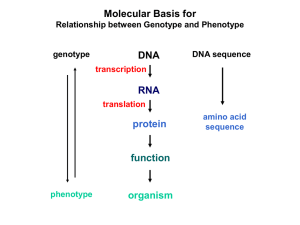
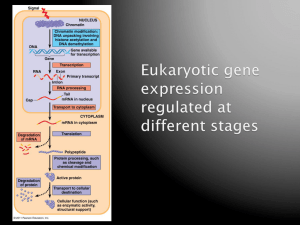
Eukaryotic Gene Expression
... • very extended and tangled during interphase • condensed into discrete chromosomes during mitosis ...
... • very extended and tangled during interphase • condensed into discrete chromosomes during mitosis ...
Cellular Control miniQUIZ
... Using the diagram above answer the following questions: a) Which segment of the fruit fly develops wings? b) Are plant homeobox genes homologous to the homeobox genes in the fruit fly? 17. Apoptosis is important during development. Define the meaning of apoptosis and give an example. ...
... Using the diagram above answer the following questions: a) Which segment of the fruit fly develops wings? b) Are plant homeobox genes homologous to the homeobox genes in the fruit fly? 17. Apoptosis is important during development. Define the meaning of apoptosis and give an example. ...
Gene Regulation
... GENE REGULATION Where does regulation occur? At what step? Most regulation occurs at the DNA to RNA step—transcription! Why? Conserves the most energy! ...
... GENE REGULATION Where does regulation occur? At what step? Most regulation occurs at the DNA to RNA step—transcription! Why? Conserves the most energy! ...
2012 Boc314 TT02m(1) - Learning
... It when the genes on a Chromosome of a sequenced genome Occur in the same order to those On the chromosome of a related plant ...
... It when the genes on a Chromosome of a sequenced genome Occur in the same order to those On the chromosome of a related plant ...
Regulation of Gene Expression
... that play some structural role in the cell Regulatory genes encode proteins involved in the control of gene expression of other genes There are regulatory elements (sequences) in the DNA where regulatory proteins will bind Prokaryotic gene regulation One fundamental difference between prokaryo ...
... that play some structural role in the cell Regulatory genes encode proteins involved in the control of gene expression of other genes There are regulatory elements (sequences) in the DNA where regulatory proteins will bind Prokaryotic gene regulation One fundamental difference between prokaryo ...
homework
... D. the sequential development of an animal’s basic body plan The lac operon is found in _______________________ A. prokaryotes B. eukaryotes The TATA box sequence is found in _____________________ cells A. prokaryotes B. eukaryotes The function of the TATA box is to ________________________________. ...
... D. the sequential development of an animal’s basic body plan The lac operon is found in _______________________ A. prokaryotes B. eukaryotes The TATA box sequence is found in _____________________ cells A. prokaryotes B. eukaryotes The function of the TATA box is to ________________________________. ...
Concept Check Questions with answers
... genes for expression •DNA methylation usually flags them for not being expressed ...
... genes for expression •DNA methylation usually flags them for not being expressed ...
Genetics: Chapter 7
... • Repressor gene(codes for repressor protein) outside of operon coding region inhibits transcription unless something else bind to the repressor protein ...
... • Repressor gene(codes for repressor protein) outside of operon coding region inhibits transcription unless something else bind to the repressor protein ...
Chapter 7_microbialgeneticspart1_7e
... • Repressor gene(codes for repressor protein) outside of operon coding region inhibits transcription unless something else bind to the repressor protein ...
... • Repressor gene(codes for repressor protein) outside of operon coding region inhibits transcription unless something else bind to the repressor protein ...
The genetic engineers toolkit
... humans. • Agriculture and conservation. Eg. Checking that closely related endangered animals are not mated together. • To establish how closely related different seed stocks are • To place a suspect at the crime scene in forensic science. ...
... humans. • Agriculture and conservation. Eg. Checking that closely related endangered animals are not mated together. • To establish how closely related different seed stocks are • To place a suspect at the crime scene in forensic science. ...
4-5
... Circle the letter of the answer that best completes the statement. A group of genes that work together in a pathway and are controlled by one on/off switch is known as a(n) _______________________ A. codon B. operator C. operon D. gene group When the lac repressor protein binds to the ______________ ...
... Circle the letter of the answer that best completes the statement. A group of genes that work together in a pathway and are controlled by one on/off switch is known as a(n) _______________________ A. codon B. operator C. operon D. gene group When the lac repressor protein binds to the ______________ ...
Other Plasmid Maps Feature list descriptions
... LacO is a regulatory gene of the lac operon. If lactose is missing from the growth medium, the repressor binds very tightly to a short DNA sequence just downstream of the promoter near the beginning of lacZ called the lac operator. The repressor binding to the operator interferes with binding of RNA ...
... LacO is a regulatory gene of the lac operon. If lactose is missing from the growth medium, the repressor binds very tightly to a short DNA sequence just downstream of the promoter near the beginning of lacZ called the lac operator. The repressor binding to the operator interferes with binding of RNA ...
