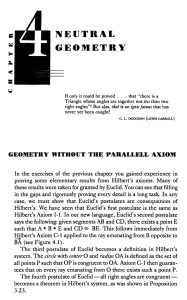
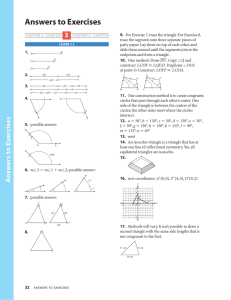
(Greater than 90 degrees)
... • An angle is in standard position if the vertex of the angle is at the origin and the initial arm lies along the positive x-axis. The terminal arm can be anywhere on the arc of rotation y ...
... • An angle is in standard position if the vertex of the angle is at the origin and the initial arm lies along the positive x-axis. The terminal arm can be anywhere on the arc of rotation y ...
mc_fp2-ch - WordPress.com
... Section A: 3 compulsory questions, each worth about 18 marks, total: 54 marks. Section B: One question to be chosen from two, both worth 18 marks, total: 18 marks. Coursework None Assumed Knowledge Candidates are expected to know the content for C1, C2, C3, C4 and FP1. Topic ...
... Section A: 3 compulsory questions, each worth about 18 marks, total: 54 marks. Section B: One question to be chosen from two, both worth 18 marks, total: 18 marks. Coursework None Assumed Knowledge Candidates are expected to know the content for C1, C2, C3, C4 and FP1. Topic ...