the H and N influenza proteins are integral membrane proteins. The M (matrix ...
... Two types of spikes project from the s urface: One is composed of H protein and the second of N protein. [Note: This is in contrast to the paramyxoviruses, in which H and N activities reside in the same spike protein.] Both the H and N influenza proteins are integral membrane proteins. The M (matrix ...
virus - DrMinkovskyScienceWiki
... • Adsorption – specific attachment • Penetration – entry of viral genome • Uncoating – release of viral genome • Synthesis – new viral products made • Assembly – new viruses are made in the cell • Release – often causes the host cell to lyse ...
... • Adsorption – specific attachment • Penetration – entry of viral genome • Uncoating – release of viral genome • Synthesis – new viral products made • Assembly – new viruses are made in the cell • Release – often causes the host cell to lyse ...
Viruses
... Viruses are not living!!! 1) Viruses are not made of cells 2) Viruses do not grow 3) Viruses can’t reproduce on their own ...
... Viruses are not living!!! 1) Viruses are not made of cells 2) Viruses do not grow 3) Viruses can’t reproduce on their own ...
6 Viruses and Other Acellular Infectious Agents
... 1. Envelopes are membrane structures surrounding some (but not all) viruses a. Lipids and carbohydrates are usually derived from the host membranes b. Proteins are virus-specific c. Many have protruding glycoprotein spikes (peplomers) such as the enzymes neuraminidase and hemagglutinin 2. Although v ...
... 1. Envelopes are membrane structures surrounding some (but not all) viruses a. Lipids and carbohydrates are usually derived from the host membranes b. Proteins are virus-specific c. Many have protruding glycoprotein spikes (peplomers) such as the enzymes neuraminidase and hemagglutinin 2. Although v ...
20 Notes Bacteria and Virus
... - Viruses only reproduce by ______________________ - Most viruses can only be seen with an electron microscope - The first virus isolated was the tobacco mosaic virus in 1935 Structure of Viruses - _____________ – protein coat surrounding the virus - Genetic information – ___________________ - Virus ...
... - Viruses only reproduce by ______________________ - Most viruses can only be seen with an electron microscope - The first virus isolated was the tobacco mosaic virus in 1935 Structure of Viruses - _____________ – protein coat surrounding the virus - Genetic information – ___________________ - Virus ...
C) Viral Life Cycles - Mr. Lesiuk
... ultimately causing the host cell to break open and release the reproduced viruses to spread to many more host cells. ...
... ultimately causing the host cell to break open and release the reproduced viruses to spread to many more host cells. ...
2_Viral _Genetics
... it is the exchange of genes between two chromosomes that is based on crossing over within regions of significant base sequence homology. It can be readily demonstrated for viruses with double stranded DNA as the genetic material and has been used to determine their genetic map. ...
... it is the exchange of genes between two chromosomes that is based on crossing over within regions of significant base sequence homology. It can be readily demonstrated for viruses with double stranded DNA as the genetic material and has been used to determine their genetic map. ...
`Virophage` suggests viruses are alive
... a genome harbouring more than 900 proteincoding genes3 — at least three times more than that of the biggest previously known viruses and bigger than that of some bacteria. It was named Acanthamoeba polyphaga mimivirus (for mimicking microbe), and is thought to be part of a much larger family. “It Gi ...
... a genome harbouring more than 900 proteincoding genes3 — at least three times more than that of the biggest previously known viruses and bigger than that of some bacteria. It was named Acanthamoeba polyphaga mimivirus (for mimicking microbe), and is thought to be part of a much larger family. “It Gi ...
Plant virus

Plant viruses are viruses that affect plants. Like all other viruses, plant viruses are obligate intracellular parasites that do not have the molecular machinery to replicate without a host. Plant viruses are pathogenic to higher plants. While this article does not intend to list all plant viruses, it discusses some important viruses as well as their uses in plant molecular biology.