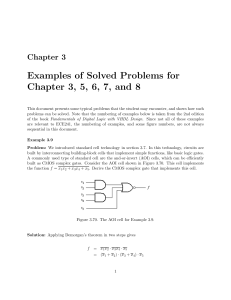
Chapter 3 Special-Purpose Diodes
... Introduction to Network Theorems This chapter will introduce the important fundamental theorems of network analysis. Included are the superposition, Thevenin’s, Norton’s, and maximum power transfer theorems. We will consider a number of areas of application for each. A through understanding of each ...
... Introduction to Network Theorems This chapter will introduce the important fundamental theorems of network analysis. Included are the superposition, Thevenin’s, Norton’s, and maximum power transfer theorems. We will consider a number of areas of application for each. A through understanding of each ...
DTC P0700 - JustAnswer
... Important: Additional DTCs may set when disconnecting the automatic transmission inline 20-way connector. 1. Ignition OFF, disconnect the automatic transmission (AT) inline 20-way connector at the transmission. 2. Install the J 44152 on the engine side of the AT inline 20-way connector. 3. Ignition ...
... Important: Additional DTCs may set when disconnecting the automatic transmission inline 20-way connector. 1. Ignition OFF, disconnect the automatic transmission (AT) inline 20-way connector at the transmission. 2. Install the J 44152 on the engine side of the AT inline 20-way connector. 3. Ignition ...
Electric Currents and Circuits Review
... An electrical heater raises the temperature of a bucket of water. If 6000 J of energy is absorbed by the water from the heater in 30 s, what is the minimum power rating of the heater? Ans. 200 W ...
... An electrical heater raises the temperature of a bucket of water. If 6000 J of energy is absorbed by the water from the heater in 30 s, what is the minimum power rating of the heater? Ans. 200 W ...
Ohm`s Law / The Basic Circuit
... by a battery or generating source. This source of electric pressure, electromotive force ( EMF ), provides the energy required to push current through the circuit. It can be referred to as the supply voltage. Every circuit offers some opposition or restriction to current flow, which is called circui ...
... by a battery or generating source. This source of electric pressure, electromotive force ( EMF ), provides the energy required to push current through the circuit. It can be referred to as the supply voltage. Every circuit offers some opposition or restriction to current flow, which is called circui ...
Current-Phase relation
... MHz. With Q = 150 the tank circuit served to improve the match of the low impedance of the ring to that of the rf amplifier. As shown in Fig. 4, an rf oscillator coupled to the tank through an extremely small capacitor provided a constant current source. To set the phase p a steady external flux 4d, ...
... MHz. With Q = 150 the tank circuit served to improve the match of the low impedance of the ring to that of the rf amplifier. As shown in Fig. 4, an rf oscillator coupled to the tank through an extremely small capacitor provided a constant current source. To set the phase p a steady external flux 4d, ...
... In a series RLC circuit. The current lags behind or leads the applied voltage depending upon the values of XL and Xc. XL causes the total current to lag behind the applied voltage while Xc causes the total current to lead the applied voltage.When XL >Xc the circuit is predominantly inductive, and wh ...
pptx
... degree of coupling between the two circuits. enhances the link efficiency In WBANs for body tissues safety: k < 0.45 ...
... degree of coupling between the two circuits. enhances the link efficiency In WBANs for body tissues safety: k < 0.45 ...
Chapter 7 Gate Drive circuit Design
... A recommended the gate on state voltage value (+ VGE) is +15V. Notes when + VGE is designed are shown as follows. (1) Set +VGE so that is remains under the maximum rated G-E voltage, VGES =±20V. (2) It is recommended that supply voltage fluctuations are kept to within ±10%. (3) The on-state C-E satu ...
... A recommended the gate on state voltage value (+ VGE) is +15V. Notes when + VGE is designed are shown as follows. (1) Set +VGE so that is remains under the maximum rated G-E voltage, VGES =±20V. (2) It is recommended that supply voltage fluctuations are kept to within ±10%. (3) The on-state C-E satu ...
Chapter 7 Gate Drive circuit Design
... A recommended the gate on state voltage value (+ VGE) is +15V. Notes when + VGE is designed are shown as follows. (1) Set +VGE so that is remains under the maximum rated G-E voltage, VGES =±20V. (2) It is recommended that supply voltage fluctuations are kept to within ±10%. (3) The on-state C-E satu ...
... A recommended the gate on state voltage value (+ VGE) is +15V. Notes when + VGE is designed are shown as follows. (1) Set +VGE so that is remains under the maximum rated G-E voltage, VGES =±20V. (2) It is recommended that supply voltage fluctuations are kept to within ±10%. (3) The on-state C-E satu ...
4 Electricity and Magnetism Chapter 2 Electric Circuit 2 Electric
... total voltage = 1.5 3 = 4.5 V In Fig d, since the cells are connected in parallel, total voltage = 1.5 V Ohm’s law is not applicable beyond the ...
... total voltage = 1.5 3 = 4.5 V In Fig d, since the cells are connected in parallel, total voltage = 1.5 V Ohm’s law is not applicable beyond the ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.