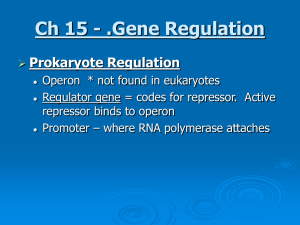
Ch 15 - .Gene Regulation
... 1 – always “on” = repressor cannot bind, therefore RNA polymerase can attach and protein is made. • Ex. Trp operon -To turn off the protein product binds to repressor = repressor can bind & transcription ceases ...
... 1 – always “on” = repressor cannot bind, therefore RNA polymerase can attach and protein is made. • Ex. Trp operon -To turn off the protein product binds to repressor = repressor can bind & transcription ceases ...
Distinguish between these 3 root types: - mvhs
... mRNA for this protein contains a signal recognition sequence that is recognized by a signal recognition particle (SRP). The SRP brings the growing polypeptide to the receptor protein in the ___________________. ...
... mRNA for this protein contains a signal recognition sequence that is recognized by a signal recognition particle (SRP). The SRP brings the growing polypeptide to the receptor protein in the ___________________. ...
Antibody Diversity 02/16/06
... by special sequences (RSS—recombination signal sequences) of two sizes ...
... by special sequences (RSS—recombination signal sequences) of two sizes ...
04/03
... regulatory proteins that bind to enhancer elements and promoterproximal elements with RNA polymerase initiates transcription at appropriate levels. Architectural proteins allow bending of the DNA to bring all components together, both spatially and functionally. ...
... regulatory proteins that bind to enhancer elements and promoterproximal elements with RNA polymerase initiates transcription at appropriate levels. Architectural proteins allow bending of the DNA to bring all components together, both spatially and functionally. ...
regulatory gene
... of repressors (always on at a low rate) Regulatory sequence: stretch of DNA that interacts with regulatory proteins to control transcription (promoter, terminator, enhancer) inducer: small molecule that inactivates the repressor (allows transcription) ...
... of repressors (always on at a low rate) Regulatory sequence: stretch of DNA that interacts with regulatory proteins to control transcription (promoter, terminator, enhancer) inducer: small molecule that inactivates the repressor (allows transcription) ...
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
... are thousands of base pairs away from the gene they control. Binding increases the rate of transcription of the gene. Enhancers can be located upstream, downstream, or even within the gene they control. How does the binding of a protein to an enhancer regulate the transcription of a gene thousands ...
... are thousands of base pairs away from the gene they control. Binding increases the rate of transcription of the gene. Enhancers can be located upstream, downstream, or even within the gene they control. How does the binding of a protein to an enhancer regulate the transcription of a gene thousands ...
lesson x - MisterSyracuse.com
... 5. When the repressor protein is bound, transcription can’t happen. 6. However, if another molecule binds to the repressor protein, it changes shape and can no longer bind to the operator. - Demonstration with boxes. 7. This frees up the operator, and the gene can be transcribed! 8. This is in proka ...
... 5. When the repressor protein is bound, transcription can’t happen. 6. However, if another molecule binds to the repressor protein, it changes shape and can no longer bind to the operator. - Demonstration with boxes. 7. This frees up the operator, and the gene can be transcribed! 8. This is in proka ...
Ch 18.2-18.5 PPT
... transcription DNA methylation: methyl groups added to DNA; tightly packed; transcription Histone acetylation: acetyl groups added to histones; loosened; transcription ...
... transcription DNA methylation: methyl groups added to DNA; tightly packed; transcription Histone acetylation: acetyl groups added to histones; loosened; transcription ...
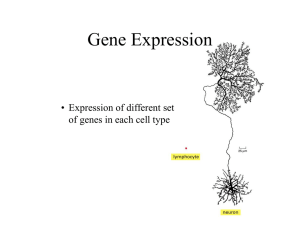
Gene Expression
... remaining exons together forming mRNA. This leaves the nucleus and travels through the nuclear pore to the cytoplasm where translation occurs. ...
... remaining exons together forming mRNA. This leaves the nucleus and travels through the nuclear pore to the cytoplasm where translation occurs. ...
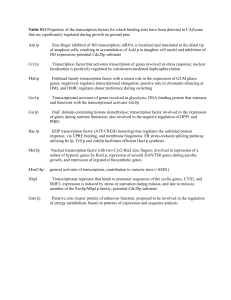
Table S11 Properties of the transcription factors for which binding
... Transcriptional repressor that binds to promoter sequences of the cyclin genes, CYS3, and SMF2; expression is induced by stress or starvation during mitosis, and late in meiosis; member of the Swi4p/Mbp1p family; potential Cdc28p substrate ...
... Transcriptional repressor that binds to promoter sequences of the cyclin genes, CYS3, and SMF2; expression is induced by stress or starvation during mitosis, and late in meiosis; member of the Swi4p/Mbp1p family; potential Cdc28p substrate ...
Promoter (genetics)
In genetics, a promoter is a region of DNA that initiates transcription of a particular gene. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, on the same strand and upstream on the DNA (towards the 5' region of the sense strand).Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long